Concept explainers
Consider the following sequence of DNA:
- What dipeptide is formed from this DNA after transcription and translation?
- If a mutation converts CGG to CGT in DNA, what dipeptide is formed?
- If a mutation converts CGG to CCG in DNA, what dipeptide is formed?
- If a mutation converts CGG to AGG in DNA, what dipeptide is formed?
(a)
Interpretation:
Dipeptide formed from DNA 3' TTA CGG 5' after transcription and translation should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Transcription − Copying of information stored as a deoxyribo nucleotide sequence of DNA into a ribonucleotide sequence of RNA.
Translation −Copying of information stored as a ribonucleotide sequence of RNA into an amino acid sequence of a peptide chain.
Genetic code − DNA and RNA transform genetic information of the living cells through triplet code, which is a sequence of three nucleotides on DNA or RNA molecules codes for a specific amino acid in protein synthesis.
Answer to Problem 22.77P
Dipeptide is Asn-Ala.
Explanation of Solution
Nucleotides are the monomer molecules for both DNA and RNA molecules. DNA has deoxyribo nucleotides and RNA has ribonucleotides.
DNA molecules consist of 2 DNA strands, which binds with base pairs as below.
Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T).
Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G).
In RNA;
Adenine (A) pairs with Uracil (U). Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G).
Codons are written from 5 prime end (5) to 3 prime end (3) of mRNA. mRNA has a base sequence which is complementary to the template DNA strand. Adenine (A) pairs with Uracil (U) in mRNA or Thymine (T) in DNA; by using two H bonds and Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G) by using three H bonds. Therefore; mRNA sequence can be represented as below,

Codons are written from 5 prime end (5') to 3 prime end (3') of mRNA. There is a specific sequence of nucleotides for each amino acid. Below mentioned table represent the relationship between nucleotides and amino acids.
The Genetic Code- Triplets in Messenger RNA
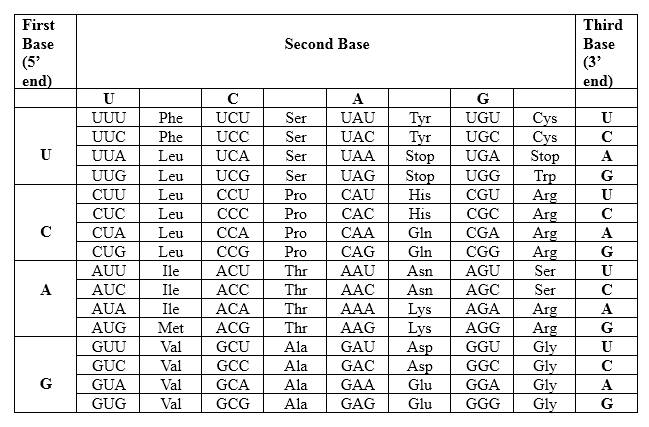
According to the above table; one amino acid has several triplets, but triplet code is unique for amino acid. For Asparagine amino acid (Asn) there are 2 different but unique codons, which are AAU and AAC. Likewise, for each amino acid there are several triplets. Therefore, for a particular amino acid sequence there can be different triplet codes. AAU is unique for asparagine amino acid and GCC is unique for alanine amino acid.
Asn-Ala is the dipeptide which can be obtained from 3' TTA CGG 5' template DNA strand.
(b)
Interpretation:
Dipeptide formed from mutated DNA 3' TTA CGT 5' after transcription and translation should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Transcription − Copying of information stored as a deoxyribo nucleotide sequence of DNA into a ribonucleotide sequence of RNA.
Translation − Copying of information stored as a ribonucleotide sequence of RNA into an amino acid sequence of a peptide chain.
Genetic code − DNA and RNA transform genetic information of the living cells through triplet code, which is a sequence of three nucleotides on DNA or RNA molecules codes for a specific amino acid in protein synthesis.
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA.
Answer to Problem 22.77P
Dipeptide is Asn-Ala.
Explanation of Solution
Nucleotides are the monomer molecules for both DNA and RNA molecules. DNA has deoxyribo nucleotides and RNA has ribonucleotides.
DNA molecules consist of 2 DNA strands, which binds with base pairs as below.
Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T).
Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G).
In RNA;
Adenine (A) pairs with Uracil (U). Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G).
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. When mutation happens at a particular position of a DNA molecule, that mutation goes through mRNA and translate a wrong peptide.
Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule. There are three types of mutations which can be classified as follows;
- Point mutations − A substitution of one nucleotide for another nucleotide.
- Deletion mutations − One or more nucleotides is lost from a particular DNA molecule.
- Insertion mutations − One or more nucleotides is added to a DNA molecule.
Codons are written from 5 prime end (5) to 3 prime end (3) of mRNA. mRNA has a base sequence which is complementary to the template DNA strand. Adenine (A) pairs with Uracil (U) in mRNA or Thymine (T) in DNA; by using two H bonds and Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G) by using three H bonds. Therefore; mRNA sequence can be represented as below,

Codons are written from 5 prime end (5') to 3 prime end (3') of mRNA. There is a specific sequence of nucleotides for each amino acid. Below mentioned table represent the relationship between nucleotides and amino acids.
The Genetic Code- Triplets in Messenger RNA
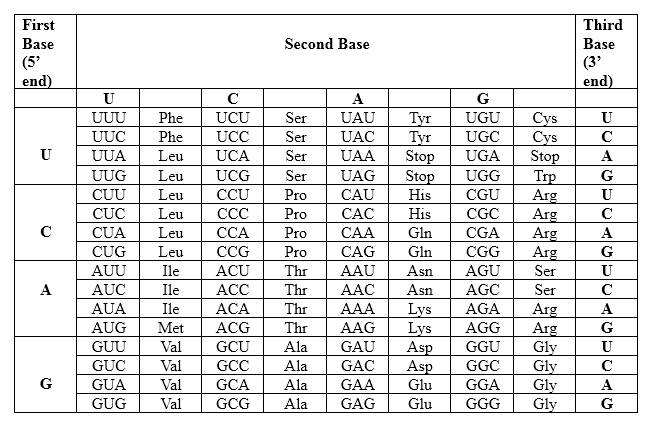
According to the above table; one amino acid has several triplets, but triplet code is unique for amino acid. For Asparagine amino acid (Asn) there are 2 different but unique codons, which are AAU and AAC. For, Alanine (Ala) there are 4 different but unique codons, which are GCU, GCC, GCA and GCG. Likewise, for each amino acid there are several triplets. Therefore, for a particular amino acid sequence there can be different triplet codes. AAU is unique for asparagine amino acid and GCA is unique for alanine amino acid. Though there is a mutation in the strand, in this example same peptide is generated as the non-mutated peptide.
Asn-Ala is the dipeptide which can be obtained from 3' TTA CGT 5' mutated template DNA strand.
(c)
Interpretation:
Dipeptide formed from mutated DNA 3' TTA CCG 5' after transcription and translation should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Transcription − Copying of information stored as a deoxyribo nucleotide sequence of DNA into a ribonucleotide sequence of RNA.
Translation − Copying of information stored as a ribonucleotide sequence of RNA into an amino acid sequence of a peptide chain.
Genetic code − DNA and RNA transform genetic information of the living cells through triplet code, which is a sequence of three nucleotides on DNA or RNA molecules codes for a specific amino acid in protein synthesis.
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA.
Answer to Problem 22.77P
Dipeptide is Asn-Gly.
Explanation of Solution
Nucleotides are the monomer molecules for both DNA and RNA molecules. DNA has deoxyribo nucleotides and RNA has ribonucleotides.
DNA molecules consist of 2 DNA strands, which binds with base pairs as below.
Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T).
Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G).
In RNA;
Adenine (A) pairs with Uracil (U). Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G).
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. When mutation happens at a particular position of a DNA molecule, that mutation goes through mRNA and translate a wrong peptide.
Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule. There are three types of mutations which can be classified as follows;
- Point mutations − A substitution of one nucleotide for another nucleotide.
- Deletion mutations − One or more nucleotides is lost from a particular DNA molecule.
- Insertion mutations − One or more nucleotides is added to a DNA molecule.
Codons are written from 5 prime end (5) to 3 prime end (3) of mRNA. mRNA has a base sequence which is complementary to the template DNA strand. Adenine (A) pairs with Uracil (U) in mRNA or Thymine (T) in DNA; by using two H bonds and Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G) by using three H bonds. Therefore; mRNA sequence can be represented as below,

Codons are written from 5 prime end (5') to 3 prime end (3') of mRNA. There is a specific sequence of nucleotides for each amino acid. Below mentioned table represent the relationship between nucleotides and amino acids.
The Genetic Code- Triplets in Messenger RNA
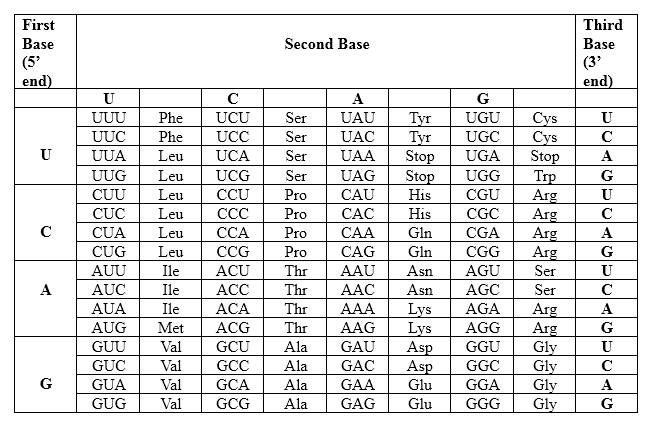
According to the above table; one amino acid has several triplets, but triplet code is unique for amino acid. For Asparagine amino acid (Asn) there are 2 different but unique codons, which are AAU and AAC. For, Glycine (Gly) there are 4 different but unique codons, which are GGU, GGC, GGA and GGG. Likewise, for each amino acid there are several triplets. Therefore, for a particular amino acid sequence there can be different triplet codes. AAU is unique for asparagine amino acid and GGC is unique for glycine amino acid. Hence, because of the mutation in the strand, in this example resulting peptide from the mutated template DNA is different from the non-mutated peptide.
Asn-Gly is the dipeptide which can be obtained from 3' TTA CCG 5' mutated template DNA strand.
(d)
Interpretation:
Dipeptide formed from mutated DNA 3' TTA AGG 5' after transcription and translation should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Transcription − Copying of information stored as a deoxyribo nucleotide sequence of DNA into a ribonucleotide sequence of RNA.
Translation − Copying of information stored as a ribonucleotide sequence of RNA into an amino acid sequence of a peptide chain.
Genetic code − DNA and RNA transform genetic information of the living cells through triplet code, which is a sequence of three nucleotides on DNA or RNA molecules codes for a specific amino acid in protein synthesis.
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA.
Answer to Problem 22.77P
Dipeptide is Asn-Ser.
Explanation of Solution
Nucleotides are the monomer molecules for both DNA and RNA molecules. DNA has deoxyribo nucleotides and RNA has ribonucleotides.
DNA molecules consist of 2 DNA strands, which binds with base pairs as below.
Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T).
Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G).
In RNA;
Adenine (A) pairs with Uracil (U). Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G).
Mutation is an alteration of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA. When mutation happens at a particular position of a DNA molecule, that mutation goes through mRNA and translate a wrong peptide.
Mutations can be classified based on the change that results in a DNA molecule. There are three types of mutations which can be classified as follows;
- Point mutations − A substitution of one nucleotide for another nucleotide.
- Deletion mutations − One or more nucleotides is lost from a particular DNA molecule.
- Insertion mutations − One or more nucleotides is added to a DNA molecule.
Codons are written from 5 prime end (5) to 3 prime end (3) of mRNA. mRNA has a base sequence which is complementary to the template DNA strand. Adenine (A) pairs with Uracil (U) in mRNA or Thymine (T) in DNA; by using two H bonds and Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G) by using three H bonds. Therefore; mRNA sequence can be represented as below,

Codons are written from 5 prime end (5') to 3 prime end (3') of mRNA. There is a specific sequence of nucleotides for each amino acid. Below mentioned table represent the relationship between nucleotides and amino acids.
The Genetic Code- Triplets in Messenger RNA
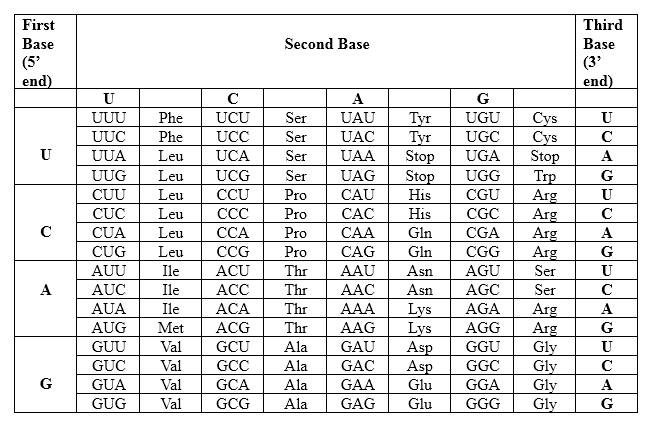
According to the above table; one amino acid has several triplets, but triplet code is unique for amino acid. For Asparagine amino acid (Asn) there are 2 different but unique codons, which are AAU and AAC. For, Serine (Ser) there are 6 different but unique codons, which are UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC. Likewise, for each amino acid there are several triplets. Therefore, for a particular amino acid sequence there can be different triplet codes. AAU is unique for asparagine amino acid and UCC is unique for serine amino acid. Hence, because of the mutation in the strand, in this example resulting peptide from the mutated template DNA is different from the non-mutated peptide.
Asn-Ser is the dipeptide which can be obtained from 3' TTA AGG 5' mutated template DNA strand.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Connect 2-Year Access Card for General, Organic and Biological Chemistry
- Consider the following DNA base sequence 3TTAATA5 a. What dipeptide is formed from the transcription and translation of this DNA segment? b. What dipeptide is formed if a DNA point mutation converts ATA to ATG? c. What dipeptide is formed if a DNA point mutation converts ATA to AGA? d. What dipeptide is formed if a DNA point mutation converts TTA to TTT?arrow_forwardWhat sequence of bases on one strand of DNA is complementary to the following sequence on another strand? (5') GGCTAATCCGT (3')arrow_forwardIs the trinucleotide in Problem 22-32 found only in DNA, found only in RNA, or found in both DNA and RNA? Explain the basis for your answer.arrow_forward
- How many total hydrogen bonds would exist between the following strands of DNA and their complementary strands? a. GCATGC b. TATGGCarrow_forwardSuppose that 30% of the nucleotides in a DNA molecule are deoxyguanosine 5'- monophosphate, and that during DNA replication the percentage amounts of available nucleotide bases are 20% A, 20% C. 30% G. and 30% T. Which base would be depleted first in the replication process?arrow_forwardWhat is the sequence of the strand of DNA complementary to CGATACGTAC?arrow_forward
- How many total hydrogen bonds would exist between the following strands of DNA and their complementary strands? a. CAGTAG b. TTGACAarrow_forwardThe DNA template strand segment 3TTCAAACCGTAC5 upon transcription and translation produces the amino acid sequence Lys-Phe-Gly-Met. What is the amino acid sequence produced if a frameshift mutation occurs in which the third A base in the original DNA sequence is removed?arrow_forward25-59 How many different bases are present in a DNA double helix?arrow_forward
- Consider the following mRNA base sequence 5CUUCAG3 a. What dipeptide is coded for by this mRNA? b. What dipeptide is formed if a point mutation converts CUU to CUC? c. What dipeptide is formed if a point mutation converts CAG to AAG? d. What dipeptide is formed if a point mutation converts CUU to CUC and CAG to AAG?arrow_forwardWhat amino acid sequence is coded for by the following DNA coding strand (sense strand)? (5') CTT-CGA-CCA-GAC-AGC-TTT (3')arrow_forwardIn what direction is a new DNA strand formed?arrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





