
Knowing that α = 35°, determine the resultant of the three forces shown.
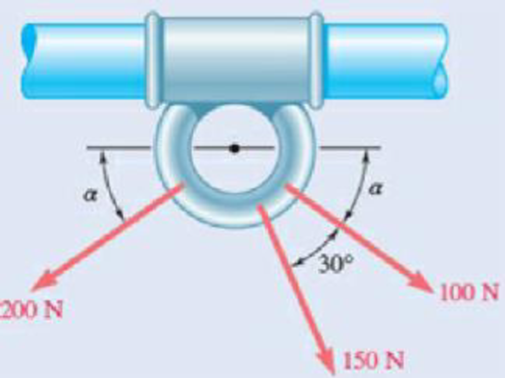
Fig. P2.35
The resultant of the three forces shown in figure P2.35.
Answer to Problem 2.35P
The resultant of three forces shown in the figure P2.35 is
Explanation of Solution
Refer figure P3.35.
The figure shows three forces of magnitude
Since these forces are making an angle with the axis of cylinder, they can be resolved into x and y components.
Write the equation to find the x component of
Here,
Write the equation to find the y component of
Here,
Similarly write the equation to find the x component of the
Here,
Write the equation to find the y component of
Here,
Write the equation to find the x component of the
Here,
Write the equation to find the y component of
Here,
Express a consolidated form of the x and y components of the three forces as shown in figure 1.
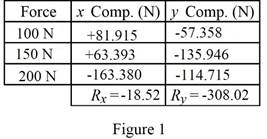
Let
Write the equation to find the resultant of all the three x components.
Here,
Write the equation to find the resultant of all the three y components.
Write the general expression of a vector with
Express the vectors
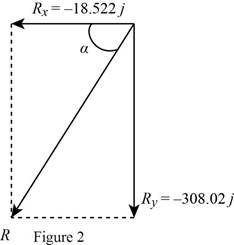
Write the equation to find the tangent of angle
Here,
Rewrite equation
Write the equation to find the y component of the resultant force vector.
Here,
Rewrite equation
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the resultant of the three forces shown in figure P2.35 is

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics, 11th Edition
- Find the magnitude and direction of the resultant of the two forces shown knowing that P=400 N and Q=300 N.arrow_forwardFind the magnitude and direction of the resultant of the two forces shown knowing that P=300 N and Q= 400 N.arrow_forwardCable AB is 65 ft long, and the tension in that cable is 3900 lb. Determine (a) the x, y, and z components of the force exerted by the cable on the anchor B, (b) the angles θx, θy, and θz defining the direction of that force.arrow_forward
- Knowing that the force intesity P is 338 N, determine the resultant of the three forces applied in A.arrow_forwardA force acts at the origin of a coordinate system in a direction defined by the angles θy=55° and θz =45°. Knowing that the x component of the force is –500 lb, determine (a) the angle θx, (b) the other components and the magnitude of the force.arrow_forwardKnowing that the tension is 425 lb in cable AB and 510 lb in cable AC, determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant of the forces exerted at A by the two cables.arrow_forward
- Knowing that the resultant of the two forces is directed along AB, determine F2.arrow_forwardKnowing that the resultant of the two forces is vertical, determine the anglearrow_forwardKnowing that the tension in cable AC is 1260 N, determine (a) the angle between cable AC and the boom AB, (b) the projection on AB of the force exerted by cable AC at point A.arrow_forward
- As shown by this image, if the distances a=2.1ft, b=3.6ft, and c=3.6ft, and the magnitudes of the forces F_B=510lb and F_C=600lb, determine the magnitude of the projection of Force F_B along AC, in lb.arrow_forwardThe man exerts a force P of magnitude 150N on the handle of the wheelbarrow. Knowing that the resultant of the force P, Q, and W (wt of the wheelbarrow) is zero, determine W.arrow_forwardDetermine the magnitude of the resultant of the system of concurrent forces having the following magnitudes and passing through the origin and the indicated points: P=520 lb (+8,-6,+5), T=270 lb (-3,-4, +10), F=280 lb (+5,-3,-6). a.) 273.272 lb b.) 476.065 lb c.) 466.966 lb d.) 720.675 lb e.) None of the abovearrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
