
Concept explainers
(a)
The possibility of the situation and any other possibility of the situation.
(a)
Answer to Problem 42P
Yes, the situation is possible and the only possibility is placing the third wire at a distance at which the force between wire 1 and 3 balances the force between wire 2 and 3.
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The
The orientation of the wires is shown in the figure below.
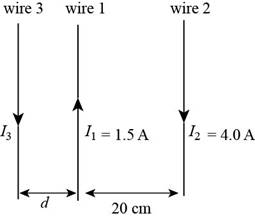
Figure (1)
The formula to calculate the magnitude of force per unit length is,
Here,
For the stability of wire 3 the magnetic force due to wire 1 on 3 must be equal to that of magnetic force due to wire 2 on 3
For equilibrium of wire 3,
From equation (1)
The above equation would be satisfied for only a particular position of wire 3 with respect to wire 1 and 2.
Thus, the situation is possible and the only possibility is placing the third wire at a distance at which the force between wire 1 and 3 balances the force between wire 2 and 3.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the situation is possible and the only possibility is placing the third wire at a distance at which the force between wire 1 and 3 balances the force between wire 2 and 3.
(b)
The position of wire 3.
(b)
Answer to Problem 42P
The position of wire 3 is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The electric current in wire 1 is
The formula to calculate the magnitude of force per unit length is,
Here,
For the stability of wire 3 the magnetic force due to wire 1 on 3 must be equal to that of magnetic force due to wire 2 on 3
For equilibrium of wire 3,
From equation (2)
Substitute
The distance of the wire 3 is
Thus, the position of wire 3 is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the position of wire 3 is
(c)
The magnitude and direction of the current in wire 3.
(c)
Answer to Problem 42P
The magnitude of current in wire 3 is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The electric current in wire 1 is
For the stability of wire 1 the magnetic force due to wire 1 on 3 must be equal to that of magnetic force due to wire 2 on 1
For equilibrium of wire 3,
From equation (2)
Here,
Substitute
The magnitude of electric current in wire 3 is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of current in wire 3 is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
- A long, straight wire lies on a horizontal table and carries a current of 1.20 μA. In a vacuum, a proton moves parallel to the wire (opposite the current) with a constant speed of 2.30 × 104 m/s at a distance d above the wire. Ignoring the magnetic field due to the Earth, determine the value of d.arrow_forwardRank the magnitudes of' the forces exerted on the following particles from largest to smallest. In your ranking, display any cases of equality, (a) an electron moving at 1 Mm/s perpendicular to a 1-mT magnetic field (b) an electron moving at 1 Mm/s parallel to a 1-mT magnetic field (c) an electron moving at 2 Mm/s perpendicular to a 1-mT magnetic field (d) a proton moving at 1 Mm/s perpendicular to a 1-mT magnetic field (e) a proton moving at 1 Mm/s at a 45 angle to a 1-mT magnetic fieldarrow_forwardA square loop whose sides are 6.0-cm long is made with copper wire of radius 1.0 mm. If a magnetic field perpendicular to the loop is changing at a rate of 5.0 mT/s, what is the current in the loop?arrow_forward
- In a long, .straight, vertical lightning stroke, electrons move downward and positive ions move upward and constitute a current of magnitude 20.0 kA. At a location 50.0 m east of the middle of the stroke, a free electron drifts through the air toward the west with a speed of 300 m/s. (a) Make a sketch showing the various vectors involved. Ignore the effect of the Earth's magnetic field. (b) Find the vector force the lightning stroke exerts on the electron. (c) Find the radius of the electrons path. (d) Is it a good approximation to model the electron as moving in a uniform field? Explain your answer. (e) If it does not collide with any obstacles, how many revolutions will the electron complete during the 60.0-s duration of the lightning stroke?arrow_forwardA thin copper rod 1.00 m long has a mass of 50.0 g. What is the minimum current in the rod that would allow it to levitate above the ground in a magnetic field of magnitude 0.100 T? (a) 1.20 A (b) 2.40 A (c) 4.90 A (d) 9.80 A (e) none of those answersarrow_forwardWhat magnetic field is required in order to confine a proton moving with a speed of 4.0 × 106 m/s to a circular orbit of radius 10 cm?arrow_forward
- A wire 2.80 m in length carries a current of 5.00 A in a region where a uniform magnetic field has a magnitude of 0.390 T. Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic force on the wire assuming the angle between the magnetic field and the current is (a) 60.0, (b) 90.0, and (c) 120.arrow_forwardDoes increasing the magnitude of a uniform magnetic field through which a charge is traveling necessarily mean increasing the magnetic force on the charge? Does changing the direction of the field necessarily mean a change in the force on the charge?arrow_forwardThe magnetic field perpendicular to a single sire loop of diameter 10.0 cm decreases fron 0.50 T to zero. The re Is made of copper and has a diameter of 2.0 mm and length 1.0 cm. How much charge moves thrnugh the re while tt field is changing?arrow_forward
- Two long, parallel wires are hung by cords of length 5.0 cm, as shown in the accompanying figure. Each wire has a mass per unit length of 30 g/m, and they carry the same current in opposite directions. What is the current if the cords hang at 6.0° with respect to the vertical?arrow_forwardThe accompanying figure shows a cross-section of a long, hollow, cylindrical conductor of inner radius r1= 3.0 cm and outer radius r2= 5.0 cm. A 50-A current distributed uniformly over the cross-section flows into the page. Calculate the magnetic field at r = 2.0 cm. r = 4.0 cm. and r = 6.0 cm.arrow_forwardSolenoid A has length L and N turns, solenoid B has length 2L and N turns, and solenoid C has length L/2 and 2N turns. If each solenoid carries the same current, rank the magnitudes of the magnetic fields in the centers of the solenoids from largest to smallest.arrow_forward

 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning




