
Concept explainers
The length of tube that must be used in the heat exchanger.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The density of ethylene glycol
The specific heat of ethylene glycol
The thermal conductivity
The Prandlt number
The dynamic viscosity
The inside diameter of tube
The outside diameter of tube
The mass flow rate of ethylene glycol
The inlet temperature of ethylene glycol
The outlet temperature of ethylene glycol
The thermal conductivity of copper
The temperature of saturated vapor
Calculation:
The figure below shows the schematic diagram of the heat exchanger.
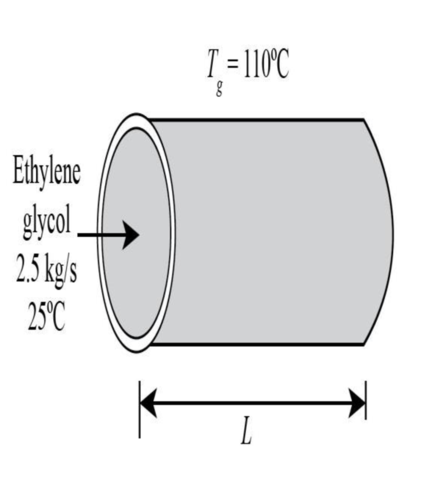
Figure-(1)
Calculate the heat transfer in the heat exchanger.
Calculate the velocity of fluid.
Calculate the Reynolds number.
Calculate the Nusselt number for water.
Calculate the heat transfer coefficient on the inner side.
Assume the wall temperature of
Calculate the heat transfer coefficient on the outer side.
Calculate the average temperature of ethylene glycol.
Now check if the assumed value is correct or not.
The assumed value is near to the obtained value. Thus it correct.
Calculate the overall heat coefficient based on the outer surface.
Calculate the log mean temperature difference.
Calculate the length of tube.
Thus, the length of the tube is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Loose Leaf For Fundamentals Of Thermal-fluid Sciences Format: Looseleaf
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





