
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Two compounds are to be identified on the basis of their chemical formulas, and IR and
Concept introduction:
Peaks in an IR spectrum help in determining functional groups in a compound.
In 13C NMR spectroscopy, we get information about the different types of carbon present in the given molecular formula.
13C NMR spectroscopy can even differentiate between primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary carbons.
If the compound only contains C, H, and O, the index of hydrogen deficiency is calculated as
If a compound contains C, H, O, and a halogen, the halogen can be treated as if it were a hydrogen for the purpose of calculating index of hydrogen deficiency.
Answer to Problem 35P
Solution:
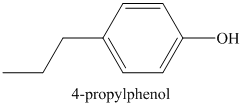
a) The structure of the compound
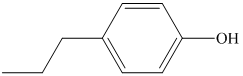
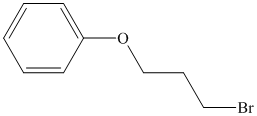
b) The structure of the compound
Explanation of Solution
The chemical formula of the compound is
The count of four indicates the possibility of a benzene ring. If a benzene ring is present, the oxygen atom would be singly bonded, either as a hydroxyl group or as an ether functional group.
The IR and 13C NMR spectra of the compound are as follows:
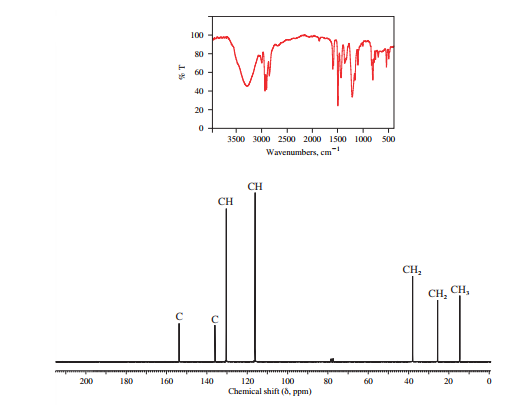
The presence of a broad peak around 3200
Chemical formula of the compound is
Therefore this compound also is likely to have a benzene ring.
The IR and 13C NMR spectra of the compound are as follows:
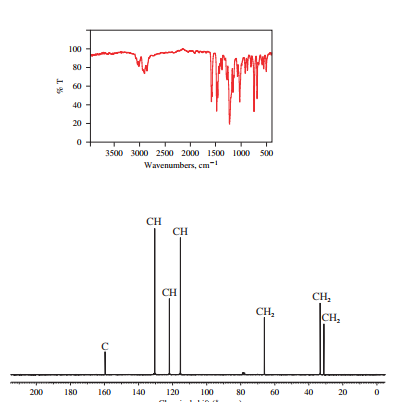
Two peaks in the IR spectrum, at about 700 and 750
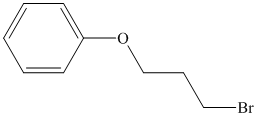
Therefore, the structure of the compound is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-W/STUD.SOLN.MAN.
- A 13C NMR spectrum of commercially available 2,4-pentanediol, shows five peaks at 23.3, 23.9, 46.5, 64.8, and 68.1 . Explain.arrow_forwardWhat is the structure of the compound if the mass spectrum shows M+ = 72, IR shows peak near 1720 cm-1, 13C-NMR shows 4 lines. The proton NMR is: 2.4 ppm (2H quartet) 2.1 ppm (3H singlet) 1.1 ppm (3H triplet)arrow_forwardWhat is the structure of the compound if M+ = 122, IR peaks 1500, 1600 and a strong peak near 3350 cm-1, the carbon-13 NMR shows six lines, the 1H-NMR spectrum is: 7.15 ppm (5H multiplet) 3.75 ppm (2H triplet) 2.75 ppm (2H triplet)arrow_forward
- Identify the compound (C9H11NO2) that would give the spectral data (IR,13C NMR and 1H) below.arrow_forwardIdentify below compound from its spectral data. Molecular formula: C4H7N IR:2250 cm−1 1H NMR data:1.08 (triplet, 3 H), 1.70 (multiplet, 2 H), and 2.34 (triplet,2 H) ppmarrow_forwardThe H1H1 NMR spectrum shown corresponds to an unknown compound with the molecular formula C6H10C6H10. There are no strong IR bands between 2100 and 2300 or 3250 and 3350 cm−1. Deduce and draw the structure of the molecule that corresponds to the spectrum.arrow_forward
- What is the structure of the compound with the formula C5H12O, if it has a strong broad IR signal centered near 3330 cm-2, and the 1H-NMR spectrum is: 0.91 ppm (3H triplet) 1.19 ppm (6H singlet) 1.50 ppm (2H quartet) 2.24 ppm (1H singlet)arrow_forward15. Compound C has a molecular weight of 94.54 and the 1H-NMR spectrum shows four signals - a triplet at 3.81 ppm, a triplet at 3.63 ppm, a singlet at 2.19 ppm, and a triplet of triplets at 2.02 ppm. The mass, IR, and 13C-NMR spectra of compound C are shown below, they are also downloadable for closer inspection by clicking the link under the spectral data. Identify C and explain your reasoning. refer to picturearrow_forwardC. explain each step with words on how to get the structure. Step 1: Calculate the Index of Hydrogen Deficiency (IHD). Step 2: Use IR to determine obvious functional groups. Step 3: Use 1H-NMR to determine structural details. Step 4: Confirm the final structure using 13C-NMR.arrow_forward
- A compound used as a moth repellant has three molecular ion peaks at m/z = 146 (100%), 148 (65%) & 150 (10%) amu in its mass spectrum. A pair of smaller peaks are seen at m/z= 111 (34%) & 113 (11%). The infrared spectrum shows sharp absorption just above 3000 cm^-1 region, and also at 1480 cm^-1. The ^1 H nmr shows a single sharp signal at delta = 7.2 ppm, and the ^13 C nmr has two signals (delta = 133 & 130 ppm).arrow_forwardIs it possible to distinguish between the following compounds using the spectroscopic techniques covered in CHE331? If so, discuss how. If not, discuss why.Benzonitrile vs Benzaldehyde(a) UV spectroscopy(b) IR spectroscopy(c) Mass spectrometry(d) 13C NMR spectroscopy(e) 1H NMR spectroscopyarrow_forward28. Shown below is the NMR spectrum of a compound with formula C.H.,0 4.0 Spectrum in the infrared has intense absorption at 1740 cm 1 and several intense bands between 1333 and 1035 cm -1 . Draw the structure of the compound. note: point out the structures on the chart for better understandingarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

