
Concept explainers
SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY
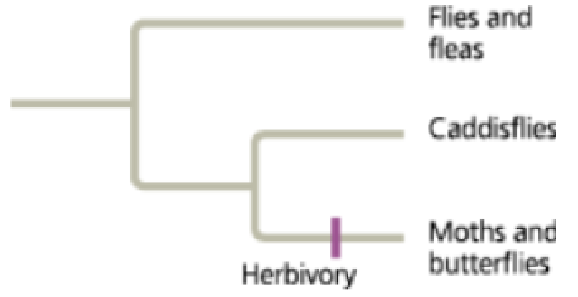
Herbivory (plant eating) has evolved repeatedly in insects, typically from meat-eating or detritus-feeding ancestors (detritus is dead organic matter). Moths and butterflies, for example, eat plants, whereas their "sister group" (the insect group to which they are most closely related), the caddisflies, feed on animals, fungi, or detritus. As illustrated in this phylogenetic tree, the combined moth/butterfly and caddis fly group shares a common ancestor with flies and fleas. Like caddisflies, flies and fleas are thought to have evolved from ancestors that did not eat plants.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 23 Solutions
Campbell Biology in Focus, Books a la Carte Edition; Modified Mastering Biology with Pearson eText - ValuePack Access Card - for Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Concepts and Investigations
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
Biology Science Notebook
Becker's World of the Cell (9th Edition)
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (8th Edition)
- Insects are the largest group of animals on Earth. Insect diversity is greatest in the tropics, where habitat destruction and species extinction are occurring at an alarming rate. What biological, economic, and ethical arguments can you advance to persuade people and governments to preserve this biological diversity? Instructions:arrow_forwardEvolutionary theory predicts that species are related, not independent. Four of the following examples provide support for this prediction, but one is irrelevant. Which of examples listed below does not support the claim that species are related? A. Many dinosaurs and other organisms went extinct following a huge asteroid impact at the end of the Cretaceous. B. Before synthetic insulin was available, diabetics used injections of purified pig insulin to manage their disease. C. The endostyle of lancelets (invertebrate chordates) and the thyroid gland of vertebrates develop similarly, and both produce iodinated proteins. D. All prokaryotes and eukaryotes use DNA to carry their genetic information. E. Ground squirrel species found on the North and South sides of the Grand Canyon are very similar to each other.arrow_forwardShow a phylogenetic tree that reflects the evolutionary relationships between the following taxa. All of the taxa should be on one (1) tree; var. stands for variety, a subspecific taxon (just as a genus can contain several to many species, a species can include several varieties). Family Fagaceae Quercus rubra var. rubra Red oak Quercus rubra var. borealis northern red oak Quercus velutina Black oak Fagus grandifolia Beech Castanea dentata American chestnut Castanea pumila var. pumila Chinquapin Castanea pumila var. ashei Coastal chinquapin Family Betulaceae Betula nigra River birch Betula papyrifera Paper birch Corylus cornuta Beaked hazel-nut Corylus americana American hazel-nut asap pleasearrow_forward
- Find a current, credible phylogenetic tree representing any group of organisms (your choice)! Draw that tree and on it indicate nodes, synapomorphes, monophyletic, polyphyletic, and paraphyletic groups (make sure the image you choose is complex enough to show all these groups). Below your drawing, in paragraph form, describe the relationships of four of the members on your tree based on how a phylogenetic tree is interpretedarrow_forwardGreen and brown algae share many common features. Both have pigments for trapping sunlight and use photosynthesis for energy. Both store their food as sugars. Both have cell walls and plant-like bodies. However, their DNA suggests that they are not even remotely related to one another. Green algae and brown algae show __________________ evolution, since they look similar, but are not close relatives. A) convergent B) divergent C) homologous D) vestigial Not Gradedarrow_forwardMake phylogenetic tree with this organisms: Gray whale,Ginger, Peacock, Tiger, Rice, Cat, Pineapple, Crocodile, Box jellyfish, Bambooarrow_forward
- For novice biologists, taxonomy and phylogenetics are difficult concepts to understand and keep separate. This confusion is made worse because modern taxonomic methods make use of molecular tools. Write an essay that contrasts taxonomy to phylogenetics and explain how both disciplines are important to our understanding of species and evolution. Your essay should include a description of taxonomy and phylogenetics, as well as a detailed explanation about how information is represented in a phylogenetic tree or a cladogram.arrow_forwardPhylogeny refers to the evolutionary descent of taxa. It refers to the relationship between ancestors and descendants and relationships among descendant taxa. It shows the lineage of taxa which can be summarized in a branching diagram called a phylogenetic tree.1. Express some basic evolutionary relationships among groups of microorganisms, plants, and animals; 2. Illustrate the relationship of organisms with their environment; and 3. Analyze environmental factors contributing to biodiversity richness and lossarrow_forwardScientists have studied, in detail, the evolution of the peppered moth, Biston betularia, over the last two hundred years. The peppered moths rest on tree trunks and are a tempting treat for birds in the area. In the mid-1800s the trees in their England habitat were covered with lichens, which are a light, grayish-green color. Although color variations occurred, the vast majority of the moths were light-colored. Because their light coloration effectively camouflaged them against the lichens-covered trees, they were not as easily seen by birds as darker colored moths. The light colored moths flourished.The environment changed, as the Industrial Revolution progressed. By 1900, the lichens had died and trees were coated with soot due to industrial pollution. The lighter colored moths were no longer "hidden" in their environment, and in fact, were easily seen by their predators. Their numbers dwindled. At the same time, the darker-colored moths flourished because of their ability to hide…arrow_forward
- Choose 5 filter feeders including sponges and whale sharks, each from a distinct animal phyla or class: Make a phylogenetic tree to show how they are related to one another propose how and why so many animals could have developed filter feeding & what would happen if we removed filter feeders from the oceanarrow_forwardOn the tree of life, branches that lead to several groups of green algae branch off from the one that leads to land plants. Which of the following statements is correct? A. Green algae are very closely related to the fungi. B. Green algae and land plants are not related. C. Land plants appeared first in the fossil record. D. Green algae are the ancestors of land plant mycorrhizae E. Land plants and algae have a common ancestor.arrow_forwardMake phylogenetic tree with this organisms : Gray whale,Ginger, Peacock, Tiger, Rice, Cat, Pineapple, Crocodile, Box jellyfish, Bamboo Make it look like the picture example.arrow_forward
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning

