
Concept explainers
(a)
The net electric flux through the cube.
(a)
Answer to Problem 32P
Net electric flux through the cube is
Explanation of Solution
Below figure shows the electric field magnitude and its direction in all face’s of the cube.
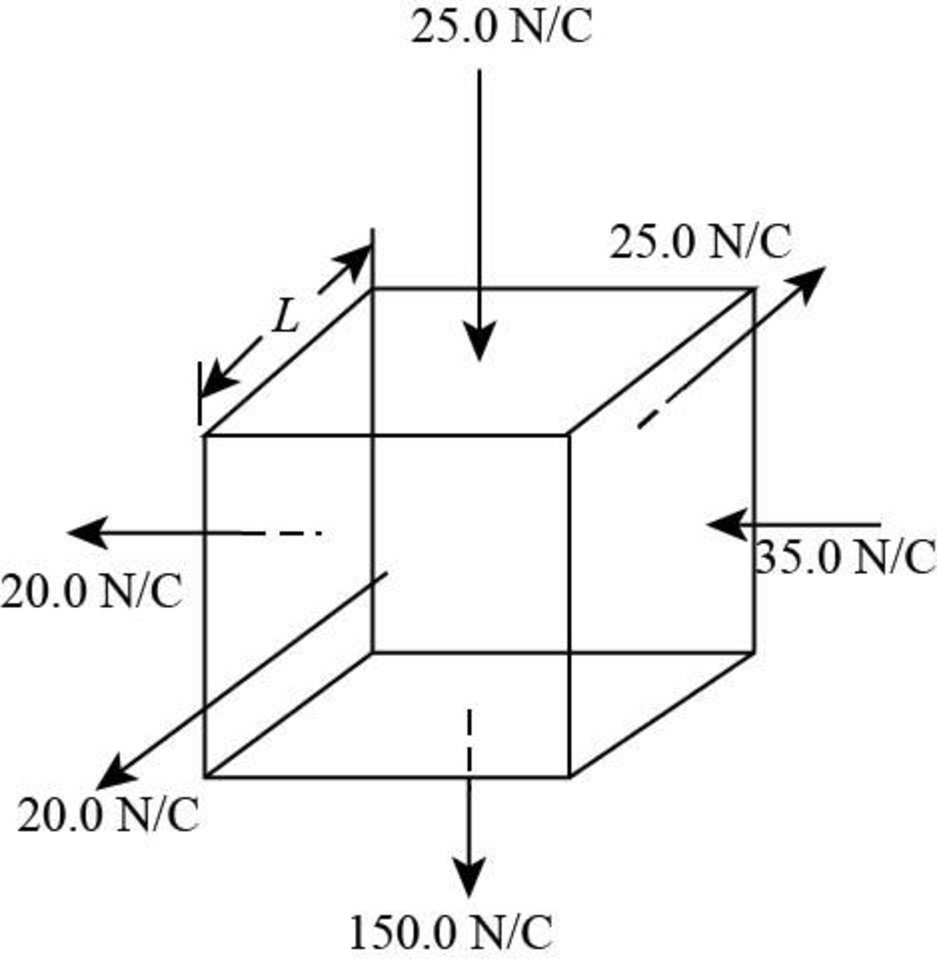
Figure (1)
From Figure (1), it is shown that, the electric fields are perpendicular to the faces of the cube. Therefore, use Gauss law for net flux through the closed Gaussian surface.
Write the expression for net flux through the closed Gaussian surface.
Here,
Write the expression for net electric flux through cube.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, net electric flux through the cube is
(b)
The net charge inside the cube.
(b)
Answer to Problem 32P
The charge enclosed within the Gaussian surface (cube) is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the charge enclosed within the Gaussian surface (cube) is.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the charge enclosed within the Gaussian surface (cube) is
(c)
Whether the net charge could be a point charge.
(c)
Answer to Problem 32P
No, the net charge can’t be a point charge.
Explanation of Solution
No, single positive charge’s magnitude is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the net charge can’t be a point charge.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics Technology Update
- A solid insulating sphere of radius a = 5.00 cm carries a net positive charge of Q = 3.00 C uniformly distributed throughout its volume. Concentric with this sphere is a conducting spherical shell with inner radius b = 10.0 cm and outer radius c = 15.0 cm as shown in Figure P24.54, having net charge q = 1.00 C Prepare a graph of the magnitude of the electric field due to this configuration versus r for O r 25.0 cm.arrow_forwardAssume the magnitude of the electric field on each face of the cube of edge L = 1.00 m in Figure P23.32 is uniform and the directions of the fields on each face are as indicated. Find (a) the net electric flux through the cube and (b) the net charge inside the cube. (c) Could the net charge he a single point charge? Figure P23.32arrow_forwardA particle with charge Q = 5.00 C is located at the center of a cube of edge L = 0.100 m. In addition, six other identical charged particles having q = 1.00 C are positioned symmetrically around Q as shown in Figure P23.19. Determine the electric flux through one face of the cube. Figure P23.19 Problems 19 and 20.arrow_forward
- A solid, insulating sphere of radius a has a uniform charge density throughout its volume and a total charge Q. Concentric with this sphere is an uncharged, conducting, hollow sphere whose inner and outer radii are b and e as shown in Figure P24.45. We wish to understand completely the charges and electric fields at all locations. (a) Find the charge contained within a sphere of radius r a. (b) From this value, find the magnitude of the electric field for r a. (c) What charge is contained within a sphere of radius r when a r b? (d) From this value, find the magnitude of the electric field for r when a r b. (e) Now consider r when b r c. What is the magnitude of the electric field for this range of values of r? (f) From this value, what must be the charge on the inner surface of the hollow sphere? (g) From part (f), what must be the charge on the outer surface of the hollow sphere? (h) Consider the three spherical surfaces of radii a, b, and c. Which of these surfaces has the largest magnitude of surface charge density? Figure P24.45 Problems 43 and 47.arrow_forwardFind an expression for the magnitude of the electric field at point A mid-way between the two rings of radius R shown in Figure P24.30. The ring on the left has a uniform charge q1 and the ring on the right has a uniform charge q2. The rings are separated by distance d. Assume the positive x axis points to the right, through the center of the rings. FIGURE P24.30 Problems 30 and 31.arrow_forwardA long, straight wire is surrounded by a hollow metal cylinder whose axis coincides with that of the wire. The wire has a charge per unit length of , and the cylinder has a net charge per unit length of 2. From this information, use Gausss law to find (a) the charge per unit length on the inner surface of the cylinder, (b) the charge per unit length on the outer surface of the cylinder, and (c) the electric field outside the cylinder a distance r from the axis.arrow_forward
- A solid conducting sphere of radius 2.00 cm has a charge 8.00 μC. A conducting spherical shell of inner radius 4.00 cm and outer radius 5.00 cm is concentric with the solid sphere and has a total charge −4.00 μC. Find the electric field at (a) r = 1.00 cm, (b) r = 3.00 cm, (c) r = 4.50 cm, and (d) r = 7.00 cm from the center of this charge configuration.arrow_forwardA conducting rod carrying a total charge of +9.00 C is bent into a semicircle of radius R = 33.0 cm, with its center of curvature at the origin (Fig.P24.75). The charge density along the rod is given by = 0 sin , where is measured clockwise from the +x axis. What is the magnitude of the electric force on a 1.00-C charged particle placed at the origin?arrow_forwardA point charge is located at the origin. Centered along the x axis is a cylindrical closed surface of radius 10 cm with one end surface located at x = 2 m and the other end surface located at x = 2.5 m. If the magnitude of the electric flux through the surface at x = 2 m is 4 N . m2 /C, what is the magnitude of the electric flux through the surface at x = 2.5 m? Select one: a. 1.8 N . m2 /C b. 2.56 N . m2 /C c. 1.0 N . m2 /C d. 4.0 N . m2 /C e. 5.0 N . m2 /Carrow_forward
- A uniformly charged disk sit in the yz-plane with its center at the origin. It has radius 2.5 cm and carries a total charge of 4.0 x 10 -12 C. What is the magnitude of the electricfield on the x-axis of the disk at the disk at distance x = 0.2 cm?What is the direction of the eletric field on the axis of the disk at x = 0.2 cm? (to the center or from the center)Is the magnitude of the electric field at x= 0.2 cm larger or smaller thant the electric field at 0.2 cm from an infinite sheet of charge with the same charge per unit area as the disk?What is the percent difference between the electric field produced by the finite disk and by an infinite sheet with the same charge per unit area at x = 0.4 cm?arrow_forwardA solid sphere, of radius a = 2.30 cm is concentric with a spherical conducting shell of inner radius b = 2.00a and outer radius c = 2.40a. The sphere has a net charge q1 = +6.00 fC which is distributed uniformly through the sphere; the shell has a net charge of q2 = −q1. (d) What is the magnitude of the electric field at radial distance r = 1.60a? (e) What is the magnitude of the electric field at radial distance r = 2.20a? (f) What is the magnitude of the electric field at radial distance r = 3.30a?arrow_forwardAssume the magnitude of the electric field on each face of the cube of edge L = 1.00 m in Figure P23.32 is uniform and the directions of the fields on each face are as indicated. Find (a) the net electric flux through the cube and (b) the net charge inside the cube. (c) Could the net charge he a single point charge?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning




