
Concept explainers
(a)
The charge on the insulating sphere.
(a)
Answer to Problem 57AP
The charge on the insulating sphere is
Explanation of Solution
Draw a Gaussian sphere from the centre of the insulating sphere such that the radius of the Gaussian sphere is between
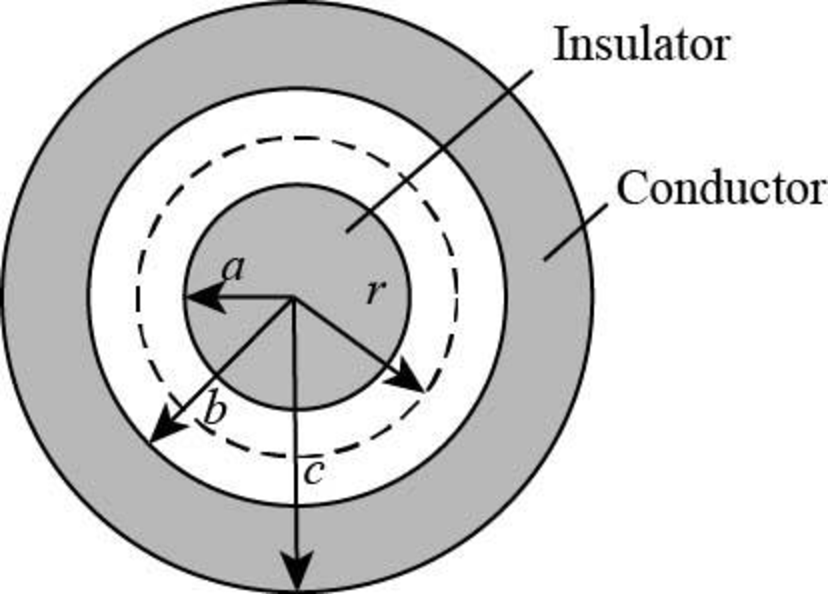
Figure-(1)
Here,
Write the expression to calculate the electric field at the radial distance
Here,
Conclusion:
Convert the units of
Substitute
The electric field at
Therefore, the charge on the insulating sphere is
(b)
The net charge on the hollow
(b)
Answer to Problem 57AP
The net charge on the hollow conducting sphere is
Explanation of Solution
Draw a Gaussian sphere from the centre of the insulating sphere such that the radius of the Gaussian sphere is greater than
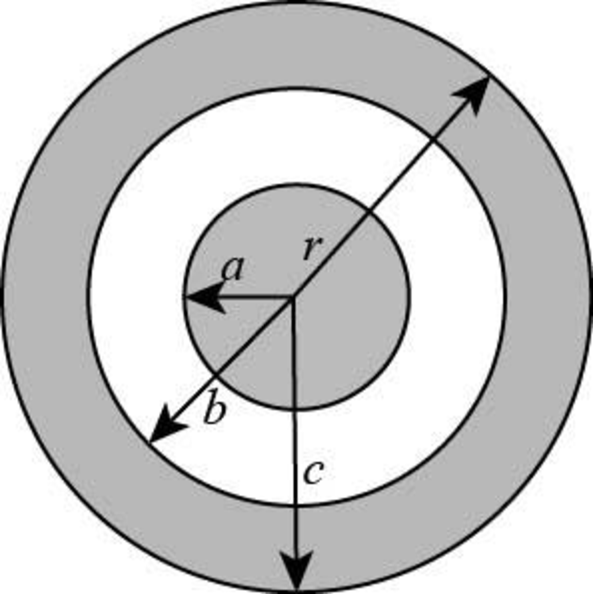
Figure-(2)
Here,
Write the expression to calculate the electric field at the radial distance
Here,
Write the expression to calculate the total charge.
Here,
Conclusion:
Convert the units of
Substitute
The electric field at
Substitute
Therefore, the net charge on the hollow conducting sphere is
(c)
The charge on the inner surface of the hollow conducting sphere.
(c)
Answer to Problem 57AP
The charge on the inner surface of the hollow conducting sphere is
Explanation of Solution
The insulating sphere induces a charge on the inner surface of the hollow conducting sphere that has the same magnitude but has an opposite sign.
Therefore, the charge on the inner surface of the hollow conducting sphere is
(d)
The charge on the outer surface of the hollow conducting sphere.
(d)
Answer to Problem 57AP
The charge on the outer surface of the hollow conducting sphere is
Explanation of Solution
The charge on the outer surface of the hollow conducting sphere is equal to the net charge on the hollow conducting sphere minus the charge on the inner surface of the hollow conducting sphere.
Write the expression to calculate the charge on the outer surface of the hollow conducting sphere.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the charge on the outer surface of the hollow conducting sphere is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics Technology Update
- A total charge Q is distributed uniformly on a metal ring of radius R. a. What is the magnitude of the electric field in the center of the ring at point O (Fig. P24.61)? b. What is the magnitude of the electric field at the point A lying on the axis of the ring a distance R from the center O (same length as the radius of the ring)? FIGURE P24.61arrow_forwardA solid insulating sphere of radius a = 5.00 cm carries a net positive charge of Q = 3.00 C uniformly distributed throughout its volume. Concentric with this sphere is a conducting spherical shell with inner radius b = 10.0 cm and outer radius c = 15.0 cm as shown in Figure P24.54, having net charge q = 1.00 C Prepare a graph of the magnitude of the electric field due to this configuration versus r for O r 25.0 cm.arrow_forwardA uniformly charged conducting rod of length = 30.0 cm and charge per unit length = 3.00 105 C/m is placed horizontally at the origin (Fig. P24.37). What is the electric field at point A with coordinates (0, 0.400 m)?arrow_forward
- A solid, insulating sphere of radius a has a uniform charge density throughout its volume and a total charge Q. Concentric with this sphere is an uncharged, conducting, hollow sphere whose inner and outer radii are b and e as shown in Figure P24.45. We wish to understand completely the charges and electric fields at all locations. (a) Find the charge contained within a sphere of radius r a. (b) From this value, find the magnitude of the electric field for r a. (c) What charge is contained within a sphere of radius r when a r b? (d) From this value, find the magnitude of the electric field for r when a r b. (e) Now consider r when b r c. What is the magnitude of the electric field for this range of values of r? (f) From this value, what must be the charge on the inner surface of the hollow sphere? (g) From part (f), what must be the charge on the outer surface of the hollow sphere? (h) Consider the three spherical surfaces of radii a, b, and c. Which of these surfaces has the largest magnitude of surface charge density? Figure P24.45 Problems 43 and 47.arrow_forwardFind an expression for the magnitude of the electric field at point A mid-way between the two rings of radius R shown in Figure P24.30. The ring on the left has a uniform charge q1 and the ring on the right has a uniform charge q2. The rings are separated by distance d. Assume the positive x axis points to the right, through the center of the rings. FIGURE P24.30 Problems 30 and 31.arrow_forwardA solid plastic sphere of radius R1 = 8.00 cm is concentric with an aluminum spherical shell with inner radius R2 = 14.0 cm and outer radius R3 = 17.0 cm (Fig. P25.67). Electric field measurements are made at two points: At a radial distance of 34.0 cm from the center, the electric field has magnitude 1.70 103 N/C and is directed radially outward, and at a radial distance of 12.0 cm from the center, the electric field has magnitude 9.10 104 N/C and is directed radially inward. What are the net charges on a. the plastic sphere and b. the aluminum spherical shell? c. What are the charges on the inner and outer surfaces of the aluminum spherical shell? FIGURE P25.67arrow_forward
- A conducting rod carrying a total charge of +9.00 C is bent into a semicircle of radius R = 33.0 cm, with its center of curvature at the origin (Fig.P24.75). The charge density along the rod is given by = 0 sin , where is measured clockwise from the +x axis. What is the magnitude of the electric force on a 1.00-C charged particle placed at the origin?arrow_forwardThree charged spheres are suspended by nonconducting light rods of length L = 0.625 m from the point O. The rods are fixed in position so that the middle rod is vertical and the rods on the left and right make an angle of 30.0 with the vertical (Fig. P24.50). a. What is the total electric field due to the charged spheres at point O? b. What is the electric force on a particle with charge q = +5.00 C placed at point O? FIGURE P24.50arrow_forwardA uniform electric field given by E=(2.655.35j)105N/C permeates a region of space in which a small negatively charged sphere of mass 1.30 g is suspended by a light cord (Fig. P24.53). The sphere is found to be in equilibrium when the string makes an angle = 23.0. a. What is the charge on the sphere? b. What is the magnitude of the tension in the cord? FIGURE P24.53arrow_forward
- A positively charged disk of radius R = 0.0366 m and total charge 56.8 C lies in the xz plane, centered on the y axis (Fig. P24.35). Also centered on the y axis is a charged ring with the same radius as the disk and a total charge of 34.1 C. The ring is a distance d = 0.0050 m above the disk. Determine the electric field at the point P on the y axis, where P is y = 0.0100 m above the origin. FIGURE P24.35 Problems 35 and 36.arrow_forwardA uniformly charged disk sit in the yz-plane with its center at the origin. It has radius 2.5 cm and carries a total charge of 4.0 x 10 -12 C. What is the magnitude of the electricfield on the x-axis of the disk at the disk at distance x = 0.2 cm?What is the direction of the eletric field on the axis of the disk at x = 0.2 cm? (to the center or from the center)Is the magnitude of the electric field at x= 0.2 cm larger or smaller thant the electric field at 0.2 cm from an infinite sheet of charge with the same charge per unit area as the disk?What is the percent difference between the electric field produced by the finite disk and by an infinite sheet with the same charge per unit area at x = 0.4 cm?arrow_forwardAn electric field of intensity 3.40 kN/C is applied along the x-axis. Calculate the electric flux through a rectangular plane 0.350 m wide and 0.700 m long if the following conditions are true. (a) The plane is parallel to the yz-plane.____________N · m2/C(b) The plane is parallel to the xy-plane._____________N · m2/C(c) The plane contains the y-axis, and its normal makes an angle of 35.0° with the x-axis.______________N · m2/Carrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning



