
Concept explainers
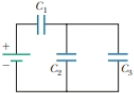
Three capacitors are connected to a battery as shown in Figure P25.10. Their capacitances are C1 = 3C, C2 = C, and C3 = 5C. (a) What is the equivalent capacitance of this set of capacitors? (b) State the ranking of the capacitors according to the charge they store from largest to smallest. (c) Rank the capacitors according to the potential differences across them from largest to smallest. (d) What If? Assume C3 is increased. Explain what happens to the charge stored by each capacitor.
Figure P25.10
(a)
Answer to Problem 10P
Explanation of Solution
Given information: The value of capacitor 1 is
Explanation:
The capacitors
Formula to calculate the equivalent capacitance of the system when they are connected in parallel.
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the equivalent capacitance of the system when they are connected in parallel is
The capacitors
Formula to calculate the equivalent capacitance of the system when they are connected in series.
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the equivalent capacitance of this set of capacitors is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the equivalent capacitance of this set of capacitors is
(b)
Answer to Problem 10P
Explanation of Solution
Given information: The value of capacitor 1 is
Explanation:
Calculate the voltage across
Here,
Substitute
Calculate the charge for the capacitor
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the charge for the capacitor
Calculate the charge for the capacitor
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the charge for the capacitor
Calculate the voltage across
Here,
Substitute
Calculate the charge for the capacitor
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the charge for the capacitor
The ranking of the capacitors according to the charge they store from largest to smallest is
Thus, the ranking of the capacitors according to the charge they store from largest to smallest is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the ranking of the capacitors according to the charge they store from largest to smallest is
(c)
Answer to Problem 10P
Explanation of Solution
Given information: The value of capacitor 1 is
Explanation:
Calculate the potential difference across
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the potential difference across
Calculate the potential difference across
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the potential difference across
Calculate the potential difference across
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the potential difference across
The ranking of the capacitors according to the potential differences across them from largest to smallest is
Thus, the ranking of the capacitors according to the potential differences across them from largest to smallest is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the ranking of the capacitors according to the potential differences across them from largest to smallest is
(d)
Answer to Problem 10P
Explanation of Solution
Given information: The value of capacitor 1 is
Explanation:
If the value of capacitor 3 is increased, the total capacitance will increase which results in increasing the total charge.
Due to this, the charge across capacitor 1 increases.
Since, the charge across capacitor 1 is directly proportional to the voltage across the capacitor 1. So, the voltage across
Since the voltage across the capacitor 2 decreases, charge across the capacitor 2 also decreases and the voltage across the capacitor 3 decreases, charge across the capacitor 3 also decreases.
Thus, if
Conclusion:
Therefore, if
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
PHYSICS FOR SCI. & ENGR(LL W/WEBASSIGN)
- An arrangement of capacitors is shown in Figure P27.23. a. If C = 9.70 105 F, what is the equivalent capacitance between points a and b? b. A battery with a potential difference of 12.00 V is connected to a capacitor with the equivalent capacitance. What is the energy stored by this capacitor? Figure P27.23 Problems 23 and 24.arrow_forwardFour capacitors are connected as shown in Figure P25.11. (a) Find the equivalent capacitance between points a and b. (b) Calculate the charge on each capacitor, taking Vab = 15.0 V. Figure P25.11arrow_forwardGiven the arrangement of capacitors in Figure P27.23, find an expression for the equivalent capacitance between points a and b. Figure P27.23 Problems 23 and 24.arrow_forward
- Find (a) the equivalent capacitance of the capacitors in Figure P26.26, (b) the charge on each capacitor, and (c) the potential difference across each capacitor.arrow_forwardA spherical capacitor is formed from two concentric spherical conducting spheres separated by vacuum. Tire inner sphere has radius 12.5 cm and the outer sphere has radius 14.8 cm. A potential difference of 120 V is applied to the capacitor, (a) What is the capacitance of the capacitor? tb) What is the magnitude of the electrical field at r = 12.6 cm, just outside the inner sphere? (c) What is the magnitude of the electrical field at r = 14.7 cm, just inside the outer sphere? (d) For a parallel-plate capacitor the electrical field is uniform in the region between the plates, except near the edges of the plates. Is this also true for a spherical capacitor?arrow_forwardFind the equivalent capacitance between points a and b in the combination of capacitors shown in Figure P25.13. Figure P25.13arrow_forward
- An air-filled capacitor is made from two flat parallel plates 1.0 mm apart. The inside area of each plate is 8.0cm2. (a) What is the capacitance of this set of plates? (b) If the region between the plates is filled with a material whose dielectric constant is 6.0, what is the new capacitance?arrow_forwardA parallel-plate capacitor with plates of area LW and plate separation t has the region between its plates filled with wedges of two dielectric materials as shown in Figure P25.48. Assume t is much less than both L and W. (a) Determine its capacitance. (b) Should the capacitance be the same if the labels 1 and 2 are interchanged? Demonstrate that your expression does or does not have this property. (c) Show that if 1 and 2 approach equality to a common value , your result becomes the same as the capacitance of a capacitor containing a single dielectric: C = 0LW/t. Figure P25.48arrow_forward(a) Find the equivalent capacitance between points a and b for the group of capacitors connected as shown in Figure P25.12 (page 686). Take C1 = 5.00 F, C2 = 10.0 F, and C3 = 2.00 F. (b) What charge is stored on C3 if the potential difference between points a and b is 60.0 V? Figure P25.12arrow_forward
- A spherical capacitor consists of a spherical conducting shell of radius b and charge 2Q that is concentric with a smaller conducting sphere of radius a and charge +Q (Fig. P20.36). (a) Show that its capacitance is C=abke(ba) (b) Show that as b approaches infinity, the capacitance approaches the value a/ke = 40a. Figure P20.36arrow_forward(a) Find the equivalent capacitance between points a and b for the group of capacitors connected as shown in Figure P20.44. Take C1 = 5.00 F, C2 = 10.0 F, and C3 = 2.00 F. (b) What charge is stored on C3 if the potential difference between points a and b is 60.0 V? Figure P20.44arrow_forwardFor the system of capacitors shown in Figure P16.41, find (a) the equivalent capacitance of the system, (b) the charge on each capacitor, and (c) the potential difference across each capacitor. Figure P16.41 Problems 41 and 60.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





