
To determine: What happens to private savings, private investment spending and the investment rate in the given scenario.
Concept Introduction:
Closed Economy: It is a type of economy in which there is no external trade that means there is no import and export.
Investment spending: All those spending which are done on physical capital which means that only expenses that increase economy level of physical capital is known as investment spending.
The formula to calculate investment spending is:
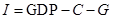
Here,
- I is investment spending.
- GDP is
gross domestic product . - C is consumption spending.
- G is government spending.
Private Saving: It is the saving made by people for times of emergency or bad financial conditions in the future.
The formula to calculate private saving is:
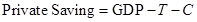
Here,
- T is tax revenue.
- GDP is gross domestic product.
- C is consumption spending.
Budget Balance: The budget is considered to be balanced when revenue collected from tax and expenditures made by government are equal. When it is deficit it is represented by a negative value, when it is surplus it is represented by a positive value and in case of balanced budget it is zero.
Loanable Funds Market: It is an imaginary market which illustrates the market result of the demand for funds which are generated by borrowers and supply of funds which are provided by the lenders.
Demand for Loanable Funds: It is represented by a downward sloping curve which shows that as the interest rate increases the demand for such funds decreases and vice versa.
Supply for Loanable Fund: It is represented by the s curve that slopes upward which means that as the interest rate increases the supply of such fund also rises and vice versa.
Explanation of Solution
a. Budget balance is zero.
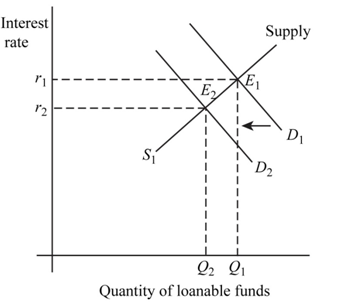
Fig 1
- In the above figure, vertical axis shows interest rate and horizontal axis shows quantity of loanable funds.
 and
and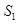 represents demand and supply curve for loanable funds respectively. The intersection of demand and supply curve gives equilibrium point
represents demand and supply curve for loanable funds respectively. The intersection of demand and supply curve gives equilibrium point 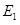 where the interest rate is
where the interest rate is 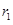 and quantity of funds is
and quantity of funds is 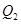
- Due to reduction in deficit the demand curve will shift from
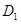 to
to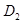 There is no change in supply curve. The new equilibrium is achieved at point
There is no change in supply curve. The new equilibrium is achieved at point 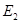 where the new interest rate is
where the new interest rate is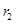 and. quantity of fund demanded is
and. quantity of fund demanded is 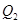 Hence, interest rate as well as quantity of loanable fund decreases at new level of equilibrium.
Hence, interest rate as well as quantity of loanable fund decreases at new level of equilibrium. - Due to decrease in interest rate and income, private savings will decrease as the
opportunity cost of saving has decreased. Private investment spending will increase because at lower interest rate people will borrow more to invest.
Conclusion:
Thus, private saving and interest rate decreases and private investment spending increases.
b. Consumers save more.
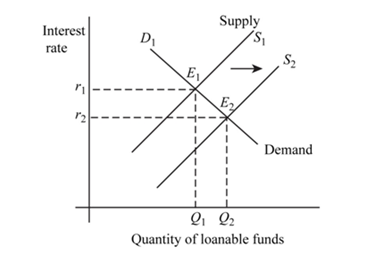
Fig 2
- In the above figure, vertical axis shows interest rate and horizontal axis shows quantity of loanable funds.
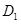 and
and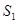 represents demand and supply curve for loanable funds respectively. The intersection of demand and supply curve gives equilibrium point
represents demand and supply curve for loanable funds respectively. The intersection of demand and supply curve gives equilibrium point 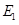 where the interest rate is
where the interest rate is 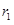 and quantity of funds is
and quantity of funds is 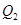
- Due to increase in saving by consumer supply curve will shift from
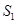 to
to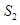 There is no change in demand curve. The new equilibrium is achieved at point
There is no change in demand curve. The new equilibrium is achieved at point 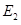 where the new interest rate is
where the new interest rate is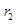 and. quantity of fund demanded is
and. quantity of fund demanded is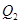 Hence, interest rate has decreased and quantity has increased at new level of equilibrium.
Hence, interest rate has decreased and quantity has increased at new level of equilibrium. - Due to decrease in interest rate private savings will decrease as the opportunity cost of saving has decreased and due to increase in output income will increase which will induce more saving.
- Hence, savings will increase or decrease, this cannot be concluded. Private investment spending will increase because at lower interest rate people will borrow more to invest.
Conclusion:
Thus, interest rate decreases and private investment spending increases. Private saving may decrease or increase.
c. Businesses become optimistic for future profitability.
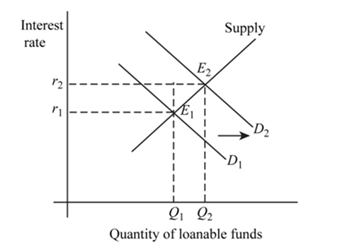
Fig 3
- In the above figure, vertical axis shows interest rate and horizontal axis shows quantity of loanable funds.
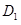 and
and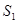 represents demand and supply curve for loanable funds respectively. The intersection of demand and supply curve gives equilibrium point
represents demand and supply curve for loanable funds respectively. The intersection of demand and supply curve gives equilibrium point 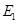 where the interest rate is
where the interest rate is 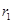 and quantity of funds is
and quantity of funds is 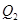
- Businesses are optimistic about future profitability which means that the investment will increase. This will lead to rise in demand for loanable fund. As a result the demand curve will shift from
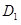 to
to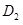
- There is no change in supply curve. The new equilibrium is achieved at point
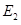 where the new interest rate is
where the new interest rate is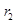 Hence, interest rate as well as quantity of loanable fund increases to a new level of equilibrium.
Hence, interest rate as well as quantity of loanable fund increases to a new level of equilibrium. - Due to an increase in interest rate, income private savings will increase as the opportunity cost of saving has increased. Private investment spending will decrease because at higher interest rate people will borrow less to invest.
Conclusion:
Thus, private saving and interest rate increases and private investment spending decreases.
Want to see more full solutions like this?

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





