
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of an example of a saturated fat is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Saturated fats are those in which the bond between carbon and hydrogen molecules is saturated. They consist of a single bond between them. These fats are solid at room temperature.
(a)
Answer to Problem 25.14SP
The structure of an example of a saturated fat is shown in Figure 1.
Explanation of Solution
Saturated fats are those in which the bond between carbon and hydrogen molecules is saturated. They consist of a single bond between them. These fats are solid at room temperature.
An example of a saturated fat is tristearin. It is a triglyceride with chemical formula
The structure of tristearin is shown below.
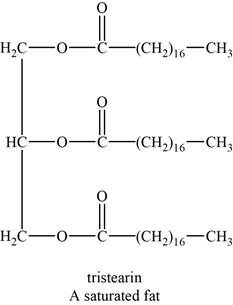
Figure 1
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of an example of polyunsaturated oil is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Polyunsaturated fats are those in which the bond between carbon and hydrogen molecules is unsaturated. They consist of a double bond between them. These fats are liquid at room temperature.
(b)
Answer to Problem 25.14SP
The structure of an example of a polyunsaturated fat is shown in Figure 2.
Explanation of Solution
Polyunsaturated fats are those in which the bond between carbon and hydrogen molecules is unsaturated. They consist of a double bond between them. These fats are liquid at room temperature.
An example of a polyunsaturated fat is triolein. It is a triglyceride with chemical formula
The structure of triolein is shown below.
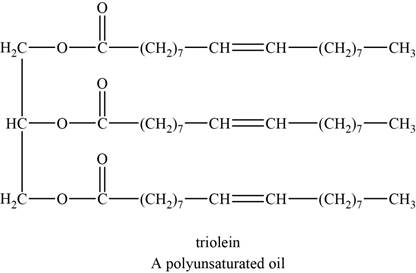
Figure 2
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of an example of wax is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Waxes occur widely in nature and are esters of long chain fatty acids with long chain alcohols.
(c)
Answer to Problem 25.14SP
The structure of an example of a polyunsaturated fat is shown in Figure 3.
Explanation of Solution
Waxes occur widely in nature and are esters of long chain fatty acids with long chain alcohols.
An example of wax can be spermaceti. It helps animals to regulate the buoyancy for deep diving.
The structure of spermaceti is shown below.
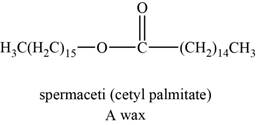
Figure 3
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of an example of soap is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The reaction of fatty acids with sodium hydroxide leads to the formation of sodium salt of fatty acid and soap is the sodium salt of a fatty acid. The carboxylate group is negatively charged and is hydrophilic in nature, whereas long hydrocarbon is hydrophobic and lipophilic in nature.
(d)
Answer to Problem 25.14SP
The structure of an example of soap is shown in Figure 4.
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of fatty acids with sodium hydroxide leads to the formation of sodium salt of fatty acid and soap is the sodium salt of a fatty acid. The carboxylate group is negatively charged and is hydrophilic in nature, whereas long hydrocarbon is hydrophobic and lipophilic in nature.
An example of soap is sodium stearate. The structure of sodium stearate is shown below.
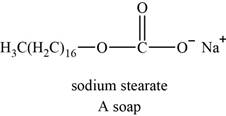
Figure 4
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure of an example of detergent is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Synthetic detergents are the sodium salts of sulfonic acids. Carboxylic acid is less acidic than sulfonic acids; therefore salts of sulfonic acids do not protonate in acidic wash water. The salts of sulfonic acid are soluble in water and can be used in hard water without formation of scum.
(e)
Answer to Problem 25.14SP
The structure of an example of detergent is shown in Figure 5.
Explanation of Solution
Synthetic detergents are the sodium salts of sulfonic acids. Carboxylic acid is less acidic than sulfonic acids; therefore salts of sulfonic acids do not protonate in acidic wash water. The salts of sulfonic acid are soluble in water and can be used in hard water without formation of scum.
An example of detergent is alkylbenzenesulfonate. The structure of alkylbenzenesulfonate is shown below.
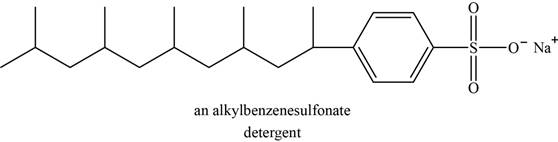
Figure 5
(f)
Interpretation:
The structure of an example of phospholipids is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Lipids that contain groups derived from phosphoric acid are phospholipids. The common phospholipids are phosphogylcerides. Generally it contains phosphoric acid in place of one fatty acids of a triglyceride.
(f)
Answer to Problem 25.14SP
The structure of an example of soap is shown in Figure 6.
Explanation of Solution
Lipids that contain groups derived from phosphoric acid are phospholipids. The common phospholipids are phosphogylcerides. Generally it contains phosphoric acid in place of one fatty acids of a triglyceride.
An example of phospholipids can be phosphatidic acids. The structure of phosphatidic acids is shown below.
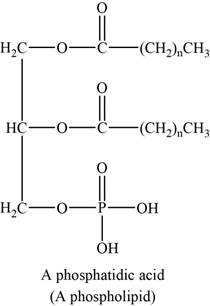
Figure 6
(g)
Interpretation:
The structure of an example of prostaglandins is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Prostaglandins are the powerful biochemical regulators than steroids. These are the fatty derivatives and are isolated from the secretions of the prostate gland. They have an important role in regulating blood pressure, blood clotting.
They have cyclopentane ring with two long side chains that are trans to each other. And one side chain end with a carboxylic acid.
(g)
Answer to Problem 25.14SP
The structure of an example of prostaglandin is shown in Figure 7.
Explanation of Solution
Prostaglandins are the powerful biochemical regulators than steroids. These are the fatty derivatives and are isolated from the secretions of the prostate gland. They have an important role in regulating blood pressure, blood clotting.
They have cyclopentane ring with two long side chains that are trans to each other. And one side chain ends with a carboxylic acid.
The structure of prostaglandin is shown below.
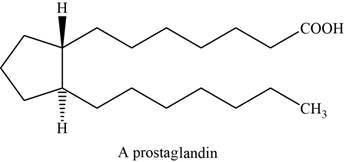
Figure 7
(h)
Interpretation:
The structure of an example of steroid is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Steroids are the polycyclic molecules found in all plants and animals. They do not undergo hydrolysis; therefore they are classified as simple lipids. Their structure is based on the tetracyclic andostane ring.
(h)
Answer to Problem 25.14SP
The structure of an example of steroid is shown in Figure 8.
Explanation of Solution
Steroids are the polycyclic molecules found in all plants and animals. They do not undergo hydrolysis; therefore they are classified as simple lipids. Their structure is based on the tetracyclic andostane ring.
An example of steroid is androsterone. The structure of androsterone is shown below.
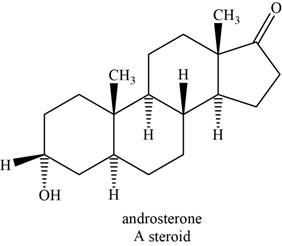
Figure 8
(i)
Interpretation:
The structure of an example of sesquiterpene is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
An isoprene unit is bunched of five-carbon atoms. In terpenes, the isoprene units are connected to each other in head to tail fashion. The head part of an isoprene unit is branched, whereas the tail part of an isoprene unit is unbranched.
(i)
Answer to Problem 25.14SP
The structure of an example of sesquiterpene is shown in Figure 9.
Explanation of Solution
An isoprene unit is bunched of five-carbon atoms. In terpenes, the isoprene units are connected to each other in head to tail fashion. The head part of an isoprene unit is branched, whereas the tail part of an isoprene unit is unbranched.
An example of sesquiterpene is
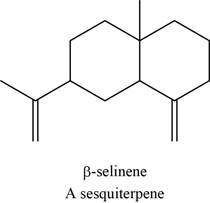
Figure 9
There are three isoprene units in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
Organic Chemistry&mod Mstgchem Ac Pkg
- The plasmalogens are a group of lipids found in nerve and muscle cells. How do plasmalogens differ from fats?arrow_forwardDescribe the structure of a micelle formed by the association of fatty acid molecules in water. What forces hold the micelle together?arrow_forwardMost recipes for making homemade soap recommend using excess fat. Explain why this is beneficial.arrow_forward
- Which statement is NOT true? Group of answer choices a. There are many different types of lipids. b. Lipids are soluble in organic solvents. c. Some hormones are lipids. d. All lipids contain fatty acids. e. Lipids are found in cell membranes.arrow_forwardIf a person produces and exudes a polyunsaturated oil from their skin, how does it ultimatum make closeness smell bad and how does baking soda remove the odorarrow_forward14. Which lipid does not contain any fatty acids?A.GlycerophospholipidB. triglycerideC. steroidD. wax E. sphingolipidarrow_forward
- Explain the hydrolysis reaction of fats and explain how animals obtain lipidsarrow_forwardHow does esterification help identify lipids?arrow_forwardA hydrogen bond is distinct from ionic and covalent bonds in that it a. forms between adjacent molecules rather than within molecules. b. forms only between two hydrogen atoms. c. is considerably stronger than the other two types of bonds. d. occurs more commonly in lipids than in other types of moleculesarrow_forward
- 1. What is the difference between fats and oils? 2. Explain the difference between saturated and unsaturated triglycerides? 3. What is the difference between a monounsaturated and a polyunsaturated fat? 4. Which is more beneficial, saturated or unsaturated fatty acids? Why? 5. What are the functions of glycerides?arrow_forward1. Define and give, at least, two examples for the different classes of lipids. Draw their structure. a. Saturated fatty acids b. Unsaturated fatty acids c. Triglycerides d. Phospholipids e. Steroids 2. Explain why a waxy surface coating is valuable for the survival of succulent plants in arid regions. 3. Why are vegetables and fruits coated with wax during shipping and upon storage? 4. From a health standpoint, how do cholesterol and lecithin in egg yolk complement each other? 5. Why do animals that live in cold climates tend to have higher percentages of polyunsaturated fatty acid and deposits in their lipids than animals that live in warm climates?arrow_forwardhow does sapnification worksarrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning 
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





