
(a)
Interpretation:
Appropriate curved arrows and products for the homolysis of the
Concept introduction:
The breaking of a covalent bond, whereby the electrons making up that bond are distributed equally to the atoms which are disconnected, is known as the homolytic bond dissociation or homolysis. In homolysis, generally radicals are formed. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical, and a single barbed arrow (![]() ) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process.
) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process.
Answer to Problem 25.1P
Appropriate curved arrow for the homolysis of the
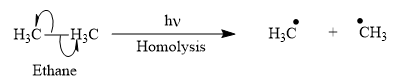
The product for the homolysis of the
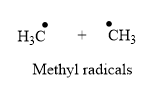
Explanation of Solution
The homolysis of the

A single barbed arrow (![]() ) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical. Thus, the product of the homolysis of the
) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical. Thus, the product of the homolysis of the
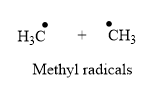
Appropriate curved arrows and products for the homolysis of the
(b)
Interpretation:
Appropriate curved arrows and products for the homolysis of the
Concept introduction:
The breaking of a covalent bond, whereby the electrons making up that bond are distributed equally to the atoms which are disconnected, is known as the homolytic bond dissociation or homolysis. In homolysis, generally radicals are formed. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical, and a single barbed arrow (![]() ) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process.
) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process.
Answer to Problem 25.1P
Appropriate curve arrow for the homolysis of the
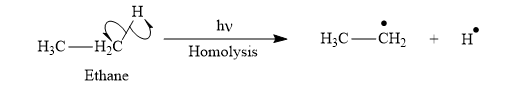
The product for the homolysis of the
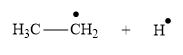
Explanation of Solution
The homolysis of the

A single barbed arrow (![]() ) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical. Thus the product of the homolysis of the
) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical. Thus the product of the homolysis of the
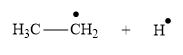
Appropriate curved arrows and products for the homolysis of a
(c)
Interpretation:
Appropriate curved arrows and products for the homolysis of the
Concept introduction:
The breaking of a covalent bond, whereby the electrons making up that bond are distributed equally to the atoms which are disconnected, is known as the homolytic bond dissociation or homolysis. In homolysis, generally radicals are formed. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical, and a single barbed arrow (![]() ) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process.
) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process.
Answer to Problem 25.1P
The appropriate curve arrow for the homolysis of t the
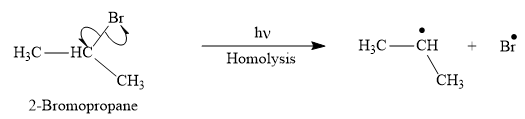
The product for the homolysis of the
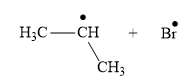
Explanation of Solution
The homolysis of the

A single barbed arrow (![]() ) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical. Thus the product of the homolysis of the
) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical. Thus the product of the homolysis of the

Appropriate curved arrows and products for the homolysis of the
(d)
Interpretation:
Appropriate curved arrows and products for the homolysis of the
Concept introduction:
The breaking of a covalent bond, whereby the electrons making up that bond are distributed equally to the atoms which are disconnected, is known as the homolytic bond dissociation or homolysis. In homolysis, generally radicals are formed. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical, and a single barbed arrow (![]() ) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process.
) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process.
Answer to Problem 25.1P
The appropriate curve arrow for the homolysis of the
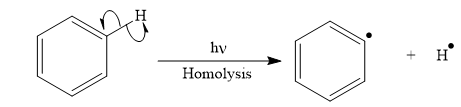
The product for the homolysis of the
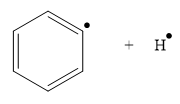
Explanation of Solution
The homolysis of the

A single barbed arrow (![]() ) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical. Thus the product of the homolysis of the
) is used to represent the movement of a single electron in a homolysis process. In homolysis, a covalent bond is broken down equally and each atom acquires a single electron, which is called a radical. Thus the product of the homolysis of the

Appropriate curved arrows and products for the homolysis of a
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
ORG.CHEM W/TEXT+SOLU.MANUAL
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





