
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product formed when
Concept Introduction:
Pyridine is a heterocyclic compound which contains nitrogen atom. Pyridine nitrogen atom contain a lone pair. The lone pair of pyridine is not involved in the resonance with the
Answer to Problem 26.27AP
The product formed when
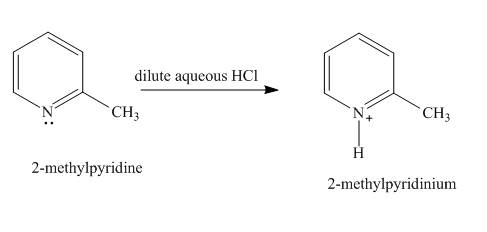
Explanation of Solution
In the given compound, the lone pair of the pyridine nitrogen is not involved in the resonance with the ring. Pyridine acts as base in the presence of acid. The nitrogen abstracts the proton from acid. The product formed is

Figure 1
The product formed in the given reaction is
(b)
Interpretation:
The product formed when
Concept Introduction:
Pyridine is a heterocyclic compound which contains nitrogen atom. Pyridine nitrogen atom contain a lone pair. The lone pair of pyridine is not involved in the resonance with the aromatic ring. No delocation of electron takes place, hence pyridine acts as a base. The hydrogen atoms of pyridine ring are not highly acidic, so mild base can’t abstract proton from pyridine. It requires a strong base for abstraction of proton.
Answer to Problem 26.27AP
No reaction takes place when
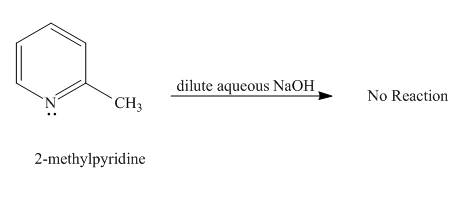
Explanation of Solution
Protons of pyridine are not highly acidic in nature. Sodium hydroxide cannot abstract proton from pyridine. It requires a very strong base for the removal of proton from pyridine to takes place. Hence, no reaction takes place between

Figure 2
No product is formed in the given reaction.
(c)
Interpretation:
The product formed when
Concept Introduction:
Pyridine is a heterocyclic compound which contains nitrogen atom. Pyridine nitrogen atom contain a lone pair. The lone pair of pyridine is not involved in the resonance with the aromatic ring. No delocation of electron takes place, hence pyridine acts as a base. The hydrogen atoms of pyridine ring are not highly acidic, so mild base can’t abstract proton from pyridine. It requires a strong base for abstraction of proton.
Answer to Problem 26.27AP
The product formed when
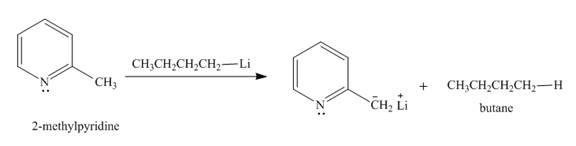
Explanation of Solution
The butyl-lithium compound is a very strong base. It will abstract proton from the methyl group of
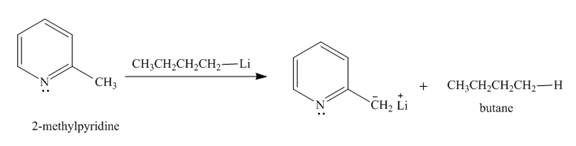
Figure 3
The product formed in the given reaction is
(d)
Interpretation:
The product formed when
Concept Introduction:
Nitration reaction is aromatic electrophilic substitution reaction. The nitrating mixture contains nitric acid and sulfuric acid. The nitrosonium ion is formed as electrophile. The methyl group is an activating group, so it promotes electrophilic substitution reaction at ortho-para position.
Answer to Problem 26.27AP
The product formed when
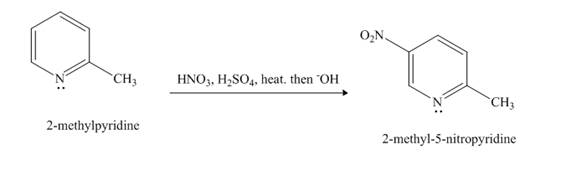
Explanation of Solution
The compound

Figure 4
The product formed in the given reaction is
(e)
Interpretation:
The product formed when
Concept Introduction:
Pyridine is a heterocyclic compound which contains nitrogen atom. Pyridine nitrogen atom contain a lone pair. The lone pair of pyridine is not involved in the resonance with the aromatic ring. Hydrogen peroxide is a strong oxidizing agent. It will oxidize the nitrogen atom of pyridine to form
Answer to Problem 26.27AP
The product formed when
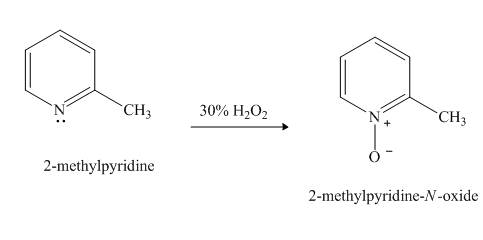
Explanation of Solution
Hydrogen peroxide is an oxidizing agent. It will oxidize the given compound. The oxidation reaction takes place at the nitrogen atom.

Figure 5
The product formed in the given reaction of
(f)
Interpretation:
The product formed when
Concept Introduction:
Pyridine is a heterocyclic compound which contains nitrogen atom. Pyridine nitrogen atom contain a lone pair. The lone pair of pyridine is not involved in the resonance with the aromatic ring. No delocation of electron takes place, hence pyridine acts as a base. The nitrogen atom lone pair attacks the methyl group of methyl iodide.
Answer to Problem 26.27AP
The product formed when
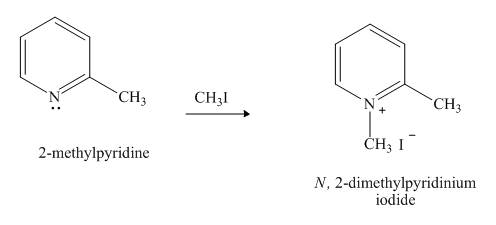
Explanation of Solution
The lone pair of nitrogen atom of pyridine is not involved in the resonance with the aromatic ring. The lone pair makes the pyridine compound basic in nature. When compound

Figure 6
The product formed in the given reaction of
(g)
Interpretation:
The product formed when
Concept Introduction:
Pyridine is a heterocyclic compound which contains nitrogen atom. Pyridine nitrogen atom contain a lone pair. The lone pair of pyridine is not involved in the resonance with the aromatic ring. No delocation of electron takes place, hence pyridine acts as a base. Lithiated pyridine compound reacts with
Answer to Problem 26.27AP
The product formed when
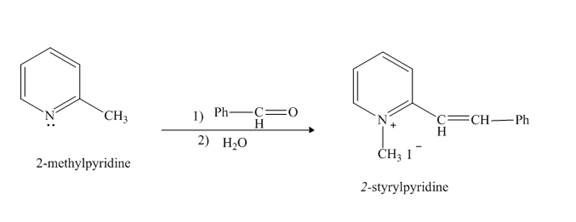
Explanation of Solution
The lithiation product formed reacts with benzaldehyde, nucleophilic addition reaction takes place to form

Figure 7
The product formed when
(h)
Interpretation:
The product formed when
Concept Introduction:
Pyridine is a heterocyclic compound which contains nitrogen atom. Pyridine nitrogen atom contain a lone pair. The lone pair of pyridine is not involved in the resonance with the aromatic ring. Hydrogen peroxide is a strong oxidizing agent. It will oxidize the nitrogen atom of pyridine to form
Answer to Problem 26.27AP
The product formed when
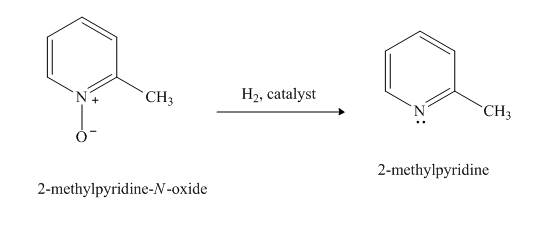
Explanation of Solution
The compound

Figure 8
The product formed when
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY SAPLING ACCESS + ETEX
- (a) Compound Z is a tertiary aromatic amine with the formula, C8H11N. Provide a chemical structure for compound Z. (b)nDraw the structure of the product formed exclusively when nitrous acid reacts with Z.arrow_forwardOne frequently used method for preparing methyl esters is by reaction of carboxylic acids with diazomethane, CH2N2. The reaction occurs in two steps: (l) protonation of diazomethane by the carboxylic acid to yield methyldiazonium ion, CH3N2+, plus a carboxylate ion; and (2) reaction of the carboxylate ion with CH3N2+. (a) Draw two resonance structures of diazomethane, and account for step 1. (b) What kind of reaction occurs in step 2?arrow_forwardWrite reactions of ethyl chloride with the following reagents: a. KOH, aqueous solution b. NaCNarrow_forward
- Compound A (C6H12O2) reacts with water, acid, and heatto yield compound B (C5H10O2) and compound C (CH4O).Compound B is acidic. Deduce possible structures of compounds A, B, and Carrow_forwardSeveral sulfonylureas, a class of compounds containing RSO2NHCONHR, are useful drugs as orally active replacements for injected insulin in patients with adult-onset diabetes. These drugs decrease blood glucose concentrations by stimulating b cells of the pancreas to release insulin and by increasing the sensitivity of insulin receptors in peripheral tissues to insulin stimulation. Tolbutamide is synthesized by the reaction of the sodium salt of p-toluenesulfonamide and ethyl N-butylcarbamate . Propose a mechanism for this step.arrow_forwardDraw a resonance structure of the acetonitrile anion, -: CH2CN, and account for the acidity of nitriles.arrow_forward
- An organic compound A of unknown structure was found to have a molecular formula C8H16. When A was poured in water and heated, compound B having a molecular formula C8H18O was formed. B upon heating with sulfuric acid was converted to C as the major product which is identical to A. Ozonolysis of C gave one molecule each of two different products D and E, both having a molecular formula C4H8O. Write the reactions involved and determine the structure of A,B,C,D and E.arrow_forwardAn unknown hydrocarbon A with the formula C6H12 reacts with 1 molar equivalent of H2 over a palladium catalyst to give hydrocarbon B. Hydrocarbon A also reacts with OsO4 to give the glycol C. When oxidized with KMnO4 in acidic solution, A gives two fragments. One fragment is propanoic acid, CH3CH2COOH, and the other fragment is ketone D (R2C=O). What are the structures of A, B, C and D? Write all reactions.arrow_forwardDescribe the trends in the acidityand physical properties of carboxylicacids, and explain how their acidityvaries with their substituents.arrow_forward
- 2,3-Dimethylfumaric acid has a molecular formula C6H8O4. It undergoes oxidativecleavage to form two identical compound N. Compound N is then reacted withethylmagnesium bromide to form compound O. Compound O is then hydrolysed inacidic condition to form compound P. Draw the structure of compound N, O and P. PLEASE PROVIDE CLEAR HANDWRITING, and explantionarrow_forwardWhich of the following produces only butanoic acid (CH3CH2CH2 CO2H) being 'hydrolyzed in acid medium?arrow_forward4. Compound A has the formula C 8H 8. It reacts rapidly with KMnO 4 to give CO 2 and a carboxylic acid, B (C 7H 6O 2), but reacts with only 1 molar equivalent of H 2 on catalytic hydrogenation over a palladium catalyst. On hydrogenation under conditions that reduce aromatic rings, 4, equivalents of H 2 are taken up and hydrocarbon C (C 8H 16) is produced. What are the structures of A, B, and C.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


