
(a)
Interpretation:
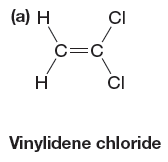
Monomer shown here can undergo free radical
Concept introduction:
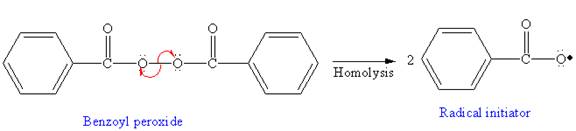
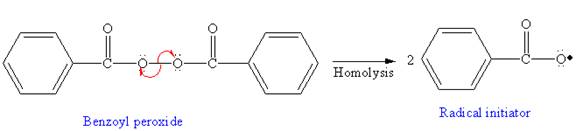
The first step of free radical polymerization is initiation. Homolysis of benzoyl peroxide takes place in the first step. Benzoyl peroxide is used as a radical initiator. Homolysis of benzoyl peroxide is further promoted by the additional resonance stabilization in the resulting radical. After initiation, propagation occurs via radical addition. In first step propagation, the initial radical adds to the C=C bond of the monomer giving a new radical. The new radical reacts with the other molecule of monomer in the second propagation. From the growing polymer chain, one can identify the structural pattern that is repeated which is the condensed formula showing repeating unit. The name of the polymer is written by writing poly followed by the monomer’s name, and we can enclose the monomer’s name in parenthesis as it consists of two or more words.
Answer to Problem 26.33P
The mechanism for the first two propagation steps using benzoyl peroxide as the initiator is shown below:
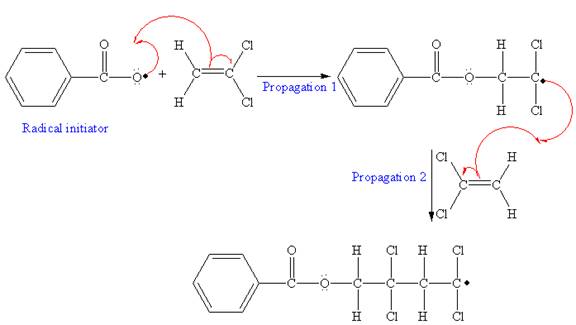
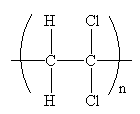
The condensed formula for the polymer showing the repeating unit is shown below:
A name for the polymer is: Poly(vinylidene chloride)
Explanation of Solution
The given monomer is
In the initiation step, homolysis of benzoyl peroxide takes place to form a radical initiater as follows:
After initiation, propagation occurs via radical addition. In first step propagation, the initial radical adds to the C=C bond of the monomer giving a new radical. The new radical reacts with the other molecule of the monomer in the second propagation. The mechanism for the first two propagation steps is shown below:
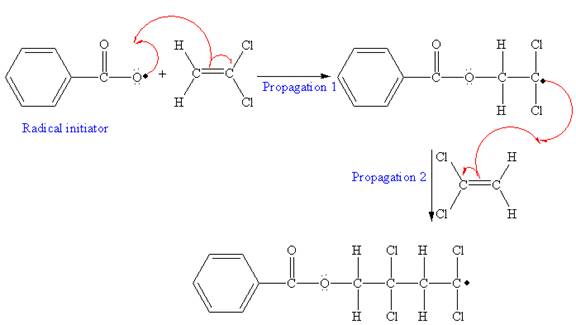
The condensed formula showing repeating unit is shown below:

A name for the polymer is written by writing poly- followed by the monomer’s name, and we can enclose the monomer’s name in parenthesis as it consists of two or more words. Therefore, the name of the polymer is: Poly(vinylidene chloride).
The mechanism for the first two propagation steps for the given monomer is drawn on the basis of chain-growth polymerization. The condensed formula is drawn identifying the structural pattern that is repeated in the growing chain.
(b)
Interpretation:
Monomer shown here can undergo free radical polymerization. For its polymerization: the mechanism for the first two propagation steps using benzoyl peroxide as the initiator is to drawn. The condensed formula for the polymer showing the repeating unit is to be drawn, and a name for the polymer is to be provided.
Concept introduction:
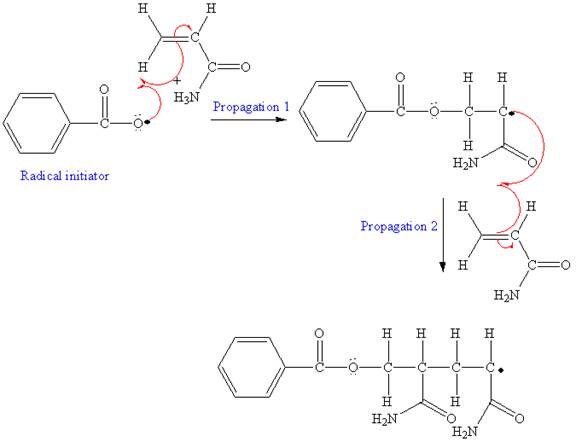
The first step of free radical polymerization is initiation. Homolysis of benzoyl peroxide takes place in first step. Benzoyl peroxide is used as a radical initiator. Homolysis of benzoyl peroxide is further promoted by the additional resonance stabilization in the resulting radical. After initiation, propagation occurs via radical addition. In first step propagation, the initial radical adds to the C=C bond of the monomer giving a new radical. The new radical reacts with the other molecule of the monomer in the second propagation. From the growing polymer chain, one can identify the structural pattern that is repeated which is the condensed formula showing the repeating unit. The name of the polymer is written by writing poly followed by the monomer’s name, and we can enclose the monomer’s name in parenthesis as it consists of two or more words.
Answer to Problem 26.33P
The mechanism for the first two propagation steps using benzoyl peroxide as the initiator is shown below:
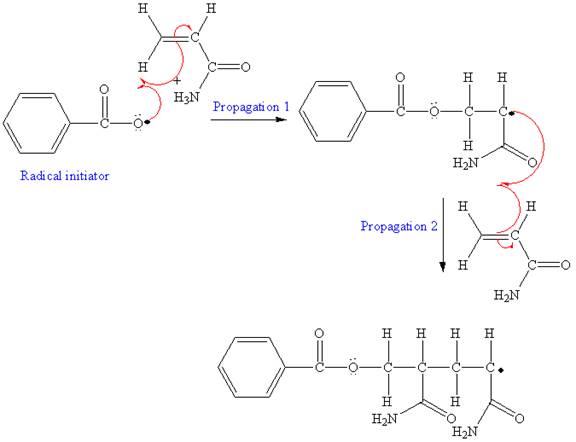
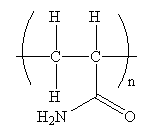
The condensed formula for the polymer showing the repeating unit is shown below:
A name for the polymer is: Polyacrylamide.
Explanation of Solution
The given monomer is,
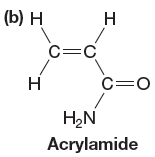
In the initiation step, homolysis of benzoyl peroxide takes place to form a radical initiator as follows:
After initiation, propagation occurs via radical addition. In first step propagation, the initial radical adds to the C=C bond of the monomer giving a new radical. The new radical reacts with the other molecule of the monomer in the second propagation. The mechanism for the first two propagation steps is shown below:
The condensed formula showing repeating unit is shown below:

A name for the polymer is written by writing poly- followed by the monomer’s name, and we can enclose the monomer’s name in parenthesis as it consists of two or more words. Therefore, the name of the polymer is: Polyacrylamide.
The mechanism for the first two propagation steps for given monomer are drawn on the basis of chain-growth polymerization. The condensed formula is drawn identifying the structural pattern that is repeated in the growing chain.
(c)
Interpretation:
Monomer shown here can undergo free radical polymerization. For its polymerization: the mechanism for the first two propagation steps using benzoyl peroxide as the initiator is to drawn. The condensed formula for the polymer showing the repeating unit is to be drawn, and a name for the polymer is to be provided.
Concept introduction:
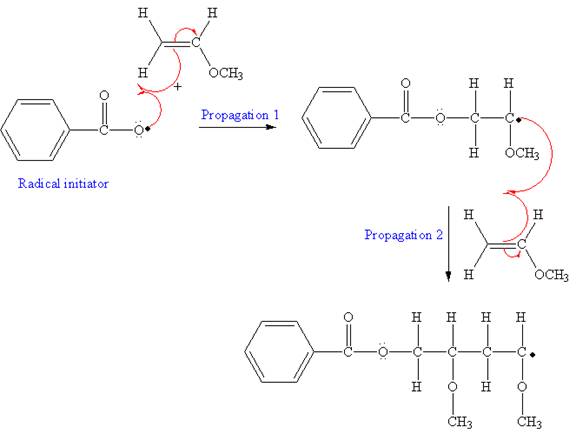
The first step of free radical polymerization is initiation. Homolysis of benzoyl peroxide takes place in first step. Benzoyl peroxide is used as a radical initiator. Homolysis of benzoyl peroxide is further promoted by the additional resonance stabilization in the resulting radical. After initiation, propagation occurs via radical addition. In first step propagation, the initial radical adds to the C=C bond of the monomer giving a new radical. The new radical reacts with the other molecule of the monomer in the second propagation. From the growing polymer chain, one can identify the structural pattern that is repeated which is the condensed formula showing the repeating unit. The name of the polymer is written by writing poly followed by the monomer’s name, and we can enclose the monomer’s name in parenthesis as it consists of two or more words.
Answer to Problem 26.33P
The mechanism for the first two propagation steps, using benzoyl peroxide as the initiator is shown below:
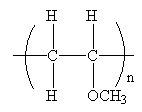
The condensed formula for the polymer showing the repeating unit is shown below:
A name for the polymer is: Poly(methyl vinyl ether).
Explanation of Solution
The given monomer is
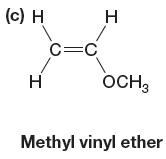
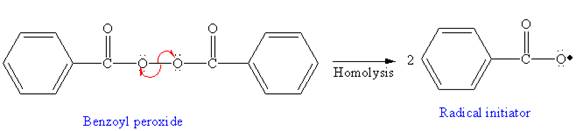
In the initiation step, the homolysis of benzoyl peroxide takes place to form radical initiator as follows:
After initiation, propagation occurs via radical addition. In first step propagation, the initial radical adds to the C=C bond of the monomer giving a new radical. The new radical reacts with the other molecule of monomer in the second propagation. The mechanism for the first two propagation steps is shown below:

The condensed formula showing repeating unit is shown below:

A name for the polymer is written by writing poly- followed by the monomer’s name, and we can enclose the monomer’s name in parenthesis as it consists of two or more words. Therefore, the name of the polymer is: Poly(methyl vinyl ether).
The mechanism for the first two propagation steps for the given monomer is drawn on the basis of chain-growth polymerization. The condensed formula is drawn identifying the structural pattern that is repeated in the growing chain.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
ORG.CHEM W/TEXT+SOLU.MANUAL
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





