
Concept explainers
Oligonucleotide Synthesis
In Section
available for use as primers for PCR and as probes for cloning DNA. Here we will examine how these oligonucleotides are prepared.
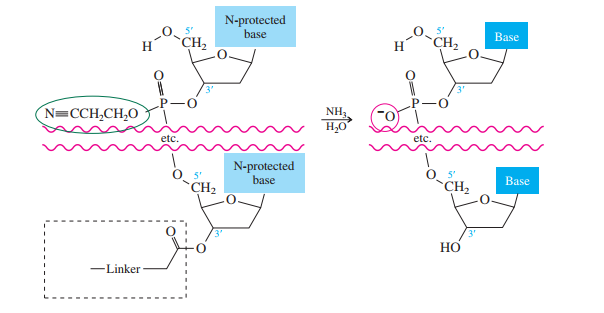
The method bears many similarities to the Merrifield solid-phase synthesis of peptides. A starter unit is attached to a solid support, nucleosides are attached one-by-one until the sequence is complete, whereupon the target oligonucleotide is removed from the support and purified. Like solid-phase peptide synthesis, the preparation of oligonucleotides relies heavily on protecting groups and bond-forming methods.
The starter units are nucleosides in which
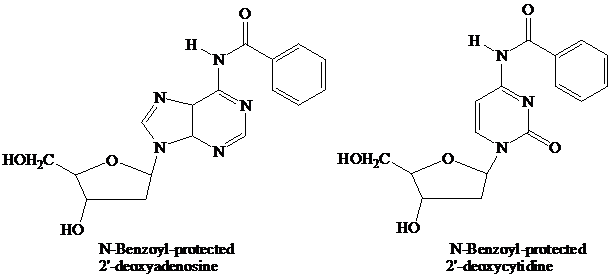
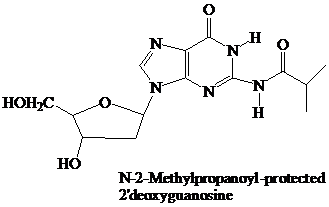
Thymidine lacks an
These
remain in place throughout the synthesis. They are the first ones added and the last ones removed. None of the further “chemistry” that takes place involves the purine or pyrimidine rings.
The
(DMT) ether.

The nucleoside that is to serve as the
controlled-pore glass (CPG) bead by ester formation between its unprotected

The stage is now set for adding the second nucleoside. The four blocked nucleosides prepared
earlier are converted to their corresponding
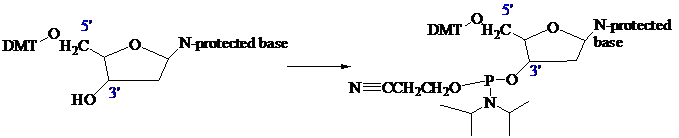
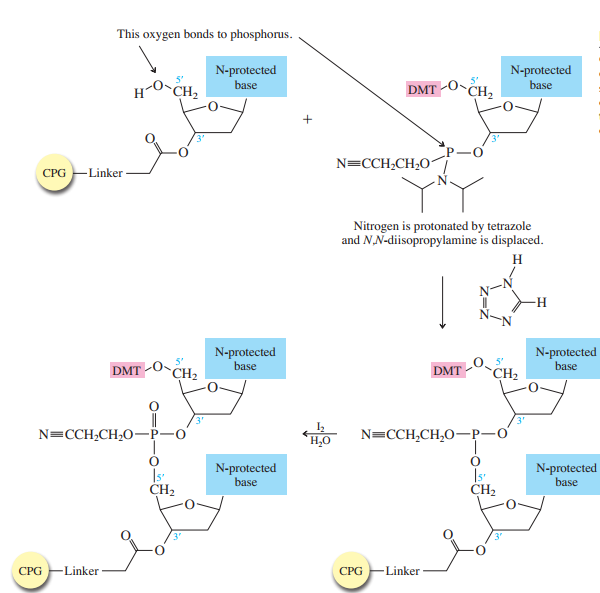
Each phosphoramidite is coupled to the anchored nucleoside by a reaction in which the free
The product of the coupling is a phosphite; it has the general formula
in the last step of Figure
The

Once all the nucleosides are in place and the last DMT is removed, treatment with aqueous
ammonia removes the acyl and cyanoethyl groups and cleaves the oligonucleotide from the CPG
support.
What is the product of the following reaction?

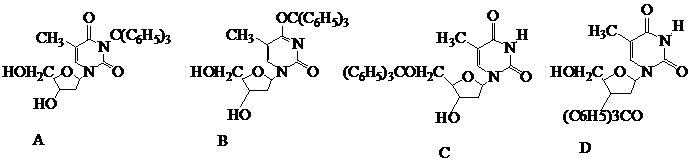
Section
Many important compounds contain two or more nucleotides joined together by
a phosphodiester linkage. The best known are those in which the phosphodiester
joins the
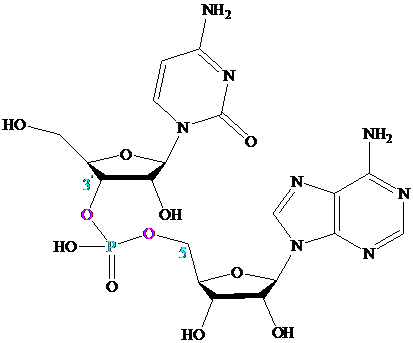
Oligonucleotides contain about
phosphodiester links; polynucleotides can contain thousands of nucleotides.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 27 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2 YEAR CONNECT ACCES
- Determine the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide from the following data: Complete hydrolysis of the peptide yields Ala, Arg, Gly, 2 Lys, Met, Phe, Pro, 2 Ser, Tyr, and Val. Treatment with Edman’s reagent releases PTH-Val. Carboxypeptidase A releases Ala. Treatment with cyanogen bromide yields the following two peptides: 1. Ala, 2 Lys, Phe, Pro, Ser, Tyr 2. Arg, Gly, Met, Ser, Val Treatment with trypsin yields the following three peptides: 1. Gly, Lys, Met, Tyr 2. Ala, Lys, Phe, Pro, Ser 3. Arg, Ser, Val Treatment with chymotrypsin yields the following three peptides: 1. 2 Lys, Phe, Pro 2. Arg, Gly, Met, Ser, Tyr, Val 3. Ala, Serarrow_forwardThree peptides were obtained from a trypsin digestion of two different polypeptides. In each case, indicate the possible sequences from the given data and tell what further experiment should be carried out in order to determine the primary structure of the polypeptide. a. polypeptide I: 1. Val-Gly-Asp-Lys 2. Leu-Glu-Pro-Ala-Arg 3. Ala-Leu-Gly-Asp b. polypeptide II: 1. Val-Leu-Gly-Glu 2. Ala-Glu-Pro-Arg 3. Ala-Met-Gly-Lysarrow_forwardShow how solid-phase peptide synthesis would be used to make Ile-gly-asnarrow_forward
- Give the sequence of the following tetrapeptide:arrow_forwardOxytocin, a nonapeptide hormone secreted by the pituitary gland, functions by stimulating uterine contraction and lactation during childbirth. Its sequence was determined from the following evidence: 1. Oxytocin is a cyclic compound containing a disulfide bridge between two cysteine residues. 2. When the disulfide bridge is reduced, oxytocin has the constitution Asn, Cys2, Gln, Gly, Ile, Leu, Pro, Tyr. 3. Partial hydrolysis of reduced oxytocin yields seven fragments: Asp-Cys, Ile-Glu, Cys-Tyr, Leu-Gly, Tyr-Ile-Glu, Glu-Asp-Cys, and Cys-Pro-Leu. 4. Gly is the C-terminal group. 5. Both Glu and Asp are present as their side-chain amides (Gln and Asn) rather than as free side-chain acids. What is the amino acid sequence of reduced oxytocin? What is the structure of oxytocin itself?arrow_forwardSomatostatin is a tetradecapeptide of the hypothalamus that inhibits the release of pituitary growth hormone. Its amino acid sequence has been determined by a combination of Edman degradations and enzymic hydrolysis experiments. On the basis of the following data, deduce the primary structure of somatostatin: 1. Edman degradation gave PTH-Ala. 2. Selective hydrolysis gave peptides having the following indicated sequences: Phe-Trp Thr-Ser-Cys Lys-Thr-Phe Thr-Phe-Thr-Ser-Cys Asn-Phe-Phe-Trp-Lys Ala-Gly-Cys-Lys-Asn-Phe 3. Somatostatin has a disulfide bridge.arrow_forward
- Determine the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide from the following data: Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis gives Ala, Arg, His, 2 Lys, Leu, 2 Met, Pro, 2 Ser, Thr, and Val. Carboxypeptidase A releases Val. Edman’s reagent releases PTH-Leu. Treatment with cyanogen bromide gives three peptides with the following amino acid compositions: 1. His, Lys, Met, Pro, Ser 2. Thr, Val 3. Ala, Arg, Leu, Lys, Met, Ser Trypsin-catalyzed hydrolysis gives three peptides and a single amino acid: 1. Arg, Leu, Ser 2. Met, Pro, Ser, Thr, Val 3. Lys 4. Ala, His, Lys, Metarrow_forwardThree peptides were obtained from a trypsin digestion of two different polypeptides. indicate the possible sequences from the given data and tell what further experiment should be carried out in order to determine the primary structure of the polypeptide. polypeptide I: 1. Val-Gly-Asp-Lys 2. Leu-Glu-Pro-Ala-Arg 3. Ala-Leu-Gly-Asparrow_forwardShow how solid-phase peptide synthesis would be used to make Ile-Gly-Asn.2arrow_forward
- In a paragraph form provide the experimental procedure of the reaction of oxazetidine-containing peptides and α-ketoacid that will result in protein that contain native serine residuesarrow_forwardIn a paragraph form, provide the experimental procedures in the chemical synthesis of protein that contain native serine residues by the reaction of oxazetidine-containing peptides and α-ketoacid.arrow_forwardSuggest a reasonable strategy for the synthesis of the dipeptide Leu-Phe, using established protocol for peptide synthesis.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

