
(a)
Interpretation:
It should be identified that will a thermal 1, 3-migrations of carbon occur with whether retention or inversion of configuration.
Concept introduction:
Pericyclic reactions are “ any concerted reaction in which bonds are formed or brocken in a cyclic transition state”. There is a single transition state from start to finish, in contrast to a stepwise reaction.
There are mainly three types of pericyclic reactions,
- 1) Electrocyclic reactions
- 2) Cycloaddition reactions
- 3) Sigmatropic reactions
In a sigmatropic reaction “ one new sigma-bond is formed as another breaks.”
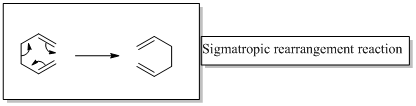
Sigmatropic rearrangement reactions are named with digits. For example a [1, 3] sigmatropic rearrangement describe a reaction in which the residue migrates from position 1 to position 3.
Migration of carbon and hydrogen will occur in a sigmatropic rearrangement reaction.
When hydrogen migrates in a sigmatropic rearrangement, the s orbital of the hydrogen is partially bonded to both the migration origin and the migration terminus in the transition state.
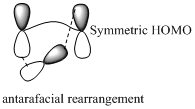
Migration of hydrogen in suprafacial and antarafacial rearrangement can be represented as follows,


Migration of carbon occurs through two ways because it has a two lobed p orbital. Carbon can simultaneously interact with the migration origin and the migration terminus using one lobe of its p orbital.
Migration of carbon in suprafacial and antarafacial rearrangement can be represented as follows,
Carbon migrating with one lobe of its p orbital interacting


Carbon migrating with both lobe of its p orbital interacting

Inversion of configuration is the inversion of a chiral center in a molecule in a
Retention of configuration is the preservation of integrity of the spatial arrangement of bonds to a chiral center during a chemical reaction.
(b)
Interpretation:
It should be identified that will a thermal 1, 5-migrations of carbon occur with whether retention or inversion of configuration.
Concept introduction:
Pericyclic reactions are “ any concerted reaction in which bonds are formed or brocken in a cyclic transition state”. There is a single transition state from start to finish, in contrast to a stepwise reaction.
There are mainly three types of pericyclic reactions,
- 1) Electrocyclic reactions
- 2) Cycloaddition reactions
- 3) Sigmatropic reactions
In a sigmatropic reaction “ one new sigma-bond is formed as another breaks.”

Sigmatropic rearrangement reactions are named with digits. For example a [1, 3] sigmatropic rearrangement describe a reaction in which the residue migrates from position 1 to position 3.
Migration of carbon and hydrogen will occur in a sigmatropic rearrangement reaction.
When hydrogen migrates in a sigmatropic rearrangement, the s orbital of the hydrogen is partially bonded to both the migration origin and the migration terminus in the transition state.
Migration of hydrogen in suprafacial and antarafacial rearrangement can be represented as follows,


Migration of carbon occurs through two ways because it has a two lobed p orbital. Carbon can simultaneously interact with the migration origin and the migration terminus using one lobe of its p orbital.
Migration of carbon in suprafacial and antarafacial rearrangement can be represented as follows,
Carbon migrating with one lobe of its p orbital interacting


Carbon migrating with both lobe of its p orbital interacting


Inversion of configuration is the inversion of a chiral center in a molecule in a chemical reaction.
Retention of configuration is the preservation of integrity of the spatial arrangement of bonds to a chiral center during a chemical reaction.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 28 Solutions
MASTERINGCHEM FOR ORGANIC CHEM STANDAL
- Predict relative intensities at m/z 34, 35, and 36 for H2S. Let the intensity of the molecular ion be 100 and disregard contributions ,0.1%.arrow_forwardWhat is the KE of translational androtational motions,in RT units, for(CN)2 and H2O? a.(CN)2 : KE(trans) = 3/2RT & KE(rot) = RT H2O : KE(trans) = 3/2RT & KE(rot) = 3/2RT b.(CN)2 : KE(trans) = 3/2RT & KE(rot) = 3/2RT H2O : KE(trans) = 3/2RT & KE(rot) = 1/2RT c.(CN)2 : KE(trans) = 3/2RT & KE(rot) = 7/2RT H2O : KE(trans) = 3/2RT & KE(rot) = 7/2RT d.(CN)2 : KE(trans) = 3/2RT & KE(rot) = 5/2RT H2O : KE(trans) = 3/2RT & KE(rot) = 3/2RT e.(CN)2 : KE(trans) = 2/2RT & KE(rot) = 5/2RT H2O : KE(trans) = 3/2RT & KE(rot) = 3/2RTarrow_forwardGive a detailed explanation of how Raman spectroscopy protocol will be used to process a sample of palm oil adulterated with Sudan IVarrow_forward
- How do I find the [FeSCN]^2+ value?arrow_forwardCan someone explain and number 1,2,3,4,5 etc how the attached is a [1,5] sigmatropic migration?arrow_forwardBased on the chromatograms, Symmetry C18 (top) is less selective than Symmetry Shield RP18 (bottom) for the analytes given, true or false?arrow_forward
- Match the chromophore with the appropriate transition Choose: only in carbonyl group, 2 saturated hydrocarbons in alkane, or carbonyl group and ethene n to p* transition: ? sigma to sigma* transition: ? p to p* transition: ?arrow_forwardBriefly explain the importance of t1 and t2 relaxation times in magnetic resonance spectrometry.arrow_forwardAcrolein (CH2=CH-CHO) shows two bands , at 210 nm (11,500) and 315 nm (15) . Assign these bands.arrow_forward
- Why can a CHN analysis of a compound notdistinguish between a monomer and dimer of thespecies? What technique would you use to confirmthat a dimer was present?arrow_forwardA radical containing two inequivalent protons with hyperfine coupling constants 2.0 mT and 2.6 mT gives a spectrum centred on 332.5 mT. At what fields do the hyperfine lines occur and what are their relative intensities?arrow_forwardDescribe how to prepare adulterated palm oil samples before analysing it with Raman spectrometer. Also the describe the process how the Raman spectrometer will analyze the adulterated palm oil samplesarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning


