
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Based on the reaction, the product has to be predicted, name and formula for the product has to be given.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given,
Three Group 2A elements magnesium, calcium, and strontium are allowed to react with liquid bromine.
The product, name and formula for the product of the reaction is given below,
The magnesium metal reaction with bromine produces magnesium bromide
The calcium metal reaction with bromine produces calcium bromide
The strontium metal reaction with bromine produces strontium bromide
(b)
Interpretation:
The balanced equation has to be written for the given reaction.
Concept introduction:
Balanced Chemical equation:
A balanced chemical equation is an equation which contains same elements in same number on both the sides (reactant and product side) of the chemical equation thereby obeying the law of conservation of mass.
Balancing the equation:
- There is a Law for conversion of mass in a
chemical reaction i.e., the mass of total amount of the product should be equal to the total mass of the reactants. - First write the skeletal reaction from the given information.
- Then count the number of atoms of each element in reactants as well as products.
- Place suitable coefficients in front of reactants as well as products until the number of atoms on each side (reactants and products) becomes equal.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given,
Three Group 2A elements magnesium, calcium, and strontium are allowed to react with liquid bromine.
The balanced equation is given below,
The magnesium metal reaction with bromine produces magnesium bromide
The calcium metal reaction with bromine produces calcium bromide
The strontium metal reaction with bromine produces strontium bromide
(c)
Interpretation:
Nature of the reaction (acid-base reaction, precipitation reaction, or an oxidation-reduction reaction) has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction: The formation of the product is insoluble when the reactant combine in the solution is called precipitation reaction.
Acid - base reaction: Formation of the salt from the cation from the base and anion from the acid.
Gas forming reaction: The reaction of acid and metal carbonates which produce carbonic acid. The carbonic acid decomposes which gives water and carbon dioxide.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given,
Three Group 2A elements magnesium, calcium, and strontium are allowed to react with liquid bromine.
The magnesium metal reaction with bromine produces magnesium bromide
The given reaction is precipitation reaction, because the formation of
The calcium metal reaction with bromine produces calcium bromide
The given reaction is precipitation reaction, because the formation of
The strontium metal reaction with bromine produces strontium bromide
The given reaction is precipitation reaction, because the formation of
(d)
Interpretation:
Formula of each product has to be predicted.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Given,
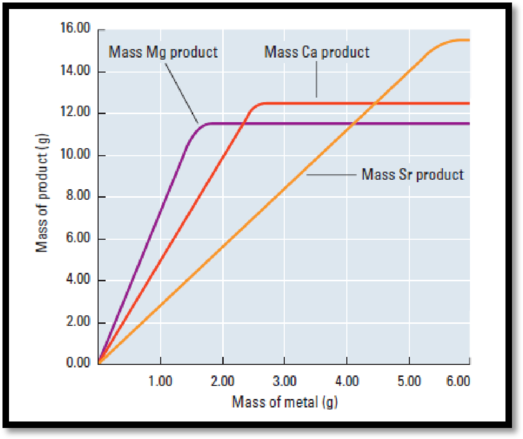
Figure 1
The mass of the metal is directly proportional to the mass of the compound formed.
From the graph, mass of sample is on the y-axis and the mass of the metal is on the x-axis and the fixed mass of the other reactant.
According to the graph (figure 1), mass of the compound is 11.4 g
Mass of the Mg (metal) is 1.6 g.
Consider the reaction takes place in 100 %. Then the mass of bromine is calculated as follows,
The molar mass of Mg is 24.3050 g/mole, the molar mass of bromine is 79.904 g/mole.
Number of moles of Mg is calculated below,
Number of moles of bromine is calculated below,
Therefore,
The ratio of the number of moles of Mg and bromine is given below,
0.066: 0.123
Divide through by smallest number:
Therefore, the Empirical formula for the given compound is
According to the graph (figure 1), mass of the compound is 12.4 g
Mass of the Ca (metal) is 2.5 g.
Consider the reaction takes place in 100 %. Then the mass of bromine is calculated as follows,
The molar mass of Ca is 40.078 g/mole, the molar mass of bromine is 79.904 g/mole.
Number of moles of Ca is calculated below,
Number of moles of bromine is calculated below,
Therefore,
The ratio of the number of moles of Ca and bromine is given below,
0.062: 0.124
Divide through by smallest number:
Therefore, the Empirical formula for the given compound is
According to the graph (figure 1), mass of the compound is 15.3 g
Mass of the Sr (metal) is 5.5 g.
Consider the reaction takes place in 100 %. Then the mass of bromine is calculated as follows,
The molar mass of Sr is 87.62 g/mole, the molar mass of bromine is 79.904 g/mole.
Number of moles of Sr is calculated below,
Number of moles of bromine is calculated below,
Therefore,
The ratio of the number of moles of Sr and bromine is given below,
0.063: 0.123
Divide through by smallest number:
Therefore, the Empirical formula for the given compound is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
- Given that the density of argon is 1.78 g/L under standard conditions of temperature and pressure, how many argon atoms are present in a room with dimensions 4.0 m 5.0 m 2.4 m that is filled with pure argon under these conditions of temperature and pressure?arrow_forwardThe present average concentration (mass percent) of magnesium ions in seawater is 0.13%. A chemistry textbook estimates that if 1.00 × 108 tons Mg were taken out of the sea each year, it would take one million years for the Mg concentration to drop to 0.12%. Do sufficient calculations to either verify or refute this statement. Assume that Earth is a sphere with a diameter of 8000 mi, 67% of which is covered by oceans to a depth of 1 mi, and that no Mg is washed back into the oceans at any time.arrow_forward4.104 When 2.750 g of the oxide Pb3O4 is heated to a high temperature, it decomposes to produce 0.0640 g of oxygen gas and 2.686 g of some new lead oxide compound. How can you use these data to determine the formula of the new compound?arrow_forward
- 4.69 The pictures below show a molecular-scale view of a chemical reaction between H2 and CO to produce methanol, CH3OH. The box on the left represents the reactants at the instant of mixing, and the box on the right shows what is left once the reaction has gone to completion. Was there a limiting reactant in this reaction? If so, what was it? Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. As usual, your equation should use the smallest possible whole number coefficients for all substances.arrow_forwardMany cereals are made with high moisture content so that the cereal can be formed into various shapes before it is dried. A cereal product containing 58% H2O by mass is produced at the rate of 1000. kg/h. What mass of water must be evaporated per hour if the final product contains only 20.% water?arrow_forwardChlorine exists mainly as two isotopes, 37Cl and 33Cl. Which is more abundant? How do you know?arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





