
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS, CASH FLOW, AND TAXES Laiho Industries’s 2017 and 2018 balance sheets (in thousands of dollars) are shown.
| 2018 | 2017 | |
| Cash | $ 102,850 | $ 89,725 |
| Accounts receivable | 103,365 | 85,527 |
| Inventories | 38,444 | 34,982 |
| Total current assets | $ 244,659 | $ 210,234 |
| Net fixed assets | 67,165 | 42,436 |
| Total assets | $ 311,824 | $ 252,670 |
| Accounts payable | $ 30,761 | $ 23,109 |
| Accruals | 30,477 | 22,656 |
| Notes payable | 16,717 | 14,217 |
| Total current liabilities | $ 77,955 | $ 59,982 |
| Long-term debt | 76,264 | 63,914 |
| Total liabilities | $ 154,219 | $ 123,896 |
| Common stock | 100,000 | 90,000 |
| 57,605 | 38,774 | |
| Total common equity | $ 157,605 | $ 128,774 |
| Total liabilities and equity | $ 311,824 | $ 252,670 |
- a. Sales for 2018 were $ 455,150,000, and EBITDA was 15% of sales Furthermore,
depreciation and amortization were 11%. of net fixed assets, interest was $ 8,575,000, the corporate tax rate was 40%, and Laiho pays 40% of its net income as dividends Given this information. construct the firm’s 2018 income statement. - b. Construct the statement of stockholders’ equity for the year ending December 31, 2018, and the 2018 statement of cash flows.
- c. Calculate 2017 and 2018 net operating working capital (NOWC) and 2018
free cash flow (FCF). Assume the firm has no excess cash. - d. If Laiho increased its dividend payout ratio, what effect would this have on corporate taxes paid’ What effect would this have on taxis, paid by the company’s shareholders?
- e. Assume that the firm’s after-tax cost of capital is 10 5%. What is the firm’s 2018 EVA?
- f. Assume that the firm’s stock price is S22 per share and that at year-end 2018 the firm has 10 million shares outstanding. What is the firm’s MVA at year-end 2018?
a.
To prepare: The income statement of company L for 2014.
Financial Statements:
It refer to the statements, which are prepared by the firm at the closure of the accounting period in particular formats and are prescribed in the accounting to show its financial position.
Income Statement:
A part of financial statements that list the income and expenses of the business for an accounting year is called the income statement. It is prepared at the closure of the accounting period to know the profitability of the business.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Sales is $455,150,000 for the year 2018.
EBITDA is 15% on sales.
11% of depreciation and amortization on net fixed asset.
Interest is $8,575,000.
40% tax.
40% of the divided on net income.
Calculation on income statement using the spreadsheet is as follows:
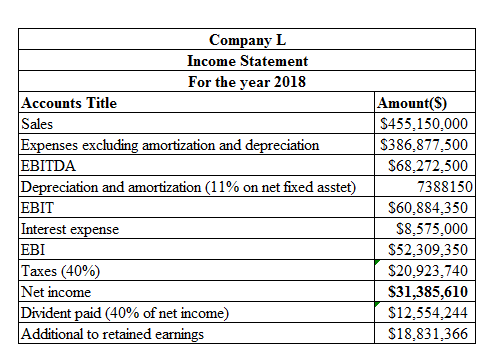
Table (1)
Therefore, Company L has a net income of $31,385,610.
b.
To prepare: The statement of stockholders’ equity of Company L for 2018.
Statement of stockholders’ equity:
The statement of stockholders’ equity reports the opening and closing balance of stockholder’s equity with the changes incurred during the accounting period.
Statement of cash flow:
The statement of cash flow is a part of fiscal statements those are comprised in the yearly report of a company. It reports the cash generated or used by the business in a specified period.
Explanation of Solution
The calculation of statement of stockholders’ equity using the spreadsheet for the year 2018 is as follows:
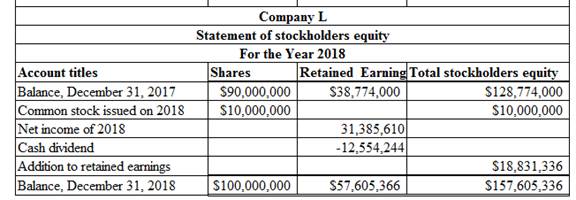
Table (2)
The calculation of statement of cash flow using the spreadsheet is as follows:
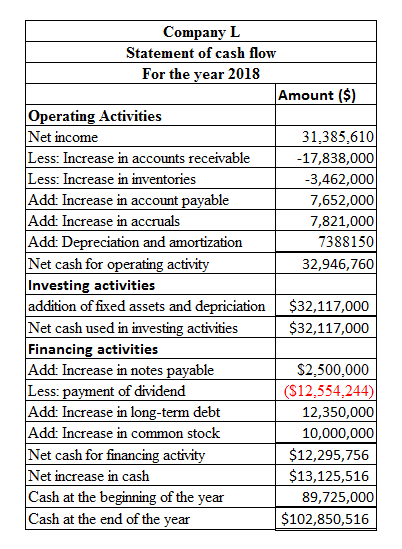
Table (3)
c.
To compute: The net operating working capital for 2017 and 2018, and the free cash flow for 2018.
The net operating working capital:
The current assets and current liabilities of active business operations are known as the operating current assets and the operating current liabilities, respectively. The difference between these two is known as the net operating working capital.
Free Cash Flow:
The performance of a company’s operations is also evaluated by its cash generation abilities. The term used to depict and report that ability is known as the free cash flow. Capital expenditures are deducted from operating cash flow to compute the free cash flow.
Explanation of Solution
The calculation of net operating working capital is as follows:
Given information:
Current assets in 2017 are $210,234,000.
Current liabilities in 2017 are $59,982,000.
Current assets in 2018 are $244,659,000
Current liabilities in 2018 are $77,955,000.
For the year 2017,
The formula to compute the net operating current assets is as follows:
Compute the net operating current assets:
Hence, the net operating current asset is $210,234,000.
For the year 2017,
The formula to compute the net operating current liabilities is as follows:
Compute the net operating current liabilities:
Hence, the net operating current liabilities is $45,765,000.
For the year 2018,
The formula to compute the net operating current assets is as follows:
Compute the net operating current assets:
Hence, the net operating current asset is $244,659,000.
For the year 2018,
The formula to compute the net operating current liabilities is as follows:
Compute the net operating current liabilities:
Hence, the net operating current liabilities is $61,238,000.
For 2017,
The formula to compute the net operating working capital is as follows:
Substitute $210,234 for the net operating current assets and $45,765,000 for the net operating current liabilities.
Hence, the net operating working capital for the year 2017 is $164,469,000.
For 2018,
The formula to compute the net operating working capital is as follows:
Substitute $244,659 for current assets and $77,955 for the current liabilities.
Hence, the net operating working capital for the year 2018 is $183,421,000.
Calculation of Free cash flow:
Given information:
EBIT is $60,884,358 (refer part a).
The tax rate is 40%.
Depreciation is $7,388,150 (refer part a).
Capital expenditure is $32,117,000 (refer part b).
Increase in the net operating working capital is $18,952,000
The formula to compute the free cash flow is as follows:
Substitute $60,884 for EBIT, 40% for tax rate, $7,388 for depreciation, $32,117 for capital expenditure and $18,952,000.
Hence, the free cash flow for the year 2018 is -$7,150,235.2.
d.
To analyze: The effect of increased dividend payment on company’s tax liability and stockholders’ liability.
Dividend Payout Ratio:
The ratio that reflects the dividends paid as the proportion of net income earned by a company during a specified time period is called the dividend payout ratio.
Answer to Problem 19SP
There will be no change in the taxes paid by the company but the stockholders’ tax liability will increase with the increase in the dividend payout.
Explanation of Solution
- The dividend payment is calculated after the tax is calculated. Therefore, there will be no change in the tax amount if the dividend payment is changed.
- The dividend is an income for the stockholders and taxable for them. Therefore their tax liability will increase if the dividend payout is increased.
Therefore, the increased dividend payment will have no change in the company’s tax liability but it will increase the stockholders’ tax liability.
e.
To compute: The economic value added (EVA) for 2018.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
EBIT is 60,884,350.
The capital invested is $250,586,000
The cost of capital is 10.5%.
The formula to compute EVA is as follows:
Substitute $31,386 for the earnings after tax, $157,605 for the capital invested, and 10.5% for the cost of capital.
Hence, the EVA for the year 2018 is $10,219,080.
f.
To compute: The market value added (MVA) for 2018.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The market price of a share is $22.
Outstanding shares are 10 million.
Common equity is $157,605,000.
The formula to compute MVA is as follows:
Substitute $22 for the market price of the share, $157,605 for the capital invested, and 10,000,000 for the number of shares.
Hence, the MVA for the year 2018 is $62,395,000.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Course List)
- Real-world annual report The financial statements for Nike, Inc. (NKE), are presented in Appendix E at the end of the text. The following additional information is available (in thousands): Instructions 1. Determine the following measures for the fiscal years ended May 31, 2017, and May 31, 2016. Round ratios and percentages to one decimal place. a. Working capital b. Current ratio c. Quick ratio d. Accounts receivable turnover e. Number of days sales in receivables f. Inventory turnover g. Number of days sales in inventory' h. Ratio of liabilities to stockholders equity i. Asset turnover j. Return on total assets, assuming interest expense is 82 million for the year ending May 31. 2017, and 33 million for the year ending May 31, 2016. k. k. Return on common stockholders equity l. Price-eamings ratio, assuming that the market price was 52.81 per share on May 31, 2017, and 54.35 per share on May 31, 2016. m. m. Percentage relationship of net income to sales 2. What conclusions can be drawn from these analyses?arrow_forwardFINANCIAL STATEMENTS, CASH FLOW, AND TAXES Laiho Industries' 2013 and 2014 balance sheets (in thousands of dollars) are shown. 2014 2013 Cash 102,850 89,725 Accounts receivable 103,365 85,527 Inventories 38,444 34,982 Total current assets 244,659 210,234 Net fixed assets 67,165 42,436 Total assets 311,824 252,670 Accounts payable 30,761 23,109 Accruals 30,477 22.656 Notes payable 16,717 14,217 Total current liabilities 77,955 59,982 long term debt 76,264 63,914 Total liabilities 154,219 123,896 Common stock 100,000 90,000 Retained earnings 57,605 38,774 Total common equity 157,605 128,774 Total liabilities and equity 311,824 252,670 a. Sales for 2014 were 455,150,000, and EBITDA was 15% of sales. Furthermore, depreciation and amortization were 11% of net fixed assets, interest was 8,575,000, the corporate tax rate was 40%, and Laiho pays 40% of its net income as dividends. Given this information, construct the firm's 2014 income statement. b. Construct the statement of stockholders' equity for the year ending December 31,2014, and the 2014 statement of cash flows. c. Calculate 2013 and 2014 net operating working capital (NOWC) and 2014 free cash flow (FCF). d. If Laiho increased its dividend payout ratio, what effect would this have on corporate taxes paid? What effect would this have on taxes paid by the company's shareholders? e. Assume that the firm's after-tax cost of capital is 105%. What is the firm's 2014 EVA? f. Assume that the firm's stock price is 22 per share and that at year-end 2014 the firm has 10 million shares outstanding. What is the firm's MVA at year-end 2014?arrow_forwardFinancial statement analysis The financial statements for Nike, Inc., are presented in Appendix D at the end of the text. Use the following additional information (in thousands): Instructions 1. Determine the following measures for the fiscal years ended May 31, 2016, and May 31, 2015. Round ratios and percentages to one decimal place. a. Working capital b. Current ratio c. Quick ratio d. Accounts receivable turnover e. Number of days sales in receivables f. Inventory turnover g. Number of days sales in inventory h. Ratio of liabilities to stockholders equity i. Asset turnover j. Return on total assets. k. Return on common stockholders equity l. Price-earnings ratio, assuming that the market price was 54.90 per share on May 29, 2016, and 52.81 per share on May 30, 2015 m. Percentage relationship of net income to sales 2. What conclusions can be drawn from these analyses?arrow_forward
 Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781285065137Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781285065137Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals Of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781337902571Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals Of Financial Management, Concise Edi...FinanceISBN:9781337902571Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





