
Concept explainers
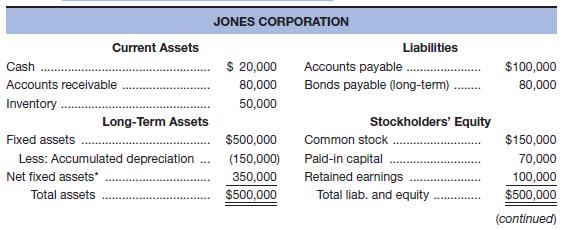
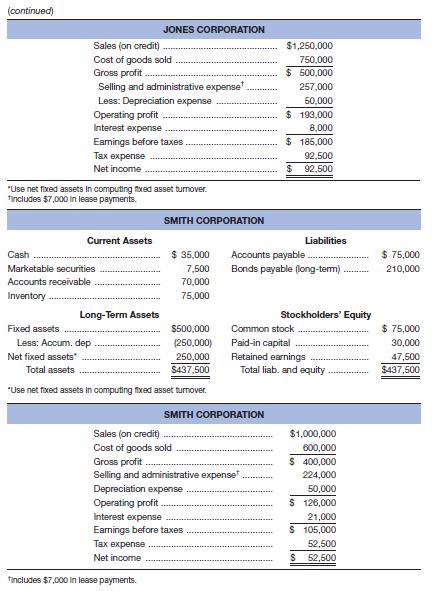
Given the financial statements for Jones Corporation and Smith Corporation shown here:
a. To which one would you, as credit manager for a supplier, approve the extension of (short-term) trade credit? Why? Compute all ratios before answering.
b. In which one would you buy stock? Why?
a.
To calculate: The relevant ratios so that the decision for the extension of short term trade credit can be taken.
Introduction:
Shortterm trade credit:
It is the type of credit that is granted to a business or an individual or a fixed loan for a period of not more than 12 months or 1 year.
Answer to Problem 37P
The Smith Corporation would get the extension of the short term trade credit as their liquidity ratios are better than those of the Jones Corporation; the suppliers and lenders are most concerned with the liquidity ratios.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of ratios for the Smith Corporation:
Calculation of current ratio:
Calculation of quick ratio:
Calculation of debt to total asset ratio:
Calculation of times interest ratio:
Calculation of fixed charge ratio:
Calculation of ratios for the Jones Corporation:
Calculation of current ratio:
Calculation of quick ratio:
Calculation of debt to total asset ratio:
Calculation of times interest ratio:
Calculation of fixed charge ratio:
b.
To determine: The company whose stock should be bought.
Introduction:
Stock:
Also termed as ordinary shares, it is a type of security that represents the corporate equity ownership. It is the best means to earn real rate of return ahead of inflation in the long run.
Answer to Problem 37P
The stocks of the Jones Corporation should be bought as their profit margin and return on assets are higher compared to the Smith Corporation; shareholders are mostly concerned with profitability.
But the return on equity is more for the Smith Corporation because it has taken a bigger financial risk. The times interest ratio and fixed charges ratio are higher for the Jones Corporation, which clearly reflects that their interest and fixed charges are well covered.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of ratios for the Smith Corporation:
Calculation of profit margin:
Calculation of return on assets:
Calculation of return on equity:
Calculation of debt to total asset ratio:
Calculation of times interest ratio:
Calculation of fixed charge ratio:
Calculation of ratios for the Jones Corporation:
Calculation of profit margin:
Calculation of return on assets:
Calculation of return on equity:
Calculation of debt to total asset ratio:
Calculation of times interest ratio:
Calculation of fixed charge ratio:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Foundations of Financial Management
- Suppose you a stock analyst are performing a ratio analysis and comparing a discount merchdiser with a high end merchandiser. Suppose further that both companies have identical ROE. IF You apply the dupont equation to both firms, would you expect the three components to be the same for both companies? If not, explain what balance balance sheet and income statements might lead to the differences in the Dupont equation components.arrow_forwardYou have been asked by your CEO to evaluate, analyse and calculate commonly used ratios relating to a company’s profitability, liquidity, solvency and management efficiency. Requirement: b. Explain how do analysts use ratios to analyse a firm’s leverage? Which ratios convey more important information to a credit analyst those revolving around the levels of indebtedness or those measuring the ability to service debt? What is the relationship between a firm’s level of indebtedness and risk? What must happen in order for an increase in leverage to be successful? Discuss and illustrate all your answer.arrow_forwardGive typing answer with explanation and conclusion A firm's DSO is just below the industry average. This most likely indicates which of the following regarding the firm's credit and collection pilicies?arrow_forward
- When firms enter into loan agreements with their bank, it is very common for the agreement to have a restriction on the minimum current ratio the firm has to maintain. So, it is important that the firm be aware of the effects of their decisions on the current ratio. Consider the situation of Advanced Autoparts (AAP) in 2009. The firm has total current assets of $1,780,195,300 and current liabilities of $1,369,381,000. What is the firm’s current ratio? If the firm were to expand its investment in inventory and finance the expansion by increasing accounts payable, how much could it increase its inventory without reducing the current ratio below 1.2? If the company needed to raise its current ratio to 1.5 by reducing its investment in current assets and simultaneously reducing accounts payable and short-term debt, how much would it have to reduce current assets to accomplish this goal?arrow_forwardWhat information can best be elicited from a receivable ratio? A. company performance with current debt collection B. credit extension effect on cash sales C. likelihood of future customer bankruptcy filings D. an increase in future credit sales to current customersarrow_forwardIf you are an investor how do you assess the financial ratios of the company? And why?arrow_forward
- When firms enter into loan agreements with their bank, it is very common for the agreement to have a restriction on the minimum current ratio the firm has to maintain. So, it is important that the firm be aware of the effects of their decisions on the current ratio. Consider the situation of Advanced Autoparts (AAP) in 2009. The firm had total current assets of $1,907,570,000 and current liabilities of $1,362,550,000. a. What is the firm's current ratio? b. If the firm were to expand its investment in inventory and finance the expansion by increasing accounts payable, how much could it increase its inventory without reducing the current ratio below 1.2? c. If the company needed to raise its current ratio to 1.5 by reducing its investment in current assets and simultaneously reducing accounts payable and short-term debt, how much would it have to reduce current assets to accomplish this goal? Question content area bottom Part 1 a. What is the firm's…arrow_forwardAssume you are proprietor of any firm you like. Briefly describe the products or servicesyour firm will offer for sale. Would you extend trade credit to your customers? Why orwhy not? How will this decision affect your sales and profits? If you choose to extendcredit, how would you ensure that your firm is paid by its customers?arrow_forwardAssume you are a bank loan officer. The President of ABC Corp. approaches you for a bank loan. What specific financial ratios of ABC Corp. are you interested about? Why are your interested in these financial ratios?arrow_forward
- Which of the following financial instruments gives a creditor relationship with the company? a. Preferred Stocks b. Bonds c. Receivables d. Common stocksarrow_forwardwhich of the following source of finance relates to suppliers ? a.Commercial Paper b.Bank Overdraft c.Trade credit d.Credit cardarrow_forwardYou have been asked by your CEO to evaluate, analyse and calculate commonly used ratios relating to a company’s profitability, liquidity, solvency and management efficiency. Explain how do analysts use ratios to analyse a firm’s leverage? Which ratios convey more important information to a credit analyst those revolving around the levels of indebtedness or those measuring the ability to service debt? What is the relationship between a firm’s level of indebtedness and risk? What must happen in order for an increase in leverage to be successful? Discuss and illustrate all your answer.arrow_forward
 Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning





