
Concept explainers
The general ledger of Zips Storage at January 1, 2018, includes the following account balances:
| Accounts | Debits | Credits |
| Cash | $ 24,600 | |
| 15,400 | ||
| Prepaid Insurance | 12,000 | |
| Land | 148,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | $ 6,700 | |
| Deferred Revenue | 5,800 | |
| Common Stock | 143,000 | |
| 44,500 | ||
| Totals | $200,000 | $200,000 |
The following is a summary of the transactions for the year:
a. January 9 Provide storage services for cash, $134,100, and on account, $52,200.
b. February 12 Collect on accounts receivable, $51,500.
c. April 25 Receive cash in advance from customers, $12,900.
d. May 6 Purchase supplies on account, $9,200.
e. July 15 Pay property taxes, $8,500.
f. September 10 Pay on accounts payable, $11,400.
g. October 31 Pay salaries, $123,600.
h. November 20 Issue shares of common stock in exchange for $27.000 cash.
i. December 30 Pay $2,800 cash dividends to stockholders.
Required:
1. Set up the necessary T-accounts and enter the beginning balances from the
2. Record each of the summary transactions listed above.
3. Post the transactions to the accounts.
4. Prepare an unadjusted trial balance.
5. Record
6. Post adjusting entries.
7. Prepare an adjusted trial balance.
8. Prepare an income statement for 2018 and a classified balance sheet as of December 31, 2018.
9. Record closing entries.
10. Post closing entries
11. Prepare a post-closing trial balance.
Requirement – 1
To prepare: The T-accounts and enter the beginning balance from the trial balance.
Explanation of Solution
T-account:
T-account refers to an individual account, where the increases or decreases in the value of specific asset, liability, stockholder’s equity, revenue, and expenditure items are recorded.
This account is referred to as the T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’.’ An account consists of the three main components which are as follows:
- (a) The title of the account
- (b) The left or debit side
- (c) The right or credit side
The T-accounts of given item in trial balance are as follows:
| Cash | |||
| Jan. 1 | $24,600 | ||
| Bal. | $20,000 | ||
| Accounts payable | |||
| Jan. 1 | $6,700 | ||
| Bal. | $6,700 | ||
| Common stock | |||
| Jan. 1 | $143,000 | ||
| Bal. | $143,000 | ||
|
Accounts receivables | |||
| Jan. 1 | $15,400 | ||
| Bal. | $15,400 | ||
| Prepaid Insurance | |||
| Jan. 1 | $12,000 | ||
| Bal. | $12,000 | ||
| Deferred revenue | |||
| Jan. 1 | $7,500 | ||
| Bal. | $7,500 | ||
| Land | |||
| Jan. 1 | 148,000 | ||
| Bal. | 148,000 | ||
| Retained earnings | |||
| Jan. 1 | $44,500 | ||
| Bal. | $44,500 | ||
Requirement – 2
To record: The journal entries for given transactions.
Explanation of Solution
Journal:
Journal is the method of recording monetary business transactions in chronological order. It records the debit and credit aspects of each transaction to abide by the double-entry system.
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
- Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
The journal entries for given transactions of Company Z are as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| 2018 | Accounts receivable | 52,200 | |
| January 9 | Cash | 134,100 | |
| Service revenue | 186,300 | ||
| (To record the recognized service revenue on account and cash) | |||
| 2018 | Cash | 51,500 | |
| February, 12 | Accounts receivable | 51,500 | |
| (To record cash collection from customer) | |||
| 2018 | Cash | 12,900 | |
| April 25 | Deferred revenue | 12,900 | |
| (To record the cash received in advance from customers) | |||
| 2018 | Supplies | 9,200 | |
| May 6 | Accounts payable | 9,200 | |
| (To record the purchase of supplies on account) | |||
| 2018 | Property tax expense | 8,500 | |
| July 15 | Cash | 8,500 | |
| (To record the payment of repairs and maintenance expense) | |||
| 2018 | Accounts payable | 11,400 | |
| September 10 | Cash | 11,400 | |
| (To record the payables on account ) | |||
| 2018 | Salaries expense | 123,600 | |
| October 31 | Cash | 123,600 | |
| (To record the payment of salaries for the current year) | |||
| 2018 | Cash | 27,000 | |
| ‘November 20 | Common stock | 27,000 | |
| (To record the payment of issuing shares of common stock) | |||
| 2018 | Dividends | 2,800 | |
| December 30 | Cash | 2,800 | |
| (To record the payment of dividends) | |||
Table (1)
Requirement – 3
To post: The transactions to T-accounts.
Explanation of Solution
T-account:
T-account refers to an individual account, where the increases or decreases in the value of specific asset, liability, stockholder’s equity, revenue, and expenditure items are recorded.
This account is referred to as the T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’.’ An account consists of the three main components which are as follows:
- (a) The title of the account
- (b) The left or debit side
- (c) The right or credit side
T-accounts of above transactions are as follows:
| Cash | |||
| Jan. 1 | $24,600 | July. 15 | $8,500 |
| Jan.9 | $134,100 | Sep. 25 | $11,400 |
| Feb. 12 | $51,500 | Oct. 19 | $123,600 |
| April.25 | $12,900 | Dec. 30 | $2,800 |
| Nov.20 | $27,000 | ||
| Total | $250,100 | Total | $146,300 |
| Bal. | $103,800 | ||
| Supplies | |||
| Jan. 1 | $0 | ||
| May.6 | $9,200 | ||
| $9,200 | |||
| Deferred revenue | |||
| $5,800 | |||
| $12,900 | |||
| $18,700 | |||
| Dividends | |||
| $0 | |||
| $2,800 | |||
| $2,800 | |||
| Salaries expense | |||
| $0 | |||
| $123,600 | |||
| $123,600 | |||
| Accounts receivable | |||
| $15,400 | |||
| $52,200 | $51,500 | ||
| Land | |||
| Jan. 1 | $148,000 | ||
| Bal. | $148,000 | ||
| Common stock | |||
| Jan. 1 | $143,300 | ||
| Bal. | $27,000 | ||
| Service revenue | |||
| Jan. 1 | $0 | ||
| Bal. | $186,300 | ||
| Insurance expense | |||
| Jan. 1 | $0 | ||
| $0 | |||
| Prepaid Insurance | |||
| $12,000 | |||
| $12,000 | |||
| Accounts payable | |||
| $6.700 | |||
| $11,400 | $9.200 | ||
| $4,500 | |||
| Retained earnings | |||
| Jan. 1 | 44,500 | ||
| Bal. | $44,500 | ||
| Property Tax Expense | |||
| $0 | |||
| $8,500 | |||
| Supplies expense | |||
| $0 | |||
| $0 | |||
Requirement – 4
To prepare: The unadjusted trial balance of Company Z.
Explanation of Solution
Unadjusted trial balance:
The unadjusted trial balance is the summary of all the ledger accounts before making adjusting journal entries at the end of the period.
| Company Z | ||
| Unadjusted Trial Balance | ||
| December 31, 2018 | ||
| Accounts | Debit | Credit |
| Cash | $103,800 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 16,100 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | 12,000 | |
| Supplies | 9,200 | |
| Land | 148,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | 4,500 | |
| Deferred Revenue | 18,700 | |
| Common stock | 170,000 | |
| Retained earnings | 44,500 | |
| Dividends | 2,800 | 60,000 |
| Service Revenue | 186,300 | |
| Property Tax expense | 8,500 | |
| Salaries expense | 123,600 | |
| Insurance expense | 0 | |
| Supplies Expense | 0 | |
| Totals | $424,000 | $424,000 |
Table (2)
Therefore, the total of debit, and credit columns of unadjusted trial balance is $424,000 and agree.
Requirement – 5
To record: The given adjusting entries of Company Z.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries:
Adjusting entries refers to the entries that are made at the end of an accounting period in accordance with revenue recognition principle, and expenses recognition principle. The purpose of adjusting entries is to adjust the revenue, and the expenses during the period in which they actually occurs.
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
- Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
Adjusting entries of Company R are as follows:
Accrued salaries:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| December 31, 2018 | Deferred Revenue | 11,800 | ||
| Service revenue | 11,800 | |||
| (To record the salaries expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) |
Table (3)
Following is the rule of debit and credit of above transaction:
- Deferred revenue is a liability, and it decreases the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, it is debited.
- Service revenue is a component of stockholders’ equity. There is an Increase in stockholders’ equity, therefore it is credited.
Depreciation expense:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| December 31, 2018 | Insurance Expense | 7,000 | ||
| Prepaid Insurance | 7,000 | |||
| (To record the amount of Reduced prepaid insurance due to passage of time) |
Table (4)
Following is the rule of debit and credit of above transaction:
- Insurance expense is an expense, and it decreased the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, it is debited.
- Prepaid Insurance is a contra-asset account. There is a decrease in assets, therefore it is credited.
Office supplies expense:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| December 31, 2018 | Supplies expense | 6,300 | ||
| Supplies | 6,300 | |||
| (To record the supplies expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) |
Table (5)
Following is the rule of debit and credit of above transaction:
- Supplies expense is an expense, and it decreased the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, it is debited.
- Supplies are an asset account. There is a decrease in assets, therefore it is credited.
Requirement – 6
To post: The adjusting entries to appropriate T-accounts.
Explanation of Solution
| Cash | |||
| Jan. 1 | $24,600 | July. 15 | $8,500 |
| Jan.9 | $134,100 | Sep. 25 | $11,400 |
| Feb. 12 | $51,500 | Oct. 19 | $123,600 |
| April.25 | $12,900 | Dec. 30 | $2,800 |
| Nov.20 | $27,000 | ||
| Total | $250,100 | Total | $146,300 |
| Bal. | $103,800 | ||
| Supplies | |||
| Jan. 1 | $0 | ||
| May.6 | $9,200 | $6,300 | |
| $2,900 | |||
| Deferred revenue | |||
| $5,800 | |||
| 11,800 | $12,900 | ||
| $6,900 | |||
| Dividends | |||
| $0 | |||
| $2,800 | |||
| $2,800 | |||
| Salaries expense | |||
| $0 | |||
| $123,600 | |||
| $123,600 | |||
| Accounts receivable | |||
| $15,400 | |||
| $52,200 | $51,500 | ||
| Land | |||
| Jan. 1 | $148,000 | ||
| Bal. | $148,000 | ||
| Common stock | |||
| Jan. 1 | $143,300 | ||
| Bal. | $27,000 | ||
| Total | $170,000 | ||
| Service revenue | |||
| Jan. 1 | $0 | ||
| Bal. | $186,300 | ||
| $11,800 | |||
| Total | $198,100 | ||
| Insurance expense | |||
| Jan. 1 | $0 | ||
| $7,000 | |||
| Total | $7,000 | ||
| Prepaid Insurance | |||
| $12,000 | |||
| $7,000 | |||
| $5,000 | |||
| Accounts payable | |||
| $6.700 | |||
| $11,400 | $9.200 | ||
| $4,500 | |||
| Retained earnings | |||
| Jan. 1 | 44,500 | ||
| Bal. | $44,500 | ||
| Property Tax Expense | |||
| $0 | |||
| $8,500 | |||
| Supplies expense | |||
| $0 | |||
| $6,300 | |||
Requirement – 7
To prepare: The adjusted trial balance of Company Z.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusted trial balance:
Adjusted trial balance is a summary of all the ledger accounts, and it contains the balances of all the accounts after the adjustment entries are journalized, and posted.
Adjusted trial balance of Company R is as follows:
| Company Z | ||
| Adjusted Trial Balance | ||
| December 31, 2018 | ||
| Accounts | Debit | Credit |
| Cash | 103,800 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 16,100 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 5,000 | |
| Supplies | 2,900 | |
| Land | 148,000 | |
| Accounts payable | 4,500 | |
| Deferred revenue | 6,900 | |
| Common stock | 170,000 | |
| Retained earnings | 44,500 | |
| Dividends | 2,800 | |
| Service revenue | 198,100 | |
| Property tax expense | 8,500 | |
| Salaries expense | 123,600 | |
| Insurance expense | 7,000 | |
| Supplies expense | 6,300 | |
| Totals | $424,000 | $424,000 |
Table (6)
Therefore, the total of debit, and credit columns of adjusted trial balance is $424,000 and agree.
Requirement – 8
To prepare: An income statement for 2018 and classified balance sheet as on December 31, 2018.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
This is the financial statement of a company which shows all the revenues earned and expenses incurred by the company over a period of time.
Classified balance sheet:
This is the financial statement of a company which shows the grouping of similar assets and liabilities under subheadings.
Income statement:
Income statement of Company Z is as follows:
| Company Z | ||
| Income statement | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2018 | ||
| $ | $ | |
| Service revenue (A) | $198,100 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Property tax | 8,500 | |
| Salaries | 123,600 | |
| Insurance | 7,000 | |
| Supplies | 6,300 | |
| Total expense (B) | 145,400 | |
| Net income
| 52,700 | |
Table (7)
Therefore, the net income of Company Z is $52,700.
Classified balance sheet:
Classified balance sheet of Company Z is as follows:
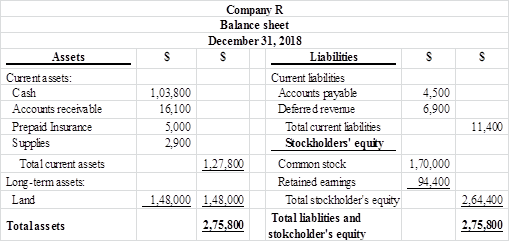
Figure (1)
Therefore, the total assets of Company Z are $275,800, and the total liabilities and stockholders’ equity are $275,800.
Working note:
Calculation of ending balance retained earnings
Requirement – 9
To record: The necessary closing entries of Company R.
Explanation of Solution
Closing entries:
Closing entries are those journal entries, which are passed to transfer the final balances of temporary accounts, (all revenues account, all expenses account and dividend) to the retained earnings. Closing entries produce a zero balance in each temporary account.
Closing entries of Company R is as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| 2018 | Service revenue | 198,100 | ||
| December 31 | Retained earnings | 198,100 | ||
| (To close all revenue account) | ||||
| 2018 | Retained earnings | 145,400 | ||
| December 31 | Property tax expense | 8,500 | ||
| Salaries expense | 123,600 | |||
| Insurance expense | 7,000 | |||
| 0 | Supplies expense | 6,300 | ||
| (To close all the expenses account) | ||||
| 2018 | Retained earnings | 2,800 | ||
| December 31 | Dividends | 2,800 | ||
| (To close the dividends account) | ||||
Table (8)
Requirement – 10
To post: The closing entries to the T-accounts.
Explanation of Solution
| Cash | |||
| Jan. 1 | $24,600 | July. 15 | $8,500 |
| Jan.9 | $134,100 | Sep. 25 | $11,400 |
| Feb. 12 | $51,500 | Oct. 19 | $123,600 |
| April.25 | $12,900 | Dec. 30 | $2,800 |
| Nov.20 | $27,000 | ||
| Total | $250,100 | Total | $146,300 |
| Bal. | $103,800 | ||
| Supplies | |||
| Jan. 1 | $0 | ||
| May.6 | $9,200 | $6,300 | |
| $2,900 | |||
| Deferred revenue | |||
| $5,800 | |||
| 11,800 | $12,900 | ||
| $6,900 | |||
| Dividends | |||
| $0 | |||
| $2,800 | $2,800 | ||
| $0 | |||
| Salaries expense | |||
| $0 | |||
| $123,600 | $123,600 | ||
| $0 | |||
| Accounts receivable | |||
| $15,400 | |||
| $52,200 | $51,500 | ||
| Land | |||
| Jan. 1 | $148,000 | ||
| Bal. | $148,000 | ||
| Common stock | |||
| Jan. 1 | $143,300 | ||
| Bal. | $27,000 | ||
| Total | $170,000 | ||
| Service revenue | |||
| Jan. 1 | $0 | ||
| Bal. | $186,300 | ||
| $11,800 | |||
| Total | $198,100 | ||
| Insurance expense | |||
| Jan. 1 | $0 | ||
| $7,000 | $7,000 | ||
| $0 | |||
| Prepaid Insurance | |||
| $12,000 | |||
| $7,000 | |||
| $5,000 | |||
| Accounts payable | |||
| $6.700 | |||
| $11,400 | $9.200 | ||
| $4,500 | |||
| Retained earnings | |||
| Jan. 1 | 44,500 | ||
| Bal. | $44,500 | ||
| Property Tax Expense | |||
| $0 | |||
| $8,500 | $8,500 | ||
| $0 | |||
| Supplies expense | |||
| $0 | |||
| $6,300 | $6,300 | ||
| $0 | |||
Requirement – 11
To prepare: A post-closing trial balance of Company Z.
Explanation of Solution
Post-closing trial balance:
The post-closing trial balance is a summary of all ledger accounts, and it shows the debit and the credit balances after the closing entries are journalized and posted. The post-closing trial balance contains only permanent (balance sheet) accounts, and the debit and the credit balances of permanent accounts should agree.
Post-closing trial balance of Company R is as follows:
| Company Z | ||
| Post-closing trial balance | ||
| December 31, 2018 | ||
| Accounts | Debit Amount($) |
Credit Amount($) |
| Cash | $103,800 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 16,100 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | 5,000 | |
| Supplies | 2,900 | |
| Land | 148,000 | |
| Accounts payable | 4,500 | |
| Deferred revenue | 6,900 | |
| Common stock | 170,000 | |
| Retained Earnings | 94,400 | |
| Totals | $275,800 | $275,800 |
Table (9)
Therefore, the total of debit, and credit columns of post-closing trial balance is $275,800 and agree.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Financial Accounting - Access
- Prepare journal entries to record the following transactions: A. December 1, collected balance due from customer account, $5,500 B. December 12, paid creditors for supplies purchased last month, $4,200 C. December 31, paid cash dividend to stockholders, $1,000arrow_forwardPost the following July transactions to T-accounts for Accounts Receivable, Sales Revenue, and Cash, indicating the ending balance. Assume no beginning balances in these accounts. A. on first day of the month, sold products to customers for cash, $13,660 B. on fifth day of month, sold products to customers on account, $22,100 C. on tenth day of month, collected cash from customer accounts, $18,500arrow_forwardThe transactions completed by AM Express Company during March 2016, the first month of the fiscal year, were as follows: Instructions 1. Enter the following account balances in the general ledger as of March 1: 2. Journalize the transactions for March 2016, using the following journals similar to those illustrated in this chapter: single-column revenue journal (p. 35), cash receipts journal (p. 31), purchases journal (p. 37, with columns for Accounts Payable, Maintenance Supplies, Office Supplies, and Other Accounts), cash payments journal (p. 34), and two-column general journal (p. 1). Assume that the daily postings to the individual accounts in the accounts payable subsidiary ledger and the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger have been made. 3. Post the appropriate individual entries to the general ledger. 4. Total each of the columns of the special journals, and post the appropriate totals to the general ledger; insert the account balances. 5. Prepare a trial balance.arrow_forward
- Analyzing the Accounts The controller for Summit Sales Inc. provides the following information on transactions that occurred during the year: a. Purchased supplies on credit, $18,600 b. Paid $14,800 cash toward the purchase in Transaction a c. Provided services to customers on credit1 $46,925 d. Collected $39,650 cash from accounts receivable e. Recorded depreciation expense, $8,175 f. Employee salaries accrued, $15,650 g. Paid $15,650 cash to employees for salaries earned h. Accrued interest expense on long-term debt, $1,950 i. Paid a total of $25,000 on long-term debt, which includes $1.950 interest from Transaction h j. Paid $2,220 cash for l years insurance coverage in advance k. Recognized insurance expense, $1,340, that was paid in a previous period l. Sold equipment with a book value of $7,500 for $7,500 cash m. Declared cash dividend, $12,000 n. Paid cash dividend declared in Transaction m o. Purchased new equipment for $28,300 cash. p. Issued common stock for $60,000 cash q. Used $10,700 of supplies to produce revenues Summit Sales uses the indirect method to prepare its statement of cash flows. Required: 1. Construct a table similar to the one shown at the top of the next page. Analyze each transaction and indicate its effect on the fundamental accounting equation. If the transaction increases a financial statement element, write the amount of the increase preceded by a plus sign (+) in the appropriate column. If the transaction decreases a financial statement element, write the amount of the decrease preceded by a minus sign (-) in the appropriate column. 2. Indicate whether each transaction results in a cash inflow or a cash outflow in the Effect on Cash Flows column. If the transaction has no effect on cash flow, then indicate this by placing none in the Effect on Cash Flows column. 3. For each transaction that affected cash flows, indicate whether the cash flow would be classified as a cash flow from operating activities, cash flow from investing activities, or cash flow from financing activities. If there is no effect on cash flows, indicate this as a non-cash activity.arrow_forwardReconstructing a Beginning Account Balance During the month, services performed for customers on account amounted to $7,500 and collections from customers in payment of their accounts totaled $6,000. At the end of the month, the Accounts Receivable account had a balance of $2,500. What was the Accounts Receivable balance at the beginning of the month?arrow_forwardOn January 24, 20Y8, Niche Consulting collected $5,700 it had hilled its clients for services rendered on December 31, 20Y7. How would you record the January 24 transaction, using the accrual basis? A. Increase Cash, $5,700; decrease Fees Earned, $5,700 B. Increase Accounts Receivable, $5,700; increase Fees Earned, $5,700 C. Increase Cash, $5,700; decrease Accounts Receivable, $5,700 D. Increase Cash, $5,700; increase Fees Earned, $5,700arrow_forward
- Krespy Corp. has a cash balance of $7,500 before the following transactions occur: A. received customer payments of $965 B. supplies purchased on account $435 C. services worth $850 performed, 25% is paid in cash the rest will be billed D. corporation pays $275 for an ad in the newspaper E. bill is received for electricity used $235. F. dividends of $2,500 are distributed What is the balance in cash after these transactions are journalized and posted?arrow_forwardInner Resources Company started its business on April 1, 2019. The following transactions occurred during the month of April. Prepare the journal entries in the journal on Page 1. A. The owners invested $8,500 from their personal account to the business account. B. Paid rent $650 with check #101. C. Initiated a petty cash fund $550 check #102. D. Received $750 cash for services rendered. E. Purchased office supplies for $180 with check #103. F. Purchased computer equipment $8,500, paid $1,600 with check #104 and will pay the remainder in 30 days. G. Received $1,200 cash for services rendered. H. Paid wages $560, check #105. I. Petty cash reimbursement office supplies $200, Maintenance Expense $140, Miscellaneous Expense $65. Cash on Hand $93. Check #106. J. Increased Petty Cash by $100, check #107.arrow_forwardPrepare journal entries to record the following transactions. Create a T-account for Cash, post any entries that affect the account, and calculate the ending balance for the account. Assume a Cash beginning balance of $16,333. A. February 2, issued stock to shareholders, for cash, $25,000 B. March 10, paid cash to purchase equipment, $16,000arrow_forward
- Domingo Company started its business on January 1, 2019. The following transactions occurred during the month of May. Prepare the journal entries in the journal on Page 1. A. The owners invested $10,000 from their personal account to the business account. B. Paid rent $500 with check #101. C. Initiated a petty cash fund $500 with check #102. D. Received $1,000 cash for services rendered. E. Purchased office supplies for $158 with check #103. F. Purchased computer equipment $2,500, paid $1,350 with check #104, and will pay the remainder in 30 days. G. Received $800 cash for services rendered. H. Paid wages $600, check #105. I. Petty cash reimbursement: office supplies $256, maintenance expense $108, postage expense $77, miscellaneous expense $55. Cash on hand $11. Check #106. J. Increased petty cash by $30, check #107.arrow_forwardThe transactions completed by AM Express Company during March, the first month of the fiscal year, were as follows: Instructions 1. Enter the following account balances in the general ledger as of March 1: 2. Journalize the transactions for March, using the following journals similar to those illustrated in this chapter: single-column revenue journal (p. 35), cash receipts journal (p. 31), purchases journal (p. 37, with columns for Accounts Payable, Maintenance Supplies, Office Supplies, and Other Accounts), cash payments journal (p. 34), and twocolumn general journal (p. 1). Assume that the daily postings to the individual accounts in the accounts payable subsidiary ledger and the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger have been made. 3. Post the appropriate individual entries to the general ledger. 4. Total each of the columns of the special journals and post the appropriate totals to the general ledger; insert the account balances. 5. Prepare a trial balance.arrow_forwardPrepare journal entries to record the following transactions. A. July 1, issued common stock for cash, $15,000 B. July 15, purchased supplies, on account, $1,800 C. July 25, billed customer for accounting services provided, $950arrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning  Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage LearningCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage LearningCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage





