
Concept explainers
The equivalent inductance for the system.
Answer to Problem 83CP
The equivalent inductance for the system is
Explanation of Solution
The flow of current in the circuit is as shown in the figure below.
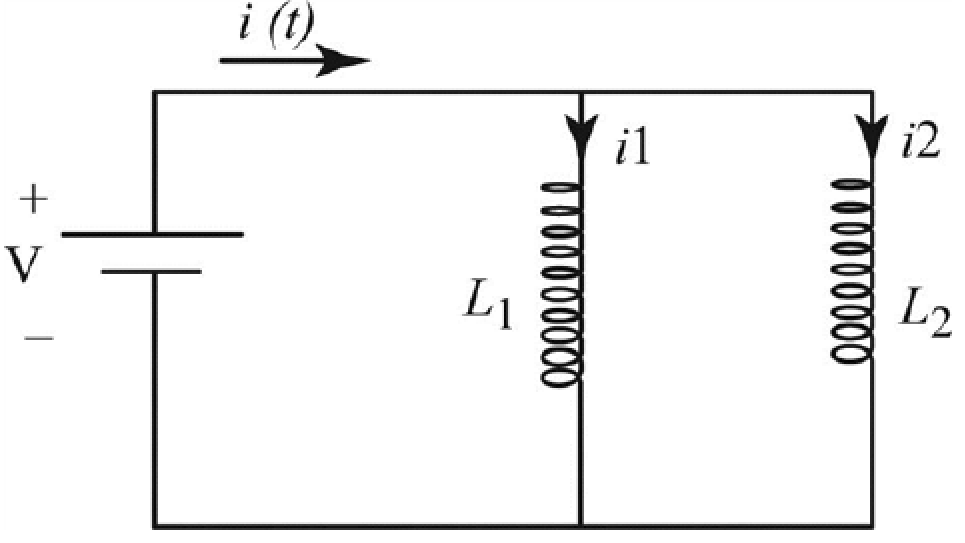
Figure-(1)
Here,
Write the expression based on junction rule.
Here,
Write the expression to obtain the loop rule.
Here,
Write the expression based on junction rule to obtain the current division in the circuit.
Here,
Differentiate the above equation with respect to time
Write the expression based on loop rule to obtain the potential drop in the left loop.
Write the expression based on loop rule to obtain the potential drop in the right loop.
As the inductor
Compare equation (III) and (IV).
Further solve the above equation.
Substitute
Write the expression to obtain the voltage across the circuit.
Here,
Substitute
Further substitute
Compare equation (V) and (VI).
Further solve the above equation.
Therefore, the equivalent inductance for the system is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 32 Solutions
Physics For Scientists And Engineers With Modern Physics, 9th Edition, The Ohio State University
- In the LC circuit in Figure 33.11, the inductance is L = 19.8 mH and the capacitance is C = 19.6 mF. At some moment, UB = UE= 17.5 mJ. a. What is the maximum charge stored by the capacitor? b. What is the maximum current in the circuit? c. At t = 0, the capacitor is fully charged. Write an expression for the charge stored by the capacitor as a function of lime. d. Write an expression for the current as a function of time.arrow_forwardA series RLC circuit driven by a source with an amplitude of 120.0 V and a frequency of 50.0 Hz has an inductance of 787 mH, a resistance of 267 , and a capacitance of 45.7 F. a. What are the maximum current and the phase angle between the current and the source emf in this circuit? b. What are the maximum potential difference across the inductor and the phase angle between this potential difference and the current in the circuit? c. What are the maximum potential difference across the resistor and the phase angle between this potential difference and the current in this circuit? d. What are the maximum potential difference across the capacitor and the phase angle between this potential difference and the current in this circuit?arrow_forwardWhen a wire carries an AC current with a known frequency, you can use a Rogowski coil to determine the amplitude Imax of the current without disconnecting the wire to shunt the current through a meter. The Rogowski coil, shown in Figure P23.8, simply clips around the wire. It consists of a toroidal conductor wrapped around a circular return cord. Let n represent the number of turns in the toroid per unit distance along it. Let A represent the cross-sectional area of the toroid. Let I(t) = Imax sin t represent the current to be measured. (a) Show that the amplitude of the emf induced in the Rogowski coil is Emax=0nAImax. (b) Explain why the wire carrying the unknown current need not be at the center of the Rogowski coil and why the coil will not respond to nearby currents that it does not enclose. Figure P23.8arrow_forward
- Two coaxial cables of length with radii a and b are carrying currents in opposite directions as shown in Figure P33.78. Determine the inductance of the system. Hint: Use Ampres law to write an expression for the magnetic field in the region between the cables, a distance r from the axis of the cables. Then calculate the magnetic flux through a narrow rectangular region between the cables such that the Field is perpendicular to the area everywhere. FIGURE P33.78arrow_forwardProblems 71 and 72 paired. Figure P33.71 shows a series RLC circuit with a 25.0- resistor, a 430.0-mH inductor, and a 24.0-F capacitor connected to an AC source with Vmax = 60.0 V operating at 60.0 Hz. What is the maximum voltage across the a. resistor, b. inductor, and c. capacitor in the circuit? FIGURE P33.71 Problems 71 and 72.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning




