
Concept explainers
The difference in positions of two rays crossing the principal axis.
Answer to Problem 55P
The difference in positions of two rays crossing the principal axis is
Explanation of Solution
The following figure gives the ray diagram of the two rays.
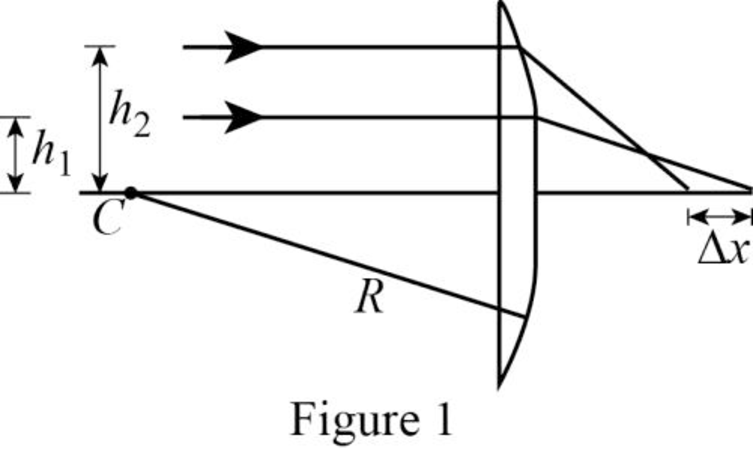
Write the expression to find the angle of incidence of the first ray.
Here,
Write the relation between the angle of incidence of the first ray and the second ray.
Write the expression for the focal length of the first ray
Write the expression for the distance crossed by the principal axis from the vertex by the first ray.
Write the expression to find the angle of incidence of the second ray.
Here,
Write the relation between the angle of incidence of the first ray and the second ray.
Write the expression for the focal length of the second ray
Write the expression for the distance crossed by the principal axis from the vertex by the second ray.
Write the expression for the difference in positions of two rays crossing the principal axis .
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the difference in positions of two rays crossing the principal axis is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 36 Solutions
Physics: for Science.. With Modern. -Update (Looseleaf)
- Figure P26.72 shows a thin converging lens for which the radii of curvature of its surfaces have magnitudes of 9.00 cm and 11.0 cm. The lens is in front of a concave spherical mirror with the radius of curvature R = 8.00 cm. Assume the focal points F1 and F2 of the lens are 5.00 cm from the center of the lens. (a) Determine the index of refraction of the lens material. The lens and mirror are 20.0 cm apart, and an object is placed 8.00 cm to the left of the lens. Determine (b) the position of the final image and (c) its magnification as seen by the eye in the figure. (d) Is the final image inverted or upright? Explain.arrow_forwardThe left face of a biconvex lens has a radius of curvature of magnitude 12.0 cm, and the right face has a radius of curvature of magnitude 18.0 cm. The index of refraction of the glass is 1.44. (a) Calculate the focal length of the lens for light incident from the left. (b) What If? After the lens is turned around to interchange the radii of curvature of the two faces, calculate the focal length of the lens for light incident from the left.arrow_forwardTwo converging lenses having focal length of f1 = 10.0 cm and f2 = 20.0 cm are placed d = 50.0 cm apart, as shown in Figure P23.44. The final image is to be located between the lenses, at the position x = 31.0 cm indicated. (a) How far to the left of the first lens should the object be positioned? (b) What is the overall magnification of the system? (c) Is the final image uptight or inserted? Figure P23.44arrow_forward
- Figure P36.95 shows a thin converging lens for which the radii of curvature of its surfaces have magnitudes of 9.00 cm and 11.0 cm. The lens is in front of a concave spherical mirror with the radius of curvature R = 8.00 cm. Assume the focal points F1 and F2 of the lens are 5.00 cm from the center of the lens, (a) Determine the index of refraction of the lens material. The lens and mirror are 20.0 cm apart, and an object is placed 8.00 cm to the left of the lens. Determine (b) the position of the filial image and (c) its magnification as seen by the eye in the figure. (d) Is the final image inverted or upright? Explain.arrow_forwardA thin plastic lens with index of refraction n = 1.67 has radii of curvature given by R1 = 12 0 cm and R2 = 40.0 cm. Determine (a) the focal length of the lens, (b) whether the lens Ls converging or diverging and the image distances for object distances of (c) infinity, (d) 8,00 cm, and (e) 50.0 cm.arrow_forwardTwo rays travelling parallel to the principal axis strike a large plano-convex lens having a refractive index of 1.60 (Fig. P23.54). If the convex face is spherical, a ray near the edge does not pass through the local point (spherical aberration occurs). Assume this face has a radius of curvature of R = 20.0 cm and the two rays are at distances h1 = 0.500 cm and h2 = 12.0 cm from the principal axis. Find the difference x in the position where each crosses the principal axis. Figure P23.54arrow_forward
- Two rays travelling parallel to the principal axis strike a large plano-convex lens having a refractive index of 1.60 (Fig. P23.54). If the convex face is spherical, a ray near the edge does not pass through the local point (spherical aberration occurs). Assume this face has a radius of curvature of R = 20.0 cm and the two rays are at distances h1 = 0.500 cm and h2 = 12.0 cm from the principal axis. Find the difference x in the position where each crosses the principal axis. Figure P23.54arrow_forwardWhy is the following situation impossible? Consider the lensmirror combination shown in Figure P35.55. The lens has a focal length of fL = 0.200 m, and the mirror has a focal length of fM = 0.500 m. The lens and mirror are placed a distance d = 1.30 m apart, and an object is placed at p = 0.300 m from the lens. By moving a screen to various positions to the left of the lens, a student finds two different positions of the screen that produce a sharp image of the object. One of these positions corresponds to light leaving the object and traveling to the left through the lens. The other position corresponds to light traveling to the right from the object, reflecting from the mirror and then passing through the lens. Figure P35.55 Problem 55 and 57.arrow_forwardTwo converging lenses having focal lengths of f1 = 10.0 cm and f2 = 20.0 cm are placed a distance d = 50.0 cm apart as shown in Figure P35.48. The image due to light passing through both lenses is to be located between the lenses at the position x = 31.0 cm indicated. (a) At what value of p should the object be positioned to the left of the first lens? (b) What is the magnification of the final image? (c) Is the final image upright or inverted? (d) Is the final image real or virtual?arrow_forward
- In Figure P26.38, a thin converging lens of focal length 14.0 cm forms an image of the square abcd, which is hc = hb = 10.0 cm high and lies between distances of pd = 20.0 cm and pa = 30.0 cm from the lens. Let a, b, c, and d represent the respective corners of the image. Let qa represent the image distance for points a and b, qd represent the image distance for points c and d, hb represent the distance from point b to the axis, and hc represent the height of c. (a) Find qa, qd, hb, and hc. (b) Make a sketch of the image. (c) The area of the object is 100 cm2. By carrying out the following steps, you will evaluate the area of the image. Let q represent the image distance of any point between a and d, for which the object distance is p. Let h represent the distance from the axis to the point at the edge of the image between b and c at image distance q. Demonstrate that h=10.0q(114.01q) where h and q are in centimeters. (d) Explain why the geometric area of the image is given by qaqdhdq (e) Carry out the integration to find the area of the image. Figure P26.38arrow_forwardIn Figure P35.30, a thin converging lens of focal length 14.0 cm forms an image of the square abed, which is he = hb = 10.0 cm high and lies between distances of pd = 20.0 cm and pa = 30.0 cm from the lens. Let a, b, c. and d represent the respective corners of the image. Let qa represent the image distance for points a and b, qd represent the image distance for points c and d, hb, represent the distance from point b to the axis, and hc represent the height of c. (a) Find qa, qd, hb, and hc. (b) Make a sketch of the image. (c) The area of the object is 100 cm2. By carrying out the following steps, you will evaluate the area of the image. Let q represent the image distance of any point between a and d, for which the object distance is p. Let h represent the distance from the axis to the point at the edge of the image between b and c at image distance q. Demonstrate that h=10.0q(114.01q) where h and q are in centimeters. (d) Explain why the geometric area of the image is given by qaqdhdq (e) Carry out the integration to find the area of the image. Figure P35.30arrow_forwardTwo thin lenses of focal lengths f1 = 15.0 and f2 = 10.0 cm, respectively, are separated by 35.0 cm along a common axis. The f1 lens is located to the left of the f2 lens. An object is now placed 50.0 cm to the left of the f1 lens, and a final image due to light passing though both lenses forms. By what factor is the final image different in size from the object? (a) 0.600 (b) 1.20 (c) 2.40 (d) 3.60 (e) none of those answersarrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





