
CONNECT ONLINE ACCESS F/MANAGERIAL ACC.
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781264445356
Author: Noreen
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3A, Problem 3A.4P
Activity-Based Absorption Costing as an Alternative to Traditional Product Costing LO3-5
Elix Company manufactures two models of ultra-high fidelity speakers—the X200 model and the X99 model. Data regarding the two products follow:
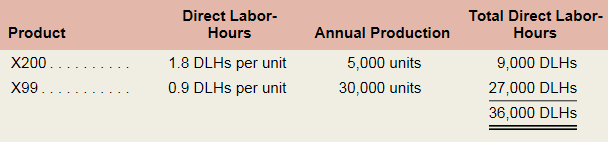
Additional information about the company follows:
- Model X200 requires S72 in direct materials per unit, and model X99 requires $50.
- The direct labor workers are paid S20 per hour.
- The company has always used direct labor-hours as the base for applying
manufacturing overhead cost to products. - Model X200 is more complex to manufacture than model X99 and requires the use of special equipment.
- Because of the special work required in (d) above, the company is considering the use of activity-based absorption costing to apply manufacturing overhead cost to products. Three activity cost pools have been identified as follows:
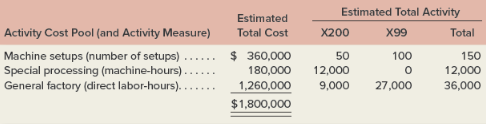
Required:
- Assume that the company continues to use direct labor-hours as the base for applying overhead cost to products.
- Compute the plantwide predetermined overhead rate.
- Compute the unit product cost of each model.
- Assume that the company decides to use activity-based absorption costing to apply overhead cost to products.
- Compute the activity rate for each activity cost pool and determine the amount of overhead cost that would be applied to each model using the activity-based approach.
- Compute the unit product cost of each model.
- Explain why overhead cost shifted from the high-volume model to the low-volume model under the activity-based approach.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Relevant costs; special order pricingKantrovitz Company is a manufacturer of industrial components. One of its products, AP110, is used as a subcomponent in appliance manufacturing. This product has the following information per unit:
Selling price
$150.00
Costs:
Direct material
$20.00
Direct labor
15.00
Variable manufacturing overhead
12.00
Fixed manufacturing overhead
30.00
Shipping and handling
3.00
Fixed selling and administrative
10.00
Total per-unit cost
$90.00
a. Kantrovitz has received a special, one-time order for 1,600 AP110 parts. Assuming Kantrovitz has excess capacity, what is the minimum price that is acceptable for beginning negotiations on this order? $Answerb. Kantrovitz has 8,000 units of AP110 in inventory that have some defects. The units cannot be sold through regular channels without a significant price reduction. What per-unit cost figure is relevant for setting a minimum selling price on these units? $Answerc. During the next year,…
Product Cost Method of Product Costing
Voice Com, Inc., uses the product cost method of applying the cost-plus approach to product
pricing. The costs of producing and selling 5,310 units of cell phones are as follows:
Variable costs:
Fixed costs:
Direct materials
$67 per unit
Factory overhead
$198,000
Direct labor
37
Selling and admin. exp.
71,400
Factory overhead
22
Selling and admin. exp.
18
Total variable cost per unit
$144 per unit
Voice Com desires a profit equal to a 16% rate of return on invested assets of $601,800.
a. Determine the amount of desired profit from the production and sale of 5,310 units of cell
phones.
2$
b. Determine the product cost per unit for the production of 5,310 of cell phones. If required,
round your answer to nearest dollar.
per unit
c. Determine the product cost markup percentage (rounded to two decimal places) for cell
phones.
%
d. Determine the selling price of cell phones. Round to the nearest dollar.
Total Cost
per unit
Markup
per unit
Selling price…
Relevant costs; special order pricingKantrovitz Company is a manufacturer of industrial components. One of its products, AP110, is used as a subcomponent in appliance manufacturing. This product has the following information per unit:
Selling price
$150.00
Costs:
Direct material
$20.00
Direct labor
15.00
Variable manufacturing overhead
12.00
Fixed manufacturing overhead
30.00
Shipping and handling
3.00
Fixed selling and administrative
10.00
Total per-unit cost
$90.00
a. Kantrovitz has received a special, one-time order for 1,600 AP110 parts. Assuming Kantrovitz has excess capacity, what is the minimum price that is acceptable for beginning negotiations on this order?
Answer: $50
d. Referring to (a), Kantrovitz has received a special, one-time order for 1,600 AP110 parts. Assume that Kantrovitz is operating at full capacity, and that the contribution of the output would be displaced by the one-time special order. Using the original data, compute the minimum…
Chapter 3A Solutions
CONNECT ONLINE ACCESS F/MANAGERIAL ACC.
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Wrappers Tape makes two products: Simple and Removable. It estimates it will produce 369,991 units of Simple and 146,100 of Removable, and the overhead for each of its cost pools is as follows: It has also estimated the activities for each cost driver as follows: Â How much is the overhead allocated to each unit of Simple and Removable?arrow_forwardroduct Cost Method of Product Costing MyPhone, Inc., uses the product cost method of applying the cost-plus approach to product pricing. The costs of producing and selling 5,160 units of cell phones are as follows: Variable costs: Fixed costs: Direct materials $90 per unit Factory overhead $199,200 Direct labor 31 Selling and admin. exp. 70,300 Factory overhead 23 Selling and admin. exp. 22 Total variable cost per unit $166 per unit MyPhone desires a profit equal to a 13% rate of return on invested assets of $600,800. a. Determine the amount of desired profit from the production and sale of 5,160 units of cell phones.$fill in the blank 1 b. Determine the product cost per unit for the production of 5,160 of cell phones. If required, round your answer to nearest dollar.$fill in the blank 2 per unit c. Determine the product cost markup percentage (rounded to two decimal places) for cell phones.fill in the blank 3 % d.…arrow_forwardRelevant costs; special order pricingKantrovitz Company is a manufacturer of industrial components. One of its products, AP110, is used as a subcomponent in appliance manufacturing. This product has the following information per unit: Selling price $150.00 Costs: Direct material $20.00 Direct labor 15.00 Variable manufacturing overhead 12.00 Fixed manufacturing overhead 30.00 Shipping and handling 3.00 Fixed selling and administrative 10.00 Total per-unit cost $90.00 a. Kantrovitz has received a special, one-time order for 1,000 AP110 parts. Assuming Kantrovitz has excess capacity, what is the minimum price that is acceptable for beginning negotiations on this order? $Answer b. Kantrovitz has 5,000 units of AP110 in inventory that have some defects. The units cannot be sold through regular channels without a significant price reduction. What per-unit cost figure is relevant for setting a minimum selling price on these units? $Answer c. During the next…arrow_forward
- ABC and CVP Analysis: Multiple Products Good Scent, Inc., produces two colognes: Rose and Violet. Of the two, Rose is more popular. Data concerning the two products follow: Rose Violet Expected sales (in cases) Selling price per case Direct labor hours Machine hours Direct labor benefits Machine costs Receiving department Packing department Total costs Receiving orders Packing orders Material cost per case Direct labor cost per case $11 The company uses a conventional costing system and assigns overhead costs to products using direct labor hours. Annual overhead costs follow. They are classified as fixed or variable with respect to direct labor hours. Fixed *All depreciation $ 51,000 10,200 $81 32,000 6,400 9,750 3,500 Break-even cases of Rose Break-even cases of Violet 182,500 $99 214,500 136,500 $533,500 50 96 $50 27 45 $44 $5 Variable $165,120 218,880 $384,000 Required: 1. Using the conventional approach, compute the number of cases of Rose and the number of cases of Violet that…arrow_forwardProduct Cost Concept of Product Costing Smart Stream Inc. uses the product cost concept of applying the cost-plus approach to product pricing. The costs of producing and selling 5,490 cellular phones are as follows: Variable costs: Fixed costs: Direct materials $90 Factory overhead $199,900 Direct labor 32 Selling and administrative expenses 70,200 Factory overhead 24 Selling and administrative expenses 19 Total $165 Smart Stream wants a profit equal to a 13% rate of return on invested assets of $599,500. a. Determine the amount of desired profit from the production and sale of 5,490 cellular phones. b. Determine the product cost and the cost amount per unit for the production of 5,490 cellular phones. If required, round your answer to nearest dollar. c. Determine the product cost markup percentage for cellular phones. Rounded to two decimal places. d. Determine the selling price of cellular phones. Round to…arrow_forwardSheridan Company manufactures and sells two products. Relevant per unit data concerning each product follow. Selling price Variable costs Machine hours (a) Product Basic $42.0 $24.0 0.5 Deluxe $55.0 $29.4 x Your answer is incorrect. 0.8 Compute the contribution margin per machine hour for each product. Contribution margin per machine hour $ Basic 40 $ Deluxe 51 Farrow_forward
- Windhoek Manufacturers produces two products, Amber and Black. The following cost estimates have been prepared using the traditional absorption costing approach. Selling price per unit Production costs per unit: Material costs Direct labour costs Manufacturing overhead cost Profit per unit Additional information. Estimates sales demand Machine hours per unit Required 1.1 1.2 Amber N$ Amber 69 27 6 12 24 9 000 0.75 Calculate the return per machine hour for each product if through put accounting approach is used. Calculate the profit for the period, using a throughput accounting approach, assuming the company priorities Black Black N$ Black 93 24 15 18 36 12 000 1.20 TIOLE.(arrow_forwardTotal Cost Concept of Product Pricing Smart Stream Inc. uses the total cost concept of applying the cost-plus approach to product pricing. The costs of producing and selling 8,500 units of cellular phones are as follows: Variable costs: Fixed costs: Direct materials $ 73 per unit Factory overhead $314,500 Direct labor 34 Selling and admin. exp. 110,500 Factory overhead 22 Selling and admin. exp. 17 Total $146 per unit Smart Stream wants a profit equal to a 15% rate of return on invested assets of $932,960. a. Determine the total costs and the total cost amount per unit for the production and sale of 8,500 units of cellular phones. Round the cost per unit to two decimal places. Total costs Cost amount per unit b. Determine the total cost markup percentage (rounded to two decimal places) for cellular phones. % c. Determine the selling price of cellular phones.…arrow_forwardABC and CVP Analysis: Multiple Products Good Scent, Inc., produces two colognes: Rose and Violet. Of the two, Rose is more popular. Data concerning the two products follow: Expected sales (in cases) Selling price per case. Direct labor hours Machine hours Receiving orders Packing orders Material cost per case $49 Direct labor cost per case $12 The company uses a conventional costing system and assigns overhead costs to products using direct labor hours. Annual overhead costs follow. They are classified as fixed or variable with respect to direct labor hours. Fixed $ Direct labor benefits Machine costs Receiving department Packing department Total costs Rose Violet 51,000 10,200 $100 36,750 9,250 52 98 All depreciation 211,000 212,500 149,000 $572 500 $83 6,400 2,700 24 51 $44 $8 Variable. $215,750 215,750 $431,500arrow_forward
- Total Cost Concept of Product Pricing Smart Stream Inc. uses the total cost concept of applying the cost-plus approach to product pricing. The costs of producing and selling 6,500 units of cellular phones are as follows: Variable costs: Fixed costs: Direct materials $ 85 per unit Factory overhead $279,000 Direct labor 39 Selling and admin. exp. 98,000 Factory overhead 26 Selling and admin. exp. 20 Total $170 per unit Smart Stream wants a profit equal to a 16% rate of return on invested assets of $833,630. a. Determine the total costs and the total cost amount per unit for the production and sale of 6,500 units of cellular phones. Round the cost per unit to two decimal places. Total costs $fill in the blank 1 Cost amount per unit $fill in the blank 2 b. Determine the total cost markup percentage (rounded to two decimal places) for cellular phones.fill in the blank 3% c. Determine the selling price of…arrow_forwardV&S Mechanical sells and services plumbing, heating, and air conditioning systems. V&S's cost accounting system tracks two cost categories: direct labor and direct materials V&S uses a time-and-materials pricing system, with direct labor marked up 100% and direct materials marked up 50% to recover indirect costs of support staff, support materials, and shared equipment and tools and to earn a profit (Click the icon to view the cost information) Read the requirements Requirement 1. If Dryden presents Lowry with the replace or repair options, what price would he quote for each? Complete the table below to determine the price Dryden would quote for each option Labor Materials Total Price Repair option Replace option Requirements 1. if Dryden presents Lowry with the replace or repair options, what price would he quote for each? 2. If the two options were equally effective for the 3 years that Lowry intends to live in the home, which option would she choose? 3. if Dryden's objective is to…arrow_forwardProduct Cost Concept of Product Costing MyPhone Inc. uses the product cost concept of applying the cost-plus approach to product pricing. The costs of producing and selling 5,060 cellular phones are as follows: Please help with problem C and d and show calculationarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337912020
Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:South-Western College Pub

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:9781947172609
Author:OpenStax
Publisher:OpenStax College
Cost Accounting - Definition, Purpose, Types, How it Works?; Author: WallStreetMojo;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AwrwUf8vYEY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY