
Loose Leaf For Introduction To Computing Systems: From Bits & Gates To C & Beyond
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9781260424744
Author: Yale N. Patt, Sanjay Patel
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 19E
Shown below is a byte-addressible memory consisting of eight locations, and its associated MAR and MDR. Both MAR and MDR consist of flip-flops that are latched at the start of each clock cycle based on the values on their corresponding input lines. A memory read is initiated every cycle, and the data is available by the end of that cycle.
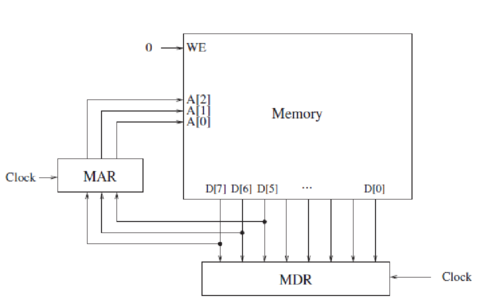
Just before the start of cycle 1, MAR contains 000, MDR contains 00010101, and the contents of each memory location is as shown.

a. What do MAR and MDR contain just before the end of cycle 1?
MAR:  MDR:
MDR: 
b. What does MDR contain just before the end of cycle 4?
MDR: 
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The use of transistors in the construction of RAM and ROM leads me to believe that there is no need for cache memory.The term "temporary storage" may also be thought of as "random access memory" (RAM) that is momentarily vacant. Imagine a machine that only had one kind of memory—is it even possible?
The write operation in Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) is using a voltage signal to
represent bit 0 and bit 1. The high voltage represent bit 1 and low voltage represent bit 0?
O a. false
O b. True
Q2- Write a program in assembly language for the 8085 microprocessor to receive one byte of data via the SID and store it at the memory address (3000H to 3009H) using a baud rate of 1200.
Information: The 8085 processor operates at a frequency of 3.072 MHz . When receive the required bytes, you must adhere to the following: The bits of two high bits will be received at the beginning of the reception(start bits 1 1 ), after that the data bits will be received, after that the low bit of the stop bit will be received (stop bit 0 ).
The following flowchart will help you.
The solution must be integrated and include the calculation of the baudrate delay time
Chapter 4 Solutions
Loose Leaf For Introduction To Computing Systems: From Bits & Gates To C & Beyond
Ch. 4 - Prob. 1ECh. 4 - Prob. 2ECh. 4 - What is misleading about the name program counter?...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4ECh. 4 - Prob. 5ECh. 4 - What are the two components of an instruction?...Ch. 4 - Prob. 7ECh. 4 - The FETCH phase of the instruction cycle does two...Ch. 4 - Prob. 10ECh. 4 - State the phases of the instruction cycle, and...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- By assuming that X = 3, and 33 is a two digit number, consider memory storage of a 64-bit word stored at memory word 33 in a byte-addressable memory (a) What is the byte address of memory word 33? (b) What are the byte addresses that memory word 33 spans? (c) Draw the number 0xF1234567890ABCDE stored at word 33 in both big endian and little-endian machines. Clearly label the byte address corresponding to each data byte value.arrow_forwardQ1- Write a program in assembly language for the 8085 microprocessor to receive 10 bytes of data via the SID and store it at the memory address (3000H to 3009H) using a baud rate of 1200. Information: The 8085 processor operates at a frequency of 3.072 MHz. When you receive each byte of the required bytes, you must adhere to the following: The bits of two high bits will be received at the beginning of the reception (start bits), after that the data bits will be received, after that the low bit of the stop bit will be received (stop bit). The following flowchart will help you, but you should notice that this flowchart deals with one byte, and you are required to deal with 10 bytes The solution must be integrated and include the calculation of the baudrate delay time Of+CD!HID+[00 Yes SIDATA Read SID Start Bit? Wait for Half-Bit Time Set up Bit Counter Wait Bit Time Read SID Save Bit Decrement Bit Counter All Bits Received? Add Bit to Previous Bits Go Back to Get Next Bit Return IMUNIarrow_forwardThe contents of memory location B0000, are FF 16, and those at B0001 6 are 0016. What is the data word stored at the address B0000? Is the word aligned or misaligned?arrow_forward
- A digital computer has a memory unit with 24 bits per word. The instruction set consists of 150 different operations. All instructions have an operation code part (opcode) and an address part (allowing for only one address). Each instruction is stored in one word of memory.Q.) What is the largest unsigned binary number that can be accommodated in one word of memory?arrow_forwardConsider memory storage of a 32-bit word stored at memory word 34 in a byte addressable memory. (a) What is the byte address of memory word 34? (b) What are the byte addresses that memory word 34 spans? (c) Draw the number 0x3F526372 stored at word 342 in both big-endian and little-endian machines. Clearly label the byte address corresponding to each data byte value.arrow_forwardThe machines that use MISD are systolic arrays. A systolic array is a "wavefront" or data processing pipeline. Because data triggers execution, these sections don't need programme counters and may function independently. When all of the clocks in a systolic array are synchronized, the CPUs are able to do calculations in what is called "lock-step."arrow_forward
- A computer has a 256K word addressable memory Module with 16 bits per word. The instruction set consists of 166 different instructions. All instructions have an operation code part (opcode) and an address part (allowing for only one address). Each instruction is stored in one word of memory. Based on the above, answer the following questions: a. How many bits are there in the main memory? (Represent it in power of 2) b. How many bits are needed for the opcode? c. How many bits are left for the address part of the instruction? d. How many additional instructions can be added to the existing 166 without affecting the assigned size of the opcode part? Justify.arrow_forwardA digital computer has a memory unit with 24 bits per word. The instruction set consists of 150 different operations. All instructions have an operation code part (opcode) and an address part (allowing for only one address). Each instruction is stored in one word ofmemory.a. How many bits are needed for the opcode?b. How many bits are left for the address part of the instruction?c. What is the maximum allowable size for memory?d. What is the largest unsigned binary number that can be accommodated in one word of memory?arrow_forwardSP=1239H, SS=9876H, the physical address is AAAFOH Non of them 1BC06H 0AAAFH 99999H if BX=1000, DS=0400, and AL=EDH, for the following instruction: MOV [BX] + 1234H, AL. the physical address is 6324H O 4244H 4234H 6234H 6243H Oarrow_forward
- Translate the following pseudo code to MIPS code: A=B+C Consider that the variables A, 8, and C should be stored in the following memory locations refeorenced by the registers listed. Memory address $s4 Ox5400 B $s3 Ox541C A $s5 Ox5438arrow_forwardThe ALU unit of a microprocessor manipulate logically or arithmetically on array of Bits. Below are two set of Bits equations placed in the ALU sequentially: Calculate 11100011 AND 11001110 and Calculate 01010111 OR 11001100 By your reasoning and application of principle of ALU solve this equations step by steparrow_forwardThe memory contains an array of 100 elements starting at addresses 500H. Write the assembly code that records the numbers between -10 and +10 in this array, starting from address 750h, respectively.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning
Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning

Systems Architecture
Computer Science
ISBN:9781305080195
Author:Stephen D. Burd
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Instruction Format (With reference to address); Author: ChiragBhalodia;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lNdy8HREvgo;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY