
Concept explainers
Preparing
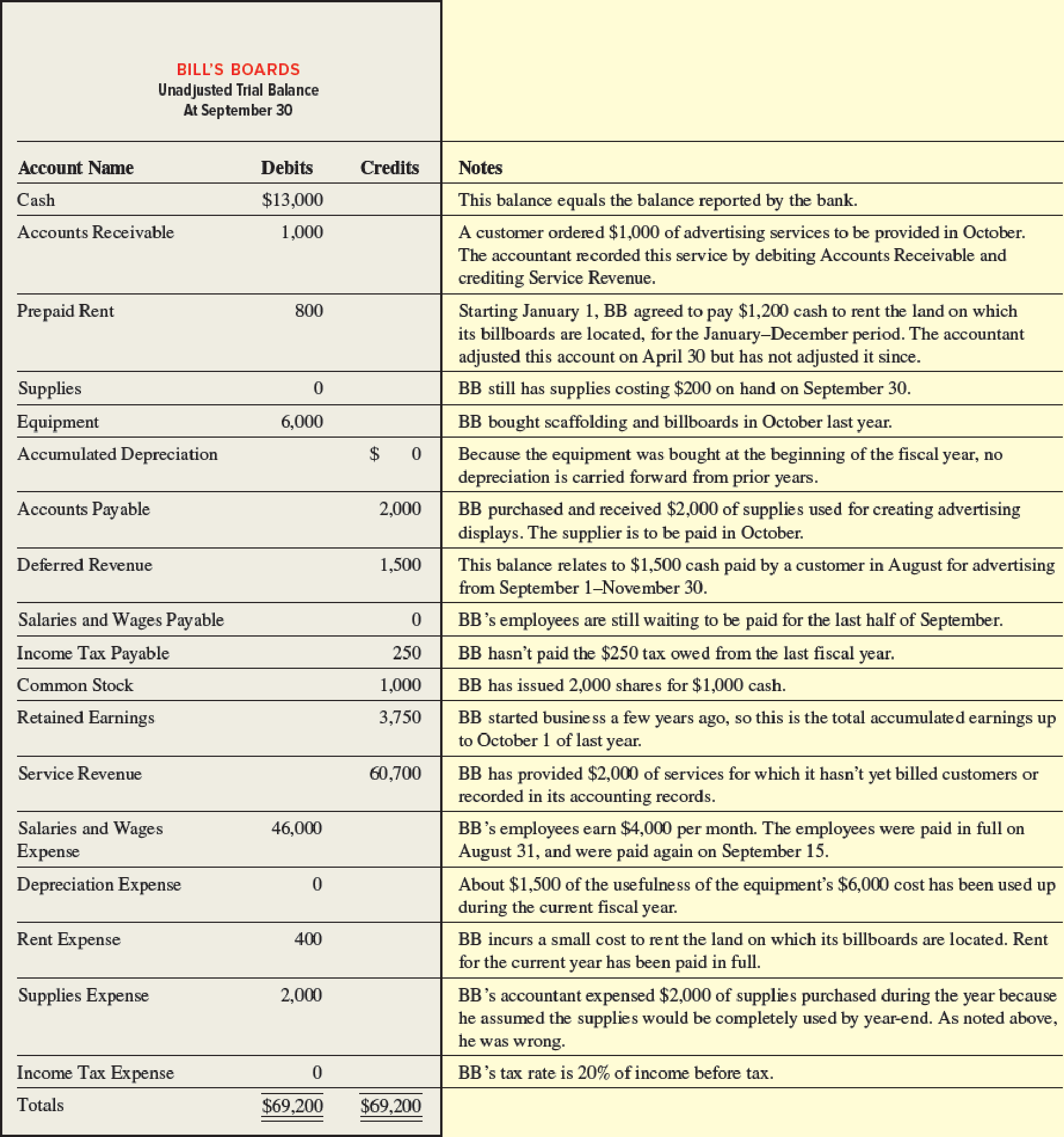
Bill’s Boards (BB) is an outdoor advertising company founded by William Longfall. William knows very little accounting so he hired a friend to “keep the books.” Unfortunately, William did not review his friend’s work and now it seems his friend has made a mess of the accounting records. William has provided you the following list of unadjusted account balances at BB’s September 30 fiscal year-end. You have reviewed the balances with William and made notes shown in the right column.
Required:
- 1. Use the notes to determine and record the adjusting
journal entries needed on September 30 to (a) fix the premature recording of advertising revenue, (b) update the rent accounts, (c) account for the use of equipment, (d) update deferred revenue, (e) accrue revenue not yet billed, (f ) accrue unpaid wages, (g) correct the supplies accounts, and (h) accrue income taxes for the year. - 2. Post the adjusting journal entries from requirement 1 to T-accounts to determine new adjusted balances, and prepare an adjusted trial balance. (If you are completing this exercise using the general ledger tool in Connect, this requirement will be completed automatically for you.)
- 3. Using the adjusted account balances from requirement 2, prepare an income statement, statement of
retained earnings , and classifiedbalance sheet .
a.
Record the adjusting journal entries needed on September 30.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries: Adjusting entries are those entries which are recorded at the end of the year, to update the income statement accounts (revenue and expenses) and balance sheet accounts (assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity) to maintain the records according to accrual basis principle.
Record the adjusting journal entries needed on September 30 as follows:
| Date | Particulars | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| (a) | Service Revenue (+R, +SE) | 1,000 | ||
| Accounts Receivable (+A) | 1,000 | |||
| (To record the service revenue recognized on account) | ||||
| (b) | Rent Expense (+E, –SE) (1) | 500 | ||
| Prepaid Rent (–A) | 500 | |||
| (To record the interest expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | ||||
| (c) | Depreciation Expense (+E, –SE) | 1,500 | ||
| Accumulated Depreciation (+xA, –A) | 1,500 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | ||||
| (d) | Deferred Revenue (–L) (2) | 500 | ||
| Service Revenue (+R, +SE) | 500 | |||
| (To record the service revenue recognized at the end of the accounting year) | ||||
| (e) | Accounts Receivable (+A) | 2,000 | ||
| Service Revenue (+R, +SE) | 2,000 | |||
| (To record the service revenue earned on account) | ||||
| (f) | Salaries and Wages Expense (+E, –SE) (3) | 2,000 | ||
| Salaries and Wages Payable (+L) | 2,000 | |||
| (To record the salaries and wages expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | ||||
| (g) | Supplies (+A) | 200 | ||
| Supplies Expense (–E, +SE) | 200 | |||
| (To record supplies expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | ||||
| (h) | Income Tax Expense (+E, –SE) ( 5) | 2,000 | ||
| Income Tax Payable (+L) | 2,000 | |||
| (To record the income tax expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) |
Table (1)
Working note 1:
Calculate the value of rent expense.
Working note 2:
Calculate the value of deferred revenue.
Working note 3:
Calculate the value of salaries and wages expense (adjusted).
Working note 4:
Calculate the unadjusted net income.
Working note 5:
Calculate the value of income tax expense:
Note: Supplies costing of $200 on hand on September 30 is considered as the supplies expense incurred at the end of the accounting year.
b.
Post the adjusting journal entries to T-accounts to determine the new adjusted balance and prepare the adjusted trial balance.
Explanation of Solution
Post the adjusting journal entries to T-accounts to determine the new adjusted balance as follows:
| Cash (A) | |||
| Beg. | 13,000 | ||
| 13,000 | |||
| Supplies (A) | |||
| Beg. | 0 | ||
| g. | 200 | ||
| 200 | |||
| Accounts Payable (L) | |||
| 2,000 | Beg. | ||
| 2,000 | |||
| Income Tax Payable (L) | |||
| 250 | Beg. | ||
| 2,000 | h. | ||
| 2,250 | |||
| Service Revenue (R) | |||
| a. | 1,000 | 60,700 | Beg. |
| 500 | d. | ||
| 2,000 | e. | ||
| 62,200 | |||
| Rent Expense (E) | |||
| Beg. | Beg. 400 | ||
| b. | 500 | ||
| 900 | |||
| Accounts Receivable (A) | |||
| Beg. | 1,000 | ||
| e. | 2,000 | 1,000 | a. |
| 2,000 | |||
| Equipment (A) | |||
| Beg | 6,000 | ||
| 6,000 | |||
| Deferred Revenue (L) | |||
| 1,500 | Beg. | ||
| d. | 500 | ||
| 1,000 | |||
| Common Stock (SE) | |||
| 1,000 | Beg. | ||
| 1,000 | |||
| Salaries and Wages Expense (E) | |||
| Beg. | 46,000 | ||
| f. | 2,000 | ||
| 48,000 | |||
| Supplies Expense (E) | |||
| Beg. | 2,000 | ||
| 200 | g. | ||
| 1,800 | |||
| Prepaid Rent (A) | |||
| Beg. | 800 | ||
| 500 | (b) | ||
| 300 | |||
| Accumulated Depreciation (xA) | |||
| 0 | Beg. | ||
| 1,500 | c. | ||
| 1,500 | |||
| Salaries and Wages Payable (L) | |||
| 0 | Beg. | ||
| 2,000 | f. | ||
| 2,000 | |||
| Retained Earnings (SE) | |||
| 3,750 | Beg. | ||
| 3,750 | |||
| Depreciation Expense (E) | |||
| Beg. | 0 | ||
| c. | 1,500 | ||
| 1,500 | |||
| Income Tax Expense | |||
| Beg. | 0 | ||
| h. | 2,000 | ||
| 2,000 | |||
Prepare the adjusted trial balance as follows:
| Company B | ||
| Adjusted Trial Balance | ||
| September, 30 | ||
| Account Titles | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 13,000 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 2,000 | |
| Prepaid Rent | 300 | |
| Supplies | 200 | |
| Equipment | 6,000 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation | 1,500 | |
| Accounts Payable | 2,000 | |
| Deferred Revenue | 1,000 | |
| Salaries and Wages Payable | 2,000 | |
| Income Tax Payable | 2,250 | |
| Common Stock | 1,000 | |
| Retained Earnings | 3,750 | |
| Service Revenue | 62,200 | |
| Salaries and Wages Expense | 48,000 | |
| Supplies Expense | 1,800 | |
| Depreciation Expense | 1,500 | |
| Rent Expense | 900 | |
| Income Tax Expense | 2,000 | |
| Totals | 75,700 | 75,700 |
Table (2)
c.
Prepare an income statement, statement of retained earnings, and classified balance sheet of company B.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Classified balance sheet: The main elements of balance sheet assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity are categorized or classified further into sections, and sub-sections in a classified balance sheet. Assets are further classified as current assets, long-term investments, property, plant, and equipment (PPE), and intangible assets. Liabilities are classified into two sections current and long-term. Stockholders’ equity comprises of common stock and retained earnings. Thus, the classified balance sheet includes all the elements under different sections.
Prepare an income statement, statement of retained earnings, and classified balance sheet as follows:
| Company B | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| For the Year Ended September 30 | ||
| Particulars | $ | $ |
| Service Revenue | 62,200 | |
| Less: Expenses | ||
| Salaries and Wages Expense | 48,000 | |
| Supplies Expense | 1,800 | |
| Depreciation Expense | 1,500 | |
| Rent Expense | 900 | |
| Income Tax Expense | 2,000 | |
| Total Expenses | 54,200 | |
| Net Income | 8,000 | |
Table (3)
| Company B | |
| Statement of Retained Earnings | |
| For the Year Ended September 30 | |
| Particulars | $ |
| Beginning Balance | 3,750 |
| Add: Net Income | 8,000 |
| Less: Dividends | - |
| Ending Balance | 11,750 |
Table (4)
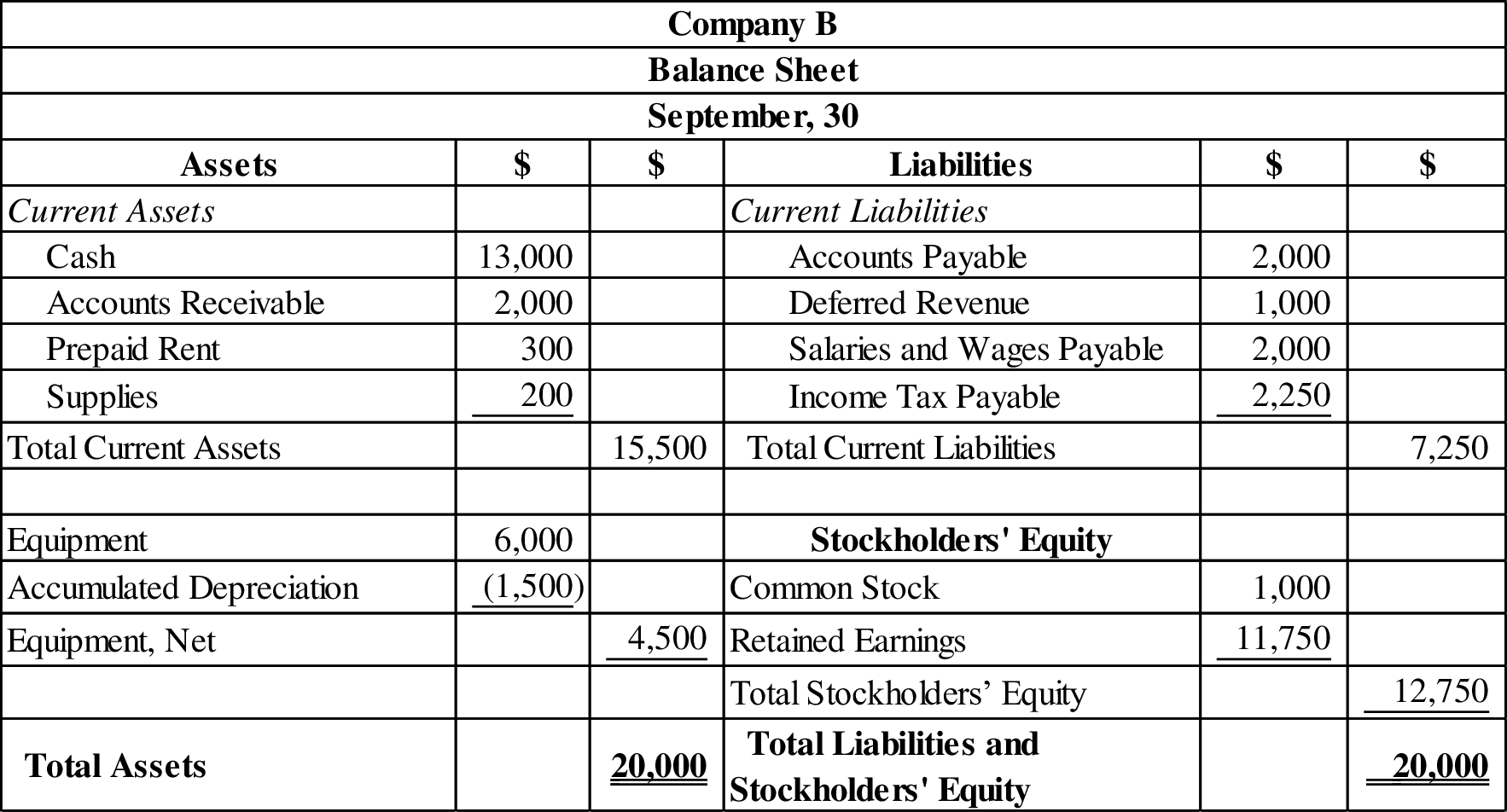
Figure (1)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
- The trial balance of Wikki Cleaners at December 31, 2012, the end of the current fiscal year, is as follows: Information for the adjusting entries is as follows: a. Cleaning supplies on hand on December 31, 2012, 18,750. b. Insurance premiums expired during the year, 1,800. c. Depreciation on equipment during the year, 21,600. d. Wages accrued but not paid at December 31, 2012, 1,830. Suppose you discover that an assistant in your department had misunderstood your instructions and had provided you with the wrong information on two of the adjusting entries. Cleaning supplies consumed during the year should have been 18,750, and insurance premiums unexpired at year-end were 1,800. Make the corrections on your worksheet and save the corrected file as F1WORK4. Reprint the worksheet.arrow_forwardSpeedy Sewing Services, owned by T. Nguyen, hired a new bookkeeper who is not entirely familiar with the process of preparing a trial balance. All of the accounts have normal balances. Find the errors and prepare a corrected trial balance for December 31 of this year.arrow_forwardDelia Alvarez, owner of Delias Lawn Service, wants to borrow money to buy new lawn equipment. A local bank has asked for financial statements. Alvarez has asked you to prepare financial statements for the year ended December 31, 20--. You have been given the unadjusted trial balance on page 175 and suspect that Alvarez expects you to base your statements on this information. You are concerned, however, that some of the account balances may need to be adjusted. Write a memo to Alvarez explaining what additional information you need before you can prepare the financial statements. Alvarez is not familiar with accounting issues. Therefore, explain in your memo why you need this information, the potential impact of this information on the financial statements, and the importance of making these adjustments before approaching the bank for a loan.arrow_forward
- Your friend Chris Stevick started a part-time business in June and has been keeping her own accounting records. She has been preparing monthly financial statements. At the end of August, she stopped by to show you her performance for the most recent month. She prepared the following income statement and balance sheet: Chris has also heard that there is a statement of owners equity, but she is not familiar with that statement. She asks if you can help her prepare one. After confirming that she has no assets other than cash, no liabilities, and made no additional investments in the business in August, you agree. REQUIRED 1. Prepare the statement of owners equity for your friends most recent month. 2. What suggestions might you give to Chris that would make her income statement more useful?arrow_forwardCORRECTING WORK SHEET WITH ERRORS A beginning accounting student tried to complete a work sheet for Dick Adys Bookkeeping Service. The following adjusting entries were to have been analyzed and entered in the work sheet: (a) Ending inventory of supplies on July 31, 130. (b) Unexpired insurance on July 31, 420. (c) Depreciation of office equipment, 325. (d) Wages earned, but not paid as of July 31, 95. REQUIRED Review the work sheet shown on page 174 for addition mistakes, transpositions, and other errors and make all necessary corrections.arrow_forwardClint Stillmore operates a private investigating agency called Stillmore Investigations. Some clients pay in advance for services; others are billed after services have been performed. Advance payments are credited to an account entitled Unearned Retainer Fees. Adjusting entries are performed on a monthly An unadjusted trial balance dated December 31, 2011, follows. (Bear in mind that adjusting entries have already been made for the first 11 months of 2011, but not for December.) Other Data Accrued but unrecorded client fees earned at December 31 amount to $2,500. Records show that $3,500 of cash receipts originally recorded as Unearned Retainer Fees had been earned as of December 31. Office supplies on hand at December 31 amount to $50. The company purchased all of its office equipment when it first began business. At that time, the equipment’s estimated useful life was six years (or 72 months). On October 1, 2011, the company renewed its rental agreement…arrow_forward
- For The DR Consulting Company you are given the following Unadjusted Trial Balance at the end of December, the second month of business. You are also given the information for adjusting entries. Prepare the necessary adjusting entries at the end of the second month presuming no adjusting entries were done at the end of November. If additional information does not require an adjusting entry, input "No transaction needed" in the first line of the journal entry. Account Debit Credit Cash $ 29,655 Accounts receivable 2,800 Interest receivable 0 Supplies 19,670 Prepaid insurance 3,420 Notes receivable 12,000 Land 100,000 Buildings 216,000 Equipment 129,600 Accumulated Depreciation - Buildings $ 0 Accumulated Depreciation - Equipment 0 Account payable 7,200 Salaries payable 0 Interest payable 0 Income tax payable 1,500 Unearned revenue 3,325 Notes payable 177,000 Common stock 309,000 Retained earnings…arrow_forwardAfter the accounts have been adjusted at January 31, the end of the year, the following balances are taken from the ledger of Harrison's Dog Walking Service Company: Harrison Taylor, Capital $348,580 Harrison Taylor, Drawing 12,760 Fees Earned 121,280 Wages Expense 42,100 Rent Expense 13,690 Supplies Expense 14,830 Miscellaneous Expense 2,150 Journalize the entries required to close the accounts. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. Jan. 31 - Select - - Select - - Select - - Select - - Select - - Select - - Select - - Select - - Select - - Select - - Select - - Select - Jan. 31 - Select - - Select - - Select - - Select -arrow_forward[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Tunstall, Inc., a small service company, keeps its records without the help of an accountant. After much effort, an outside accountant prepared the following unadjusted trial balance as of the end of the annual accounting period on December 31: Tunstall, Inc.Unadjusted Trial Balancefor the Year Ended December 31 Debit Credit Cash 46,800 Accounts receivable 11,700 Supplies 550 Prepaid insurance 630 Service trucks 16,300 Accumulated depreciation 8,400 Other assets 9,860 Accounts payable 2,220 Wages payable Income taxes payable Notes payable, long-term 15,000 Common stock (4,100 shares outstanding) 1,936 Additional paid-in capital 17,424 Retained earnings 4,600 Service revenue 85,680 Wages…arrow_forward
- Prepare adjusting journal entries, as needed, for the following items. (a) The Supplies account shows a balance of $500, but a count of supplies reveals only $200 on hand at year-end. (b) The company initially records the payments of all insurance premiums as prepaid insurance. The unadjusted trial balance at year-end shows a balance of $500 in Prepaid Insurance. A review of insurance policies reveals that $100 of insurance is unexpired. (c) Employees work Monday through Friday, and salaries of $2,500 per week are paid each Friday. The company's year-end falls on Tuesday. (d) At year-end, the company received a utility bill for December's electricity usage of $200 that will be paid in early January.arrow_forwardAzure Enterprises follows a manual accounting system. During the current fiscal year, it bought a car for $30,390. The accountant of Azure correctly journalized the transaction but wrongly entered the amount as $30,930. To make a correction of this error, the accountant should: a.draw a single line through the amount $30,930 and record the correct amount $30,390 above it. b.reverse the original entry and record the correct entry. c.erase the amount of $30,930 and record the correct amount of $30,390 in the same place. d.cross the amount of $30,930 and record the correct amount of $30,390 below it.arrow_forwardAfter the accounts have been adjusted at April 30, the end of the fiscal year, the following balances were taken from the ledger of Twin Trees Landscaping Co.: Oscar Killingsworth, Capital $503,900 Oscar Killingsworth, Drawing 8,200 Fees Earned 279,100 Wages Expense 221,600 Rent Expense 43,800 Supplies Expense 9,000 Miscellaneous Expense 10,200 Journalize the two entries required to close the accounts. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank.arrow_forward
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage LearningCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage LearningCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub





