
Subpart (a):
The consumer surplus , total surplus and deadweight loss .
Subpart (a):
Explanation of Solution
Figure -1 illustrates the
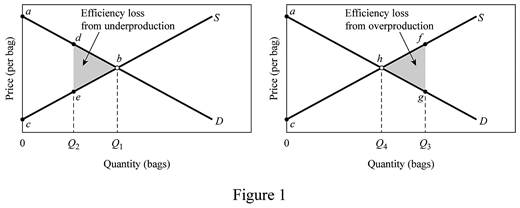
In figure -1 panel (a) and (b), the horizontal axis measures the quantity of bags and the vertical axis measures the price per bag. The curve ‘S’ represents the supply and the curve ‘D’ represents the demand.
The inverse demand function can be derived as follows:
The inverse demand functions of
The inverse supply curve can be calculated as follows:
The inverse supply functions of
The inverse demand function and supply functions reveal that the producer willing price is $5 and the consumer willing price is $85. The equilibrium price is $45. The total surplus can be calculated as follows:
The total surplus is $800.
The consumer surplus can be calculated as follows:
The consumer surplus is $400.
Concept Introduction:
Consumer surplus: It refers to the variation in the probable charge of a product that the consumer intends to pay and the actual price that he has already paid.
Subpart (b):
The consumer surplus, total surplus and deadweight loss.
Subpart (b):
Explanation of Solution
The consumer willing price at Q2 level of output (15 units) can be calculated by substituting the Q2 level of output to the inverse demand function.
The consumer new willing price is $55.
The producer willing price at Q2 level of output (15 units) can be calculated by substituting the Q2 level of output into the inverse supply function.
The producer’s new willing price is $35.
The deadweight loss can be calculated as follows:
The deadweight loss is $50.
The total surplus can be calculated as follows:
The total surplus is $750.
Concept Introduction:
Consumer surplus: It refers to the variation in the probable charge of a product that the consumer intends to pay and the actual price that he has already paid.
Producer surplus: It refers to the variation in the probable price that the producer intends to sell and the actual price that he has already sold.
Subpart c):
The consumer surplus, total surplus and deadweight loss.
Subpart c):
Explanation of Solution
The consumer willing price at Q3 level of output (27 units) can be calculated by substituting the Q3 level of output to the inverse demand function.
The consumer new willing price is $31.
The producer willing price at Q3 level of output (127 units) can be calculated by substituting the Q3 level of output to the inverse supply function.
The producer new willing price is $59.
The deadweight loss can be calculated as follows:
The deadweight loss is $98.
The total surplus can be calculated as follows:
The total surplus is $702.
Concept Introduction:
Consumer surplus: It refers to the variation in the probable charge of a product that the consumer intends to pay and the actual price that he has already paid.
Producer surplus: It refers to the variation in the probable price that the producer intends to sell and the actual price that he has already sold.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Microeconomics: Principles Problems & Policies (McGraw-Hill Series in Economics)
- Given- Qd=1000−25pQs=−200+5p A)What is the equilibrium price and quantity B)Graph these functions. Show where equilibrium price and quantity are. Show x and y intercepts C)What is the new equilibrium price if there is 5 peso tax per unit? D)What is the new equilibrium if there is a 3 peso subsidy per unit? (no tax applied here) E)Explain the welfare effects of taxes and subsidies based on equilibrium quantities and prices.arrow_forwardSuppose that there are three beachfront parcels of land available for sale in Asilomar and six people who would each like to purchase one parcel. Assume that the parcels are essentially identical and that the minimum selling price of each is $745,000. The following table states each person's willingness and ability to purchase a parcel. Person Willingness and Ability to Purchase (Dollars) Charles 900,000 Dina 810,000 Gilberto 770,000 Juanita 720,000 Lorenzo 690,000 Neha 680,000 Which of these people will buy one of the three beachfront parcels? Check all that apply. Charles Dina Gilberto Juanita Lorenzo Neha Assume that the three beachfront parcels are sold to the people that you indicated in the previous section. Suppose that a few days after the last of those beachfront parcels is sold, another essentially identical beachfront parcel becomes available for sale at a minimum price of $732,500. This fourth…arrow_forwardEnvironmental Crime and Punishment Economists tend to view the decision by an individual to comply with an environmental law in terms of economic motivations. While good citizenship—obeying the law simply because it is the law—certainly plays a role in affecting behavior, it is also useful to analyze compliance decisions in terms of benefits and costs. Figure 14.3 illustrates a hypothetical marginal cost–marginal benefit analysis for a manager in a coal-fired power plant who has to decide what percentage of the time he or she plans to be in compliance with the sulfur dioxide emission standards on his or her state permit. The benefits that come from complying with environmental laws are essentially the avoided costs of punishment: monetary costs (fines and penalties), a damaged reputation (both for corporations and individuals), and the fear of jail terms. The expected benefits depend on two factors: the magnitude of the punishment if imposed and the likelihood of…arrow_forward
- Table 10-1 Quantity (Units) Private Value (Dollars) Private Cost (Dollars) External Cost (Dollars) 1 28 16 4 2 26 18 4 3 24 20 4 4 22 22 4 5 20 24 4 6 18 26 4 7 16 28 4 Refer to Table 10-1. What is the equilibrium quantity of output in the market? Group of answer choices 3 units 2 units 5 units 4 unitsarrow_forward16. How prices allocate resources Suppose that there are three plots of mountain resort land available for sale in Niseko and six potential buyers, each interested in purchasing one plot. Assume that all of the plots are basically indistinguishable and that the minimum selling price of each is $400,000. The following table lists each potential buyer's willingness and ability to purchase a plot of land. Person Willingness and Ability to Purchase (Dollars) Felix 550,000 Janet 480,000 Larry 420,000 Megan 380,000 Raphael 340,000 Susan 330,000 Which of these people will purchase one of the three mountain resort plots? Check all that apply. Felix Janet Larry Megan Raphael Susan Now, assume that the three mountain plots have been sold to the people that you Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism.Answer completely.You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forward10. A social indifference curve showsa . all allocations that yield the same total utility to individuals in the society.b. social attitudes toward equity.c. social attitudes toward efficiency.d. social utility possibilities as a function of resources.arrow_forward
- -Suppose the market-equilibrium quantity of good x is larger than the socially-optimal quantity of good x. Does the production of good x convey a positive externality or does it convey a negative externality?arrow_forwardConversely, show geometrically the effect of a decrease in Price (i.e., BELOW the equilibrium price). What “economic problem” is created now in the market. Measure geometrically he magnitude or distance of such “economic problem”. Again, in the face of such an economic problem, where private sector buyers and suppliers could not do anything more, which economic actor should come to intervene properly? Discuss what should that intervener do amidst such economic problem faced by the microeconomic actor – NOTABLY THE PRODUCER OR SELLER. As an Economist (or beyond the limits of Economic studies), what would you recommend to the VEGETABLE PRODUCERS and to the GOVERNMENT as well? Discuss exhaustively.arrow_forwarda) Suppose that in the production of computer software, the marginal rate of technical substitution between engineers and marketer is 5 for IBM and 3 for Microsoft. Explain why this outcome violates the condition for efficiency in production and how a voluntary exchange could make both companies better off. b) Ignoring rationing problems and black markets, under rent control (or any price ceiling that produces a shortage) the price paid by consumers equals the marginal cost of producing the good. Does this mean the output level is efficient? Explain. c) What does the contract curve in an Edgeworth production box signify? Why do competitive markets generate equilibriums that lie on the contract curve?arrow_forward
- -When should a private good be produced from an efficiency standpoint? a-When the sum of all of society’s marginal benefit exceeds the marginal cost b-When the marginal benefit from consumption exceeds the marginal cost c-When the marginal cost exceeds the marginal benefit from consumption d-When the marginal cost exceeds the sum of all of society’s marginal benefit -Suppose the government provides some amount of a public good, but it results in a reduction of private market’s production of the good by the same amount as the government produced. In this case, a-the warm glow effect caused an increase in the net amount of the public good. b-private provision is fully crowded out. c-private provision is partially crowded out. d-private provision is not crowded out.arrow_forward2.- Assume that consumers are uniformly distributed along a one-mile stretch of a beach. N ice cream vendors are pondering where to position their carts. The price that they are allowed to charge is fixed by the EACAC (Equal Access to Coolness for All Coalition). (Also, each consumer will buy exactly one ice cream.) (a) Show that there is no equilibrium (in locations) if N=3. (b) Suppose N=5 and vendors position their cart each at one of the (mile) points ( 1/6, 2/6, 3/6, 4/6, 5/6 ) is that an equilibrium?arrow_forward7-) We add the demands of private goods horizontally but add the demands of public goods vertically when determining the associated marginal benefit to society. Why do we do this and why are the procedures different for public and private goods?arrow_forward
 Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305971493Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305971493Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning





