
A Thomson-type experiment with relativistic electrons. One of the earliest experiments to show that p = γmv (rather than p = mv) was that of Neumann. [G. Neumann, Ann. Physik 45:529 (1914)]. The apparatus shown in Figure P4.5 is identical to Thomson’s except that the source of high-speed electrons is a radioactive radium source and the magnetic field B is arranged to act on the electron over its entire trajectory from source to detector. The combined electric and magnetic fields act as a velocity selector, only passing electrons with speed v, where v = V/Bd (Equation 4.6), while in the region where there is only a magnetic field the electron moves in a circle of radius r, with r given by p = Bre. This latter region (E = 0, B = constant) acts as a momentum selector because electrons with larger momenta have paths with larger radii. (a) Show that the radius of the circle described by the electron is given by r = (l2 + y2)/2y. (b) Typical values for the Neumann experiment were d = 2.51 × 10−4 m, B = 0.0177 T, and l = 0.0247 m. For V = 1060 V, y, the most critical value, was measured to be 0.0024 ± 0.0005 m. Show that these values disagree with the y value calculated from p = mv but agree with the y value calculated from p = γmv within experimental error. (Hint: Find v from Equation 4.6, use mv = Bre or γmv = Bre to find r, and use r to find y.)
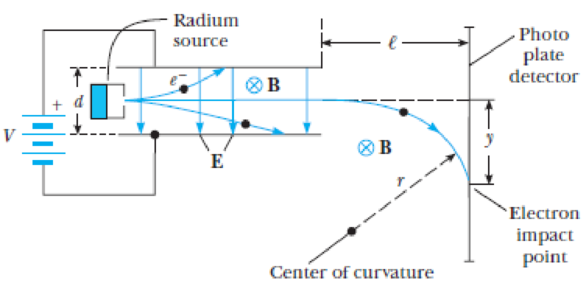
Figure P4.5 The Neumann apparatus.
(a)
To show that the radius of the circle described by th electron is given by
Answer to Problem 5P
It is showed that the radius of the circle described by th electron is given by
Explanation of Solution
The curved path of the electron is shown in figure 1.
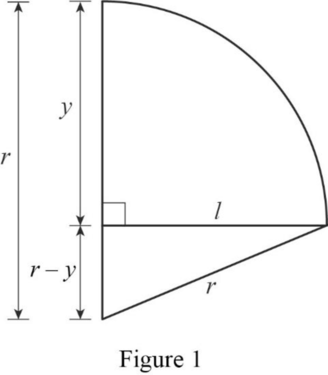
Write the equation for the curved path of the electron.
Here,
Rewrite the above equation.
Rewrite the above equation for
Conclusion:
Therefore, it is showed that the radius of the circle described by th electron is given by
(b)
To show that the value of
Answer to Problem 5P
It is showed that the calculated that the value of
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation for the velocity of the electron.
Here,
Write the equation for the momentum of the electron.
Here,
Write the classical expression for the momentum of a particle.
Here,
Equate equations (III) and (IV) and rewrite it for
Write the relativistic equation for the momentum of the particle.
Here,
Equate equations (III) and (VI) and rewrite it for
Write the equation for the Lorentz factor.
Here,
Put the above equation in equation (VII).
Write the equation for the root of a quadratic equation
Conclusion:
The mass of the electron is
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Comparison of the above equation with the quadratic equation
Substitute
The value
The value
Substitute
Substitute
Comparison of the above equation with the quadratic equation
Substitute
The value
The value
Therefore, it is showed that the calculated that the value of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK MODERN PHYSICS
- If the wavelength of an electron is 5.00 x 10-7 m, how fast is it moving? (b) If the electron has a speed equal to 1.00 x 107 m/s, what is its wavelength?arrow_forwardUV radiation having a wavelength of 84 nm falls on gold metal, to which electrons are bound by 4.82 eV. What is the maximum velocity of the ejected photoelectrons? No need to use relativistic formulas in this case, so you can just use the standard formula KE =12mv2. The correct answer is 1.87E6 m/s how do I get that?arrow_forwardWhat is the relation between the de Broglie wavelength λ, mass m, and kinetic energy K for (a) a lowenergy proton, and (b) a very high energy proton?arrow_forward
- What is the magnitude of the spin momentum of an electron? (Express you answer in terms of h.)arrow_forwardA 900-W microwave generator in an oven generates energy quanta of frequency 2560 MHz. (a) How many energy quanta does it emit per second? (b) How many energy quanta must be absorbed by a pasta dish placed in the radiation cavity to increase its temperature by 45.0 K? Assume that the dish has a mass of 0.5 kg and that its specific heat is 0.9 kcal/kg • K. (c) Assume that all energy quanta emitted by the generator are absorbed by the pasta dish. How long must we wait until the dish in (b) is ready?arrow_forward(a) What is the uncertainty in the energy released in the decay of a due to its short lifetime? (b) What traction of the decay energy is this, noting that the decay mode is (so that all the mass is destroyed)?arrow_forward
- Treat the human body as a blackbody and determine the percentage increase in the total power of its radiation when its temperature increases from 98.6 °F to 103 ° F.arrow_forwardA laser emits a pulse of light that lasts 10 ns. The light has a wavelength of 690 nm, and each pulse has an energy of 480 mJ. How many photons are emitted in each pulse? Let 1 eV = 1.60 × 10−19 J, the mass of an electron m = 9.11 × 10−31 kg, the speed of light c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, and Planck’s constant h = 4.136 × 10−15 eV ∙ s.arrow_forwardWhen an electron is accelerated through a potential difference Δφ it acquires a kinetic energy e Δφ. Calculate the momentum, and hence the de Broglie wavelength, of an electron accelerated from rest through (a) 1.00V, (b) 1.00 kV, (c) 100 kV.arrow_forward
- A muon, or mu meson, has the same charge as an electron, but is 207 times as massive. a) Compared with electron-positron pair production, the pair production of a muon and antimuon requires a photon of what energy? E = _____ MeV b) What would be the minimum frequency for such a photon? f = _________ Hzarrow_forwardElectrons accelerated to an energy of 50 GeV have a de Broglie wavelength l small enough for them to probe the structure within a target nucleus by scattering from the structure. Assume that the energy is so large that the extreme relativistic relation p = E/c between momentum magnitude p and energy E applies. (In this extreme situation, the kinetic energy of an electron is much greater than its rest energy.) (a)What is l? (b) If the target nucleus has radius R = 5.0 fm, what is the ratio R/l?arrow_forwardImagine another universe in which the value of Planck’s constant is 0.0663 J . s, but in which the physical laws and all other physical constants are the same as in our universe. In this universe, two physics students are playing catch. They are 12 m apart, and one throws a 0.25 kg ball directly toward the other with a speed of 6.0 m/s. (a) What is the uncertainty in the ball’s horizontal momentum, in a direction perpendicular to that in which it is being thrown, if the student throwing the ball knows that it is located within a cube with volume 125 cm3 at the time she throws it? (b) By what horizontal distance could the ball miss the second student?arrow_forward
 Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College





