
A T-shaped board of uniform mass density has two small holes as shown. Initially, the pivot is placedthrough the right hole, which corresponds to the center of mass of the board. The board ¡s then held in place.
1. Predict the motion of the board after it is released from rest, Explain.
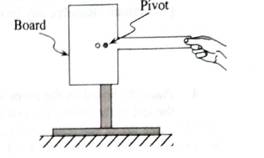
2. Check your prediction by observing the demonstration.
a. Describe the
What does your answer imply about the ne, torque about the pivot? Explain.
b. Describe the acceleration of the center of mass of the board. Explain how you can tell.
What does your answer imply about the net force acting on the board? Explain.
3. Explain how your answers about net torque and net force in question 2 would change, if at all, if there is appreciable friction between the board and the pivot and the board remains at rest.
(1)
To Predict: The motion of the board.
Answer to Problem 1aT
The board will perform a circular repetitive motion.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
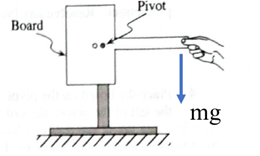
Gravitational force is acting downward on the edge of the handle.
Formula used:
Calculation:
Conclusion:
The gravitational force at the edge of the handle leads to produce torque using equation in formula. r is the distance between the edge of the handle and the pivot around which the board will rotate. Angle between r and force is 90 degree.
(2)
To Describe: The angular acceleration of the board, acceleration of the center of mass and the net torque about the pivot.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
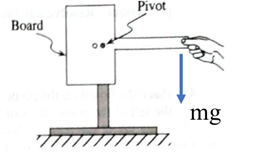
Formula used:
Where, I is the moment of inertia and
Calculation:
From part 1, the net torque is
From the rotational equation of motion:
On comparing both the equations:
The center of mass of the board lies on the axis of rotation, therefore, the acceleration of the center of mass is zero.
The net torque is
Conclusion:
Hence, the angular acceleration is
(3)
The effect of friction on the torque and force.
Answer to Problem 1aT
The net torque and force will be reduced due to friction in effect.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Gravitational force is acting downward on the edge of the handle.
Formula used:
Calculation:
Conclusion:
The frictional force acts opposite to the motion of the object. Hence, net force and torque are reduced which eventually reduces the angular acceleration and linear acceleration.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
University Physics Volume 2
Conceptual Physical Science (6th Edition)
The Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals (2nd Edition)
Life in the Universe (4th Edition)
- Right hand rule questions a. What direction is angular momentum for the vectors shown? b. What direction is the angular momentum for the wheel?arrow_forwardAn 8.79cm diameter floppy disk rotates at its fastest at 470 rpm. Part A: Express the angular velocity of the disk in revolutions per seconds? Part B: What is the time period of this revolution? Use scientific notation for your answer. Part C: What is the linear velocity of a point at the rim of the disk? What is the angular velocity at the center of the disk? If the disk took 3.2 sec to spin up to 470 rpm from rest, what was the average angular acceleration? How many revolutions did the disk complete within this time? What is the net displacement? If you turn off the floppy disk drive and the disk comes to a stop in 6.7 s, what is the average angular acceleration for this period of motion?arrow_forwardA solid, uniform disk of mass M and radius a may be rotated about any axis parallel to the disk axis, at variable distances from the center of the disk. (Figure 1) If you use this disk as a pendulum bob, what is T(d), the period of the pendulum, if the axis is a distance d from the center of mass of the disk? Express the period of the pendulum in terms of given variables. What is Tmin, the minimum period of the pendulum? Your answer for the minimum period should include given variables.arrow_forward
- An 8.79cm diameter floppy disk rotates at its fastest at 470 rpm. Part A: Express the angular velocity of the disk in revolutions per seconds? Part B: What is the time period of this revolution? Use scientific notation for your answer. Part C: What is the linear velocity of a point at the rim of the disk? Part D: What is the angular velocity at the center of the disk? Part E: If the disk took 3.2 sec to spin up to 470 rpm from rest, what was the average angular acceleration? How many revolutions did the disk complete within this time? What is the net displacement? Part F: If you turn off the floppy disk drive and the disk comes to a stop in 6.7 s, what is the average angular acceleration for this period of motion?arrow_forwardConsider a bar, of length 4.5 m, shown in the figure, is constrained to rotate about its left end. In addition to the force exerted at the left end responsible for this constraint, three forces are acting on the bar that generate torques. The magnitudes of the first two forces are 11 N and 25 N, and the first force is acting on the end of the bar at an angle of 49° as shown. a. What is the torque, in newton-meters, due to F1 on this bar relative to the left end? Use a coordinate system with positive directed out of the screen. b. What is the torque, in newton-meters, due to F2 on this bar relative to the left end, if this force is acting at the midpoint of the bar? Use a coordinate system with positive directed out of the screen. c. What is the magnitude of the force F3, in newtons, if the force is a distance 0.65 m from the left end and the bar is not rotating?arrow_forwardAfter fixing a flat tire on a bicycle you give the wheel a spin. (a) Ifits initial angular speed was 6.35 rad>s and it rotated 14.2 revolutions before coming to rest, what was its average angular acceleration? (b) For what length of time did the wheel rotate?arrow_forward
- A car starts from rest and in 75 seconds it travels 1 mile. The wheels of the car have a diameter of 30 inches. Show all work and any unit conversions step by step. a) How many revolutions did the wheel make in that 1 mile distance?b) What was the final linear velocity of the car after the 75 seconds in units of feet per second?c) What was the final angular velocity of a point on the outer edge of the wheels in units of rpm?arrow_forwardPart E: What is the angular displacement in degrees of ladybug B during a time interval of 0.7 s? Express your answer in degrees to two significant figures.arrow_forwardA horizontal 4.0 m long 5.0 N uniform bar at one end is attached to a wall by a frictionless hinge; and at the middle of the bar there is a vertical cable pulling down 7.0 N, and at the middle of the bar there is also a cable that is at 45 ° to the horizontal pulling up as shown. ii) What is the magnitude of the horizontal component of the force on the bar due to the hinge?arrow_forward
- A system of three point particles of equal masses 45 gm are initially connected by three rods of negligible mass to an axis of rotation perpendicular to the plane of the particles as shown in the figure-1.(a) What is the moment of inertia of the system of three particles?(b) If the massless rods are replaced by three rods of equal masses of 65 gm keepingtheir lengths unchanged, what is the moment of inertia of the system now?(c) If the systems rotate at 4.75 rev/s, what are the systems rotational kineticenergies?arrow_forwardConsider a bar, of length 5.5 m, shown in the figure, being acted on by three forces. The magnitudes of the first two forces are 23 N and 28 N, and the first force is acting on the end of the bar at an angle of 54° as shown. a)What is the torque, in newton-meters, due to F1 on this bar relative to the left end? Use a coordinate system with positive directed out of the screen. b)What is the torque, in newton-meters, due to F2 on this bar relative to the left end, if this force is acting at the midpoint of the bar? Use a coordinate system with positive directed out of the screen. c)What is the magnitude of the force F3, in newtons, if the force is a distance 0.65 m from the left end and the bar is not rotating?arrow_forwardAnswer the following questions given the picture. Please show clear solutions, I want to learn how to solve the problem. 1a. Which of the following is the angular acceleration of the ball? A) 116.8 rad/s2 clockwise B) 2.08 rad/s2 counterclockwise C) 25.03 rad/s2 counterclockwise D) 50.1 rad/s2 counterclockwise 1b. Which of the following describes the motion of the ball? (explain your answer)A) Rolling with slidingB) Not movingC) Rolling without slidingD) Rolling and impending to slidearrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

