
Concept explainers
A well-insulated 3-m × 4–m × 6-m room initially at 7°C is heated by the radiator of a steam heating system. The radiator has a volume of 15 L and is filled with superheated vapor at 200 kPa and 200°C. At this moment both the inlet and the exit valves to the radiator are closed. A 120-W fan is used to distribute the air in the room. The pressure of the steam is observed to drop to 100 kPa after 45 min as a result of heat transfer to the room. Assuming constant specific heats for air at room temperature, determine the average temperature of air in 45 min. Assume the air pressure in the room remains constant at 100 kPa.
FIGURE P4–136
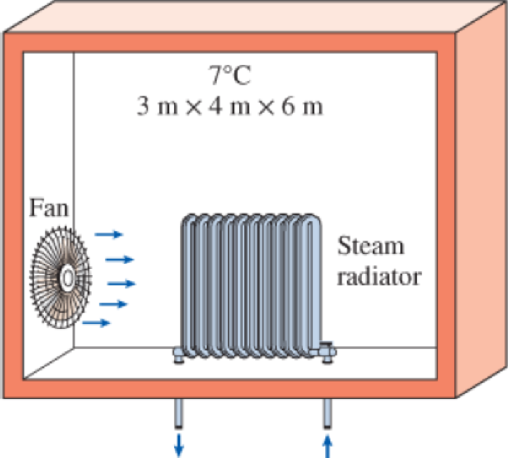
The average temperature of air in 45 min.
Answer to Problem 136RP
The average temperature of air in 45 min is
Explanation of Solution
Show the free body diagram of the well-insulated room.
Write the expression for the energy balance equation.
Here, the total energy entering the system is
Substitute
Here, the mass is
From the Table (A-4 through A-6), obtain the value of specific volume, specific internal energy at the initial and the final states.
At initial pressure and temperature of
At final pressure of
Write the expression for final quality at the final state.
Here, the specific volume of saturated liquid is
Write the expression for final specific internal energy of a well-insulated room.
Here, the specific internal energy of saturated liquid is
Write the expression for total mass of a well-insulated room.
Here, the initial specific volume is
Write expression for the volume of the well-insulated room.
Write the expression of mass of air in a well-insulated room.
Here, the initial pressure is
Write the expression for amount of fan work done in 45 min.
Conclusion:
Here, the specific volume
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
For well-insulated room the energy balance equation.\
Substitute
Express the change in internal energy and boundary work into the constant pressure expansion and compression in Equation (IX).
Here, the rate of heat transfer entering is
Substitute
Therefore, the well-insulated room temperature rises from
Thus, the average temperature of air in 45 min is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
- Steam enters an adiabatic turbine at 5 MPa, 650C, and 80 m/s and leaves at 50 kPa, 1508C, and 140 m/s. If the power output of the turbine is 8 MW, determine (a) the mass flow rate of the steam flowing through the turbine and (b) the isentropic efficiency of the turbine.arrow_forwardRefrigerant-134a at 140 kPa and 210C is compressed by an adiabatic 1.3-kW compressor to an exit state of 700 kPa and 60C. Neglecting the changes in kinetic and potential energies, determine (a) the isentropic efficiency of the compressor, (b) the volume flow rate of the refrigerant at the compressor inlet, in L/min, and (c) the maximum volume flow rate at the inlet conditions that this adiabatic 1.3-kW compressor can handle without violating the second law.arrow_forwardWhat is the minimum internal energy that steam can achieve as it is expanded adiabatically in a closed system from 1500 kPa and 320°C to 100 kPa?arrow_forward
- Steam enters an adiabatic turbine steadily at 7 MPa, 500°C, and 45 m/s and leaves at 100 kPa and 75 m/s. If the power output of the turbine is 5 MW and the isentropic efficiency is 77 percent, determine the temperature at the turbine exit.arrow_forwardSuperheated steam enters the turbine of a steam power plant at 5 MPa and 450 ºC, and exits at 10 kPa. Determine the actual turbine work when the turbine isentropic efficiency is 90% and the mass flow rate of steam is 10 kg/s.arrow_forwardA 0.05-m3 rigid tank initially contains refrigerant134a at 0.8 MPa and 100 percent quality. The tank is connected by a valve to a supply line that carries refrigerant-134a at 1.2 MPa and 40°C. Now the valve is opened, and the refrigerant is allowed to enter the tank. The valve is closed when it is observed that the tank contains saturated liquid at 1.2 MPa. Determine the mass of the refrigerant that has entered the tankarrow_forward
- Saturated refrigerant-134a vapor at 15 psia is compressed reversibly in an adiabatic compressor to 80 psia. Determine the work input to the compressor. What would your answer be if the refrigerant were first condensed at constant pressure before it was compressed?arrow_forwardSteam at 100 psia and 650F is expanded adiabatically in a closed system to 10 psia. Determine the work produced, in Btu/lbm, and the final temperature of steam for an isentropic expansion efficiency of 80 percent.arrow_forwardSteam expands in a turbine steadily at a rate of 18,000 kg/h, entering at 7 MPa and 600°C and leaving at 50 kPa as saturated vapor. Assuming the surroundings to be at 100 kPa and 25°C, determine the power output of the turbine if there were no irreversibilities present.arrow_forward
- Argon gas enters an adiabatic compressor at 14 psia and 75°F with a velocity of 60 ft/s, and it exits at 200 psia and 240 ft/s. If the isentropic efficiency of the compressor is 87 percent, determine the exit temperature of the argon.arrow_forwardOn a P-v diagram, what does the area under the process curve represent?arrow_forwardAn adiabatic diffuser at the inlet of a jet engine increases the pressure of the air that enters the diffuser at 11 psia and 30°F to 20 psia. What will the air velocity at the diffuser exit be if the diffuser isentropic efficiency, defined as the ratio of the actual kinetic energy change to the isentropic kinetic energy change, is 82 percent and the diffuser inlet velocity is 1200 ft/s?arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





