
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781305389892
Author: Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 46, Problem 2ITD
Summary Introduction
To review:
Whether the data given below suggest the protective effect of lycopene against tobacco’s effect. The data are represented by the graph shown below:
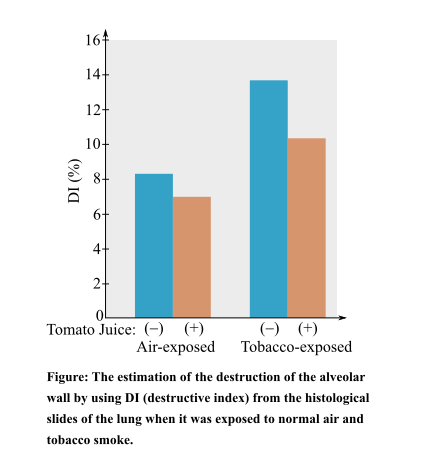
Introduction:
Lycopene is a carotenoid pigment found in tomatoes, carrots, watermelons, and papayas. It is a good source of vitamin C and is a powerful antioxidant. It is assumed to impart benefits by protecting against different types of cancers.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Dipal mitoylphosphatidylcholine is the major component of surfactant, or surface active agent (an amphipathic molecule), that is secreted into lung alveoli to reduce the surface tension of the primarily aqueous extracellular fluid of the alveolar epithelia. Alveoli, also referred to as alveolar sacs, are the functional units of respiration. Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse across the walls of alveolar sacs, which are one cell thick. The water on alveolar surfaces has a high surface tension because of the attractive forces between the molecules. If the water’s surface tension is not reduced, the alveolar sac tends to collapse, making breathing extremely difficult. If premature infants lack sufficient surfactant, they are likely to die of suffocation. This condition is called respiratory distress syndrome. Draw the structure of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine. Considering the general structural features of phospholipids, propose a reason why surfactant is effective in reducing surface…
After spending a day or more at high altitude (with an oxygen partial pressure of 75 torr), the concentration of 2,3- bisphosphoglycerate (2,3-BPG) in red blood cells increases. What effect would an increased concentration of 2,3-BPG have on the oxygen-binding curve for hemoglobin? Why would this adaptation be beneficial for functioning well at high altitude?
In carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning, CO binds to hemoglobin, therebydecreasing the uptake of O2 by hemoglobin. In addition, when CO bindsto hemoglobin, the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve shifts to theleft. How does this shift affect the ability of tissues to get O2? Explain
Chapter 46 Solutions
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 46.1 - Distinguish between the roles of the respiratory...Ch. 46.1 - What is an advantage of water over air as a...Ch. 46.2 - What advantages do gills confer on a...Ch. 46.2 - Prob. 2SBCh. 46.2 - Prob. 3SBCh. 46.2 - Distinguish between positive pressure breathing...Ch. 46.3 - Prob. 1SBCh. 46.3 - Prob. 2SBCh. 46.3 - Prob. 3SBCh. 46.4 - Explain the role of hemoglobin in gas exchange.
Ch. 46.4 - Prob. 2SBCh. 46.5 - What are the key evolutionary adaptations that...Ch. 46 - Prob. 1TYKCh. 46 - Prob. 2TYKCh. 46 - Prob. 3TYKCh. 46 - Prob. 4TYKCh. 46 - Prob. 5TYKCh. 46 - Prob. 6TYKCh. 46 - Prob. 7TYKCh. 46 - Oxygen enters the blood in the lungs because...Ch. 46 - Prob. 9TYKCh. 46 - Prob. 10TYKCh. 46 - Prob. 11TYKCh. 46 - Prob. 12TYKCh. 46 - Prob. 13TYKCh. 46 - Prob. 14TYKCh. 46 - Prob. 15TYKCh. 46 - Lycopene, which is abundant in tomatoes, is...Ch. 46 - Prob. 2ITD
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Fig. 2.1 shows photomicrographs of lung tissue at the same magnification. One shows healthylung tissue and the other shows lung tissue from a person with COPD. Line AB shows the diameter of one healthy alveolus. Line CD shows the diameter of an area oflung where the alveoli have been destroyed. The real diameter of healthy alveolus is 200 µm.If line AB in the picture is 2 cm, calculate the magnification of the picture...... Magnification: …………………… please solve with step max 15-20 minutes and no reject thank uarrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is CORRECT? Select one: a. Reduction of atmospheric air pressure increases alveolar PO2. b. Reduction of plasma protein in blood increases alveolar PO2. c. Increase in ventilation increases alveolar PO2. d. Increase in metabolism increases alveolar PO2. e. Increase in the amount of hemoglobin increases arterial PO2arrow_forwardThe partial pressure of oxygen in the venous blood of a human at rest at sea level is approximately 40 torrs a.) Calculate the fractional saturation of hemoglobin under these conditionsb.) What percentage of the oxygen originally bound to hemoglobin in the alveoli remained unreleased?c.) Is the residual oxygen bound to hemoglobin under these conditions of any benefit? Explainarrow_forward
- Patients with severe cases of COVID-19 (the disease caused by the coronavirus) may not be able to breathe on their own and so need mechanical ventilation. This condition occurs when the virus attacks the lining of the lungs, resulting in a buildup of fluid and dead cells in the alveoli. Using your knowledge of the anatomy and function of human lungs, explain why this condition makes it difficult for adequate gas exchange to occur.arrow_forwardIn addition to O2 binding, changes in other chemical conditions can result in changes in hemoglobin structure and function. Increases in blood H+ result in oxygen binding curves for hemoglobin that are shifted to the right. The effect of H+ can be understood in terms of the equilibrium:H-Hb+ + O2 → Hb-O2 + H+How does the difference in pH in the lungs and tissues help hemoglobin do its job of delivering oxygen? Use the equilibrium equation in your argument.arrow_forwardHydrogen bonding between water molecules is essential for lung expansion to occur, but also increases resistance during inspiration. Explain this contrast by describing the locations and how hydrogen bonding plays a positive and negative role in ventilation. Draw a diagram of the lung to show these opposing forces What would happen if intrapleural pressure(IPP) equaled atmospheric pressure (AtmP)? How could this happen?arrow_forward
- In the lungs of mammals, airways branch into a series of narrowing tubes that end in Alveoli. How does gas exchange occur between alveoli and blood capillaries?arrow_forwardExplain why the gas values from the alveolar air to the blood change during pulmonary gas exchange. For example: Alveolar air for CO2 has a value of 40mmHg then when entering the blood shifts to 45mmHg. Why does this occur? I tried to calculate this by using Dalton’s law but I’m not Understanding.arrow_forwardDo the following conditions cause hemoglobin to release more O2 to the tissues or to absorb more O2?(a) Raising the temperature(b) Increased production of CO2(c) Increasing the H+ concentrationarrow_forward
- Describe the airway of Emmett who is having an asthma attack. What would be the desired effect of treating this patient with medications such as beta2-agonists and corticosteroids?arrow_forwardWhat properties of air make it possible for humans and other mammals to breathe by tidal ventilation?arrow_forwardUse the table provided to show that the air travels a total distance of 273 mm from the trachea to the alveoli.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Cancer Types SIMPLY explained! MEMORIZE them QUICKLY and EASILY!; Author: CancerEdInstitute;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dEBi-yvSWmQ;License: Standard Youtube License