
Concept explainers
Inventory
Inventory refers to the stock or goods which will be sold in the near future and thus is an asset for the company. It comprises of the raw materials which are yet to be processed, the stock which is still going through the process of production and it also includes completed products that are ready for sale. Thus inventory is the biggest and the important source of income and profit for the business.
Perpetual Inventory System
In perpetual inventory system there is a continuous recording of transactions as and when they take place that is purchase and sale transactions are recorded whenever they occur.
Cost of Goods Available for Sale
It basically includes the cost of inventory which is ready for sale within an accounting period. It mainly includes the cost of beginning inventory as well as the stock purchased in that year and the production within that period (if any).
Cost of Goods Sold
Cost of goods sold is the total expenses or the cost incurred by the business during the process of manufacturing of goods and is directly related to the production. It generally includes the cost of raw material, labor and other
Gross Profit
The profit made after subtracting or debiting the costs related to the goods sold from the total revenue earned or made through sales in a fiscal year is the gross profit.
First in First out
In case of first in, first out method, also known as FIFO method, the inventory which was bought first will also be the first one to be taken out.
Last in First out
In case of last in, first out, also known as LIFO method, the inventory which was bought in the last will be taken out first.
Weighted Average Cost Method
In this method the weighted average cost is evaluated after any purchases have been made and transactions are recorded as when purchase or sales take place.
Specific Identification Method
Under this method, there is a continuous tracking of the inventory and the inventory cost at the time of purchase on the basis of unique identity which thus helps in the valuation of the ending inventory as well as the cost of goods sold. This method is used generally when the company is involved in limited expensive goods which are easily identifiable.
To compute: 1. Cost of goods available for sale and number of units available for sale.
2. Number of units in ending inventory.
3. Cost of ending inventory under the following methods:
- (a) FIFO
(b)LIFO
(c) Weighted average
(d) Specific identification
4. Gross profit for each of the four methods in part
Explanation of Solution
Given info,
| Date | Particulars | Units acquired | Cost per unit ($) | Units sold | Retail price per unit ($) |
| Apr 1 | Beginning inventory | 20 | 3,000 | ||
| Apr 6 | Purchase | 30 | 3,500 | ||
| Apr 9 | Sales | 35 | 12,000 | ||
| Apr 17 | Purchase | 5 | 4,500 | ||
| Apr 25 | Purchase | 10 | 4,800 | ||
| Apr 30 | Sales | 25 | 14,000 | ||
| Total | 65 | 60 |
The ending inventory consists of 5 units from April 17.
1.
Cost of goods available for sale
Formula to calculate Cost of goods available for sale is,
Cost and units of goods available for sale:
| Particulars | Number of units | Cost per unit($) | Amount($) |
| Beginning Inventory | 20 | 3000 | 60,000 |
| Purchases: | |||
| April 6 | 30 | 3,500 | 105,000 |
| April 17 | 5 | 4,500 | 22,500 |
| April 25 | 10 | 4,800 | 48,000 |
| Total Purchases | 45 | 175,500 | |
| Available for sale | 65 | 235,500 |
Table (1)
The cost of goods available for sale is $235,500 and the number of units available for sale is 740 units.
(2)
Number of units in ending inventory
| Particulars | Number of units |
| Number of units available for sale (given) | 65 |
| Less: units sold (given) | 60 |
| Number of units in ending inventory | 5 |
Table (2)
The number of units in ending inventory is 5 units.
3.
(a)
First in, First out method (FIFO)
Ending inventory
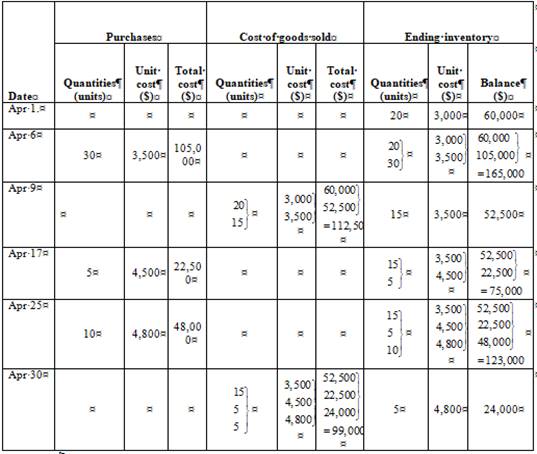
Table (3)
| Date | Purchases | Cost of goods sold | Ending inventory | ||||||
| Quantities(units) | Unit cost($) | Total cost($) | Quantities(units) | Unit cost($) | Total cost($) | Quantities(units) | Unit cost($) | Balance($) | |
| Apr 1. | 20 | 3,000 | 60,000 | ||||||
| Apr 6 | 30 | 3,500 | 105,000 | ||||||
| Apr 9 | 15 | 3,500 | 52,500 | ||||||
| Apr 17 | 5 | 4,500 | 22,500 | ||||||
| Apr 25 | 10 | 4,800 | 48,000 | ||||||
| Apr 30 | 5 | 4,800 | 24,000 | ||||||
Cost of goods sold
Formula to calculate cost of goods sold is,
Substitute $235,500 for cost of goods available for sale (calculated in part (1)) and $24,000 for cost of ending inventory (as calculated above in the table) in the above formula.
Under FIFO method, the amount of ending inventory is $24,000 and cost of goods sold is $211,500 .
(b)
Last in, first out method (LIFO)
Ending inventory
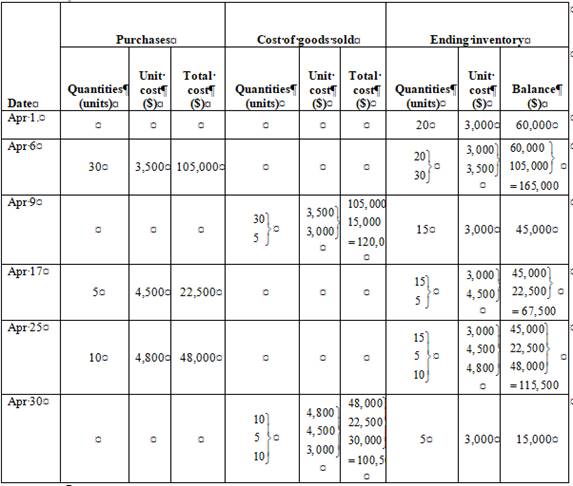
Table (4)
| Date | Purchases | Cost of goods sold | Ending inventory | ||||||
| Quantities(units) | Unit cost($) | Total cost($) | Quantities(units) | Unit cost($) | Total cost($) | Quantities(units) | Unit cost($) | Balance($) | |
| Apr 1. | 20 | 3,000 | 60,000 | ||||||
| Apr 6 | 30 | 3,500 | 105,000 | ||||||
| Apr 9 | 15 | 3,000 | 45,000 | ||||||
| Apr 17 | 5 | 4,500 | 22,500 | ||||||
| Apr 25 | 10 | 4,800 | 48,000 | ||||||
| Apr 30 | 5 | 3,000 | 15,000 | ||||||
Cost of goods sold
Formula to calculate cost of goods sold is,
Substitute $235,500 for cost of goods available for sale (calculated in part (1)) and $15,000 for cost of ending inventory (as calculated above in the table) in the above formula.
Under LIFO method, the amount of ending inventory is $15,000 and cost of goods sold is $220,500.
(c)
Weighted Average Method
Ending inventory
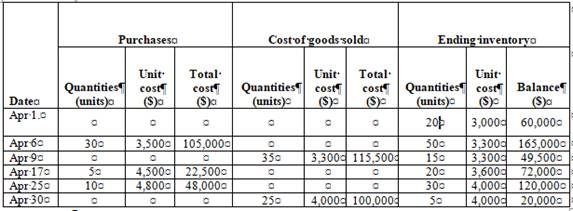
Table (5)
| Date | Purchases | Cost of goods sold | Ending inventory | ||||||
| Quantities(units) | Unit cost($) | Total cost($) | Quantities(units) | Unit cost($) | Total cost($) | Quantities(units) | Unit cost($) | Balance($) | |
| Apr 1. | 20 | 3,000 | 60,000 | ||||||
| Apr 6 | 30 | 3,500 | 105,000 | 50 | 3,300 | 165,000 | |||
| Apr 9 | 35 | 3,300 | 115,500 | 15 | 3,300 | 49,500 | |||
| Apr 17 | 5 | 4,500 | 22,500 | 20 | 3,600 | 72,000 | |||
| Apr 25 | 10 | 4,800 | 48,000 | 30 | 4,000 | 120,000 | |||
| Apr 30 | 25 | 4,000 | 100,000 | 5 | 4,000 | 20,000 | |||
Working Notes:
Calculation of weighted average cost per unit:
Cost of goods sold
Formula to calculate cost of goods sold is,
Substitute $235,500 for cost of goods available for sale (calculated in part (1)) and $20,000 for cost of ending inventory (as calculated above in the table) in the above formula.
Under weighted average method, the amount of ending inventory is $20,000 and cost of goods sold is $215,500.
(d)
Specific identification method
Given info,
The ending inventory consists of 5 units from April 17.
Cost of Ending Inventory
| Date of Purchase | Number of units(A) | Cost per unit($)(B) | Amount($) |
| April 17 | 5 | 4,500 | 22,500 |
| Cost of Ending Inventory | 22,500 | ||
Table (6)
Cost of goods sold
Formula to calculate cost of goods sold is,
Substitute $235,500 for cost of goods available for sale (calculated in part (1)) and $22,500 for cost of ending inventory (calculated above in the table) in the above formula.
The cost of ending inventory is $22,500 and the cost of goods sold is $213,000.
4.
Sales are $770,000 (working notes).
Cost of goods sold in case of FIFO is $211,500. (Calculated in part (3(a))
Cost of goods sold in case LIFO is $220,500. (Calculated in part (3(b))
Cost of goods sold in case of weighted average is $215,500 and (Calculated in part (3(c))
Cost of goods sold in case of specific identification is 213,000. (Calculated in part (3(d))
Gross Profit
Formula to calculate gross profit is,
| Particulars | FIFO | LIFO | Weighted average | Specific identification |
| Sales(working notes) | $770,000 | $$770,000 | $770,000 | $770,000 |
| Less: Cost of goods sold | $211,500 | $220,500 | $215,500 | $213,000 |
| Gross profit | $558,500 | $549,500 | $554,500 | $557,000 |
Table (7)
Working notes:
Calculation of sales
The gross profit in case of FIFO it is $558,500, of LIFO it is $549,500, of weighted average it is $554,500 and of specific identification it is $557,000.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING FUNDAMENTALS
- ( Appendix 6B) Inventory Costing Methods: Periodic System Harrington Company had the following data for inventory during a recent year: Assume that Harrington uses a periodic inventory accounting system. Required: 1. Using the FIFO, LIFO, and average cost methods, compute the ending inventory and cost of goods sold. ( Note: Use four decimal places for per-unit calculations and round all other numbers to the nearest dollar.) 2. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Which method will produce the most realistic amount for income? For inventory? 3. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Which method will produce the lowest amount paid for taxes?arrow_forwardSERIES B PROBLEM PERPETUAL: LIFO AND MOVING-AVERAGE Vozniak Company began business on January 1, 20-1. Purchases and sales during the month of January follow. REQUIRED Calculate the total amount to be assigned to cost of goods sold for January and the ending inventory on January 31, under each of the following methods: 1. Perpetual LIFO inventory method. 2. Perpetual moving-average inventory method.arrow_forwardCalculate the cost of goods sold dollar value for B74 Company for the sale on November 20, considering the following transactions under three different cost allocation methods and using perpetual inventory updating. Provide calculations for (a) first-in, first-out (FIFO); (b) last-in, first-out (LIFO); and (c) weighted average (AVG).arrow_forward
- Calculate the cost of goods sold dollar value for A74 Company for the sale on March 11, considering the following transactions under three different cost allocation methods and using perpetual inventory updating. Provide calculations for (a) first-in, first-out (FIFO); (b) last-in, first-out (LIFO); and (c) weighted average (AVG).arrow_forwardInventory Costing Methods Crandall Distributors uses a perpetual inventory system and has the following data available for inventory, purchases, and sales for a recent year. Required: 1. Compute the cost of ending inventory and the cost of goods sold using the specific identification method. Assume the ending inventory is made up of 40 units from beginning inventory, 30 units from Purchase 1, 80 units from Purchase 2, and 40 units from Purchase 3. 2. Compute the cost of ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the FIFO inventory costing method. 3. Compute the cost of ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the LIFO inventory costing method. 4. Compute the cost of ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the average cost inventory costing method. ( Note: Use four decimal places for per-unit calculations and round all other numbers to the nearest dollar.) 5. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Compare the ending inventory and cost of goods sold computed under all four methods. What can you conclude about the effects of the inventory costing methods on the balance sheet and the income statement?arrow_forward( Appendix 6B) Inventory Costing Methods: Periodic Inventory Systems. Refer to the information for Tyler Company in Brief Exercise 6-35 and assume that the company uses the periodic inventory system. Required: Calculate the cost of goods sold and the cost of ending inventory using the FIFO, LIFO, and average cost methods. ( Note: Use four decimal places for per-unit calculations and round all other numbers to the nearest whole dollar.)arrow_forward
- LIFO perpetual inventory The beginning inventory for Dunne Co. and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period are shown in Problem 6-1B. Instructions 1. Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of goods sold data in a perpetual inventory record similar to the one illustrated in Exhibit 4, using the last-in, first-out method. 2. Determine the total sales, the total cost of goods sold, and the gross profit from sales for the period. 3. Determine the ending inventory cost on June 30.arrow_forwardPerpetual inventory using LIFO Assume that the business in Exercise 6-3 maintains a perpetual inventory system, costing by the last-in, first-out method. Determine the cost of goods sold for each sale and the inventory balance after each sale, presenting the data in the form illustrated in Exhibit 4.arrow_forwardComparison of Inventory Costing Methods—Periodic System Bitten Companys inventory records show 600 units on hand on October 1 with a unit cost of $5 each. The following transactions occurred during the month of October: All expenses other than cost of goods sold amount to $3,000 for the month. The company uses an estimated tax rate of 30% to accrue monthly income taxes. Required Prepare a chart comparing cost of goods sold and ending inventory using the periodic system and the following costing methods: What does the Total column represent? Prepare income statements for each of the three methods. Will the company pay more or less tax if it uses FIFO rather than LIFO? How much more or less?arrow_forward
- Inventory by three cost flow methods Details regarding the inventory of appliances on January 1, 20Y7, purchases invoices during the year, and the inventory count on December 31. 2O’7. of Amsterdam Appliances are summarized as follows: Instructions Discuss which method (FIFO or LIFO) would be preferred for income tax purposes in periods of (a) rising prices and (b) declining prices.arrow_forwardCalculate the cost of goods sold dollar value for B65 Company for the month, considering the following transactions under three different cost allocation methods and using perpetual inventory updating. Provide calculations for first-in, first-out (FIFO).arrow_forwardInventory Write-Down Stiles Corporation uses the FIFO cost flow assumption and is in the process of applying the LCNRV rule for each of two products in its ending inventory. A profit margin of 30% on the selling price is considered normal for each product. Specific data for each product are as follows:arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Corporate Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305653535Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Corporate Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305653535Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





