
To find:
The molecular geometries of the given ions.
Answer to Problem 5.28QA
Solution:
The molecular geometries of the ions are (a) linear, (b) tetrahedral, (c) linear, and (d) trigonal pyramidal.
Explanation of Solution
a) SCN-:
i. The Lewis structure:
The total number of valence electrons in a molecule of SCN- is 16.
| Element | Valence electrons | ||
| Symbol | In one atom | Total | |
| S | 1 | 6 | 1 x 6 = 6 |
| C | 1 | 4 | 1 x 4 = 4 |
| N | 1 | 5 | 1 x 5 = 5 |
| Negative charge | 1 | ||
| Valence electrons in SCN- | 16 | ||
C is the central atom because C is least electronegative atom. The Lewis structure of SCN- is drawn by completing the octet of each element present in the molecule by adding lone pairs on it.
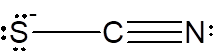
Formula to calculate steric number SN
ii. In the Lewis structure there is one S and one N atom attached to central C atom having no lone pair of electrons. So SN = 2. There is a -1 formal charge on S atom
iii. For SN = 2 and as the bond angle is 180o, molecular geometry is linear.
b) CH3PCl3+:
i. The Lewis structure:
The total number of valence electrons in a molecule of CH3PCl3+ is 32.
| Element | Valence electrons | ||
| Symbol | Number of atoms | In one atom | Total |
| C | 1 | 4 | 1 x 4 = 4 |
| H | 3 | 1 | 3 x 1 = 3 |
| P | 1 | 5 | 1 x 5 = 5 |
| Cl | 3 | 7 | 3 x 7 = 21 |
| Positive charge | -1 | ||
| Valence electrons in CH3PCl3+ | 32 | ||
P is the central atom. The Lewis structure of CH3PCl3+ is drawn by completing the octet of each element present in the molecule by adding lone pairs on it.
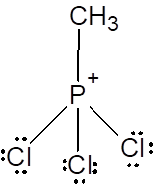
ii. In the Lewis structure there are three chlorine atoms and one CH3 group via C atom bonded to central P atom. So SN = 4. There is +1 formal charge on three O atoms. So SN = 4.
iii. For SN = 4, the molecular geometry is tetrahedral and bond angle is 109.5o.
c) ICl2-:
i. The Lewis structure:
The total number of valence electrons in a molecule of ICl2- is 22.
| Element | Valence electrons | ||
| Symbol | Number of atoms | In one atom | Total |
| I | 1 | 7 | 1 x 7 = 7 |
| Cl | 2 | 7 | 2 x 7 = 14 |
| Negative charge | 1 | ||
| Valence electrons in ICl2- | 22 | ||
I is the central atom because I is least electronegative atom. The Lewis structure of ICl2- is drawn by completing the octet of each element present in the molecule by adding lone pairs on it.
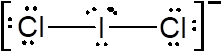
ii. In the Lewis structure there are two oxygen atoms bonded to central I atom. There are three lone pair on I atom with -1 formal charge. So SN = 5.
iii. For SN = 5, the electron geometry is trigonal bipyramidal. As all lone pairs are at equatorial position to minimize the repulsion the molecular geometry is linear.
d) PO33-:
i. The Lewis structure:
The total number of valence electrons in a molecule of PO33- is 26.
| Element | Valence electrons | ||
| Symbol | Number of atoms | In one atom | Total |
| P | 1 | 5 | 1 x 5 = 5 |
| O | 3 | 6 | 3 x 6 = 18 |
| Negative charge | 3 | ||
| Valence electrons in PO33- | 26 | ||
P is the central atom because P is least electronegative atom. The Lewis structure of PO33- is drawn by completing the octet of each element present in the molecule by adding lone pairs on it.
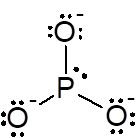
ii. In the Lewis structure there are three O atoms bonded to central P atom. There is one lone pair on P atom. So SN = 4.
iii. If SN = 4, the electron geometry is tetrahedral but as there is one lone pair on P atom and it is bonded to three O atoms the geometry is trigonal pyramidal.
Conclusion:
The molecular geometries of the ions are (a) linear, (b) tetrahedral, (c) linear, and (d) trigonal pyramidal.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Chemistry: An Atoms-Focused Approach (Second Edition)
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





