
Concept explainers
Four students divided the task of surveying the types of vehicles in parking lots of four different shopping malls. Each student examined 100 cars in each of four large suburban malls, resulting in the 5 × 4
- i. P(C)
- ii. P(G
- iii. P(V | S)
- iv. P(C | J)
- v. P(C and G)
- vi. P(T and O)
a.
Calculate each probability (i-vi) and explain it meaning.
Answer to Problem 93CE
i. The probability
ii. The probability
iii. The probability
iv. The probability
v. The probability
vi. The probability
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
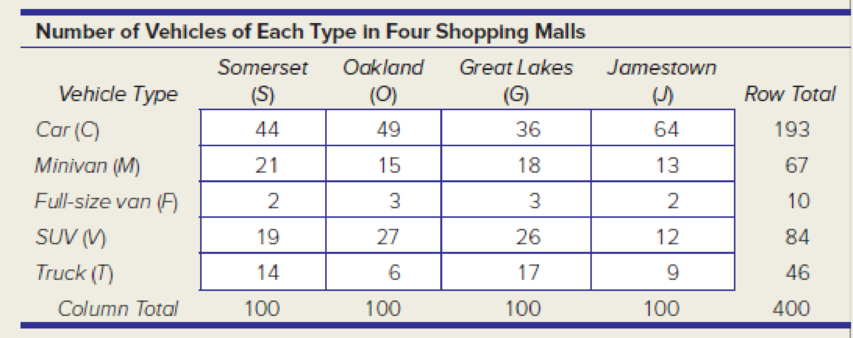
The given table shows that number of vehicles of each type in four shopping malls.
The given contingency table is,
| Vehicle Type | Somerset (S) | Oakland (O) | Great Lakes (G) | Jamestown (J) | Row Total |
| Car (C) | 44 | 49 | 36 | 64 | 193 |
| Minivan (M) | 21 | 15 | 18 | 13 | 67 |
| Full-size van (F) | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 10 |
| SUV (V) | 19 | 27 | 26 | 12 | 84 |
| Truck (T) | 14 | 6 | 17 | 9 | 46 |
| Column Total | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 400 |
For (i)
The formula for finding the probability
Substitute 193 for ‘Frequency for the class C’ and 400 for ‘Total frequencies in the distribution’
Therefore, the probability
For (ii)
The formula for finding the probability
Substitute 100 for ‘Frequency for the class G’ and 400 for ‘Total frequencies in the distribution’
Therefore, the probability
For (iii)
The formula for finding the probability
Substitute 19 for ‘Frequency for the class V and S’ and 100 for ‘Frequency for the class S’,
Therefore, the probability
For (iv)
The formula for finding the probability
Substitute 19 for ‘Frequency for the class C and J’ and 100 for ‘Frequency for the class J’,
Therefore, the probability
For (v)
The formula for finding the probability
Substitute 36 for ‘Frequency for the class C and G’ and 400 for ‘Total frequencies in the distribution’,
Therefore, the probability
For (vi)
The formula for finding the probability
Substitute 6 for ‘Frequency for the class T and O’ and 400 for ‘Total frequencies in the distribution’,
Therefore, the probability
b.
Check whether there is evidence that vehicle type is not independent of mall location and explain.
Answer to Problem 93CE
Yes, there is evidence that vehicle type is not independent because
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Special law of multiplication:
If two events A and B are independent, then
Consider vehicle type truck and mall location as Oak land.
From part (a),
The formula for checking whether there is evidence that vehicle type is not independent of mall location or not is,
Here, it is observed that
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Applied Statistics in Business and Economics with Connect Access Card with LearnSmart

