
Concept explainers
a.
Find the probability that exactly 6 of the adults have hypertension.
a.
Answer to Problem 37E
The probability that exactly 6 of the adults have hypertension is 0.1472.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
It was found that 30% of the adults have hypertension. A random sample of 25 adults is considered.
Define the random variable X as the number of adults who have hypertension. Here, a random sample (n) of 25 adults is taken. Each adult is independent of the other. Also, there are two possible outcomes, the adult have hypertension or not (success or failure). It was found that 30% of the adults have hypertension. Thus, the probability of success (p) is 0.30. Hence, X follows binomial distribution.
The probability of obtaining x successes in n independent trails of a binomial experiment is,
Where, p is the probability of success.
Substitute
The probability that exactly 6 of them have hypertension is,
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the probability using MINITAB software is given below:
- Choose Calc > Probability Distributions > Binomial Distribution.
- Choose Probability.
- Enter Number of trials as 25 and Event probability as 0.30.
- In Input constant, enter 6.
- Click OK.
The output using the Minitab software is given below:
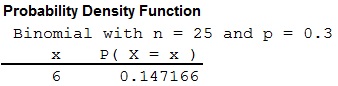
From the Minitab output, the probability value is approximately 0.1472.
Thus, the probability that exactly 6 of the adults have hypertension is 0.1472.
b.
Find the probability that more than 8 of the adults have hypertension.
b.
Answer to Problem 37E
The probability that more than 8 of the adults have hypertension is 0.3231.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The probability that more than 8 of the adults have hypertension is obtained as shown below:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the probability
- Choose Calc > Probability Distributions > Binomial Distribution.
- Choose Cumulative Probability.
- Enter Number of trials as 25 and Event probability as 0.30.
- In Input constant, enter 8.
- Click OK.
The output using the Minitab software is given below:

From the Minitab output, the probability value is approximately 0.6769. Substituting the value, the required probability becomes,
Thus, the probability that more than 8 of the adults have hypertension is 0.3231.
c.
Find the probability that fewer than 4 of the adults have hypertension.
c.
Answer to Problem 37E
The probability that fewer than 4 of the adults have hypertension is 0.0332.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The probability that fewer than 4 of the adults have hypertension is obtained as shown below:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the probability
- Choose Calc > Probability Distributions > Binomial Distribution.
- Choose Cumulative Probability.
- Enter Number of trials as 25 and Event probability as 0.30.
- In Input constant, enter 3.
- Click OK.
The output using the Minitab software is given below:

From the Minitab output, the probability value is approximately 0.0332.
Thus, the probability that fewer than 4 of the adults have hypertension is 0.0332.
d.
Check whether it is unusual if more than 10 of the adults have hypertension.
d.
Answer to Problem 37E
No, it is not unusual if more than 10 of the adults have hypertension.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Unusual:
If the probability of an event is less than 0.05 then the event is called unusual.
The probability that more than 10 of the adults have hypertension is obtained as shown below:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the probability
- Choose Calc > Probability Distributions > Binomial Distribution.
- Choose Cumulative Probability.
- Enter Number of trials as 25 and Event probability as 0.30.
- In Input constant, enter 10.
- Click OK.
The output using the Minitab software is given below:

From the Minitab output, the probability value is 0.9022. The required probability is,
Here, the probability of the event is not less than 0.05. Thus, the event that more than10 of the adults have hypertension is not unusual.
e.
Find the mean number of adults who have hypertension in a sample of 25 adults.
e.
Answer to Problem 37E
The mean number of adults who have hypertension in a sample of 25 adults is 7.5.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
A binomial experiment with n independent trials and a probability of success p has mean,
Substitute the values 25 for n and 0.30 for p,
The mean is,
Thus, the mean number of adults who have hypertension in a sample of 25 adults is 7.5.
f.
Find the standard deviation of the number adults who have hypertension in a sample of 25 adults.
f.
Answer to Problem 37E
The standard deviation of the number adults who have hypertension in a sample of 25 adults is 2.2913.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
A binomial experiment with n independent trials and a probability of success p has standard deviation,
Substitute the values 25 for n and 0.30 for p,
Thus, the standard deviation of the number adults who have hypertension in a sample of 25 adults is 2.2913.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
ESSENTIAL STATISTICS W/CONNECT
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





