
Concept explainers
a)
To draw: A decision tree for the given problem.
Introduction:
Decision tree is one of the methods used in decision-making process. It would graphically represent the available alternatives and states of nature. It would also mention the payoffs and probabilities of the alternatives. It helps to choose the best alternative that would give the best result among the alternatives.
a)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Three decision alternatives:
- 1st construct small stamping plant
- 2nd construct medium stamping plant
- 3rd construct stamping plant
Each decision has demand:
- Low demand which have 20% probability
- Low demand which have 80% probability
- If firm build small facility and demand turn out to be low than
NPV is $42,000,000 - If firm build small facility and demand turn out to be high than either subcontract or expand greatly, if sub contract than NPV is $42,000,000 and if expand greatly than $48,000,000.
- If firm build medium facility and demand turn out to be low than NPV is $22,000,000.
- If firm build medium facility and demand turn out to be high than either it do nothing or expand, if sub contract than NPV is $46,000,000 and if expand greatly than $50,000,000.
- If firm build large facility and demand turn out to be low than NPV is -$20,000,000.
- If firm build large facility and demand turn out to be high than NPV is $72,000,000.
As per given information, construct the decision tree:
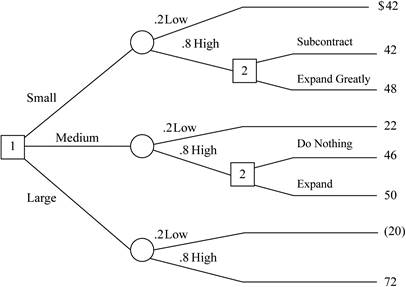
Now, calculate the value of payoff and monetary value in decision tree:
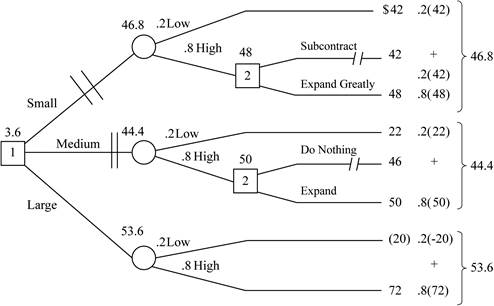
Analysis the decision from right to left:
- In the decision tree, there are two decisions making; first decision is between small, medium and large and second decision is between high demand of small and medium build facilities.
- If small facilities build with high demand then select expand greatly because the payoff of expand greatly is higher than subcontract. The payoff of expand greatly is $48,000,000 and place double slash (reject) on subcontract.
- If large facility build with high demand then select expand, because the payoff of expand greatly is higher than do nothing. The payoff of expand is $50,000,000 place double slash (reject) on do nothing.
Calculate the product of the chance probabilities and their respective payoffs for the remaining branches:
- If small facility build:
- If medium facility IS build:
- If large facility is build:
Calculation of the expected value in each alternative:
- If small facility build
- If medium facility build
- If large facility build
Here, it is obtained that large facility build have higher expected value, hence it should be selected. And small and medium facilities have to be rejected.
b)
To determine: Maximin alternatives
Introduction:
Maximin is the decision making method which is used to make decision under uncertainty. This method will find an alternative that maximizes the minimum outcome of every alternative or we can say that calculating the minimum outcome within the each alternative.
b)
Answer to Problem 9P
Explanation of Solution
Determine the worst possible alternatives from the given demand:
As definition stated above, Maximim is the selection from the best of the worst possible payoff for each alternatives.
| Alternative | Next Year’s Demand | Worst Payoff | Decision | |
| Low | High | |||
| Small | $42,000,000.00 | $48,000,000.00 | $42,000,000.00 | Best of the Worst |
| Medium | $22,000,000.00 | $50,000,000.00 | $22,000,000.00 | |
| Large | -$20,000,000.00 | $72,000,000.00 | -$20,000,000.00 | |
Hence, the best decision according to Maximin decision is to select a small medium facility.
c)
To determine: Expected value of perfect information (EVPI) and interpret it.
Expected value of perfect information: It is the rate that a person is willing to pay to gain access to perfect information. A common area which uses expected value of perfect information is the healthcare economy. This value tries to evaluate the expected cost of the uncertainty, which can be interpreted as the expected value of perfect information
The expected value of perfect information can be calculated by using below given formula:
c)
Answer to Problem 9P
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the expected value with perfection information or Expected payoff under certainty:
Calculate the expected value with perfect information:
Therefore, EVPI is $12,400,000.
d)
To determine: The sensitive analysis on P (high).
Introduction
Decision table is formats or visual representations were data is expressed arranged, determined and calculated to make a effective decision making. A decision table is a tabular representation that is used to analyze decision alternatives and states of nature.
d)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
Here we draw each alternative to P (high), low demand should be on the left hand side and high demand value on the right hand side:
| Next Year’s Demand | ||
| Alternative | Low | High |
| Small | $42,000,000.00 | $48,000,000.00 |
| Medium | $22,000,000.00 | $50,000,000.00 |
| Large | -$20,000,000.00 | $72,000,000.00 |
Graph plot:
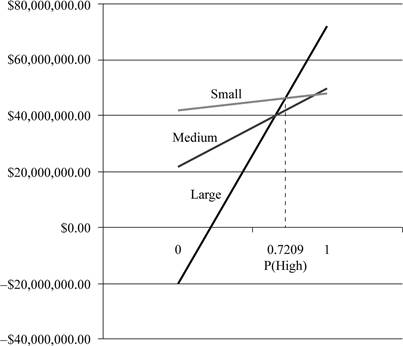
From the above graph, we can determine the value of P (high) where each alternative are optimal.
From the graph, we can obtain that small build facility is best option, because of higher expected value. For low value of P(high) while for higher and intermediate value of P(high) large is the best option.
Calculate the range needed to determine upper part of line intersects:
For each line, b is the slope of the line and x = P(High). The slope of each line
Determination of equation:
Small build facility = 42+6P (because high demand $48 million which is subtracted with low demand value $42 million)
Large build facility =-20+92P (because high demand $72million which is subtracted with low demand value -$20million)
Determination of intersection between small and large
Hence, the intersection between small and large is 0.7209.
Therefore, optimal range can be derived as:
Small: P (High) = 0 to < .7209
Large: P (High) > .7209 to 1.00
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Operations Management (McGraw-Hill Series in Operations and Decision Sciences)
- A manager is trying to decide whether to build a small, medium or large facility. Demand can be low, average, or hit, with the estimated probabilities being 0.25, 0.40, and 0.35 respectively A small facility is expected to earn an after-tax net present value of just $18,000 if demand is low. If demand is average, the small facility is expected to earn $75,000; it can be increased to medium size to earn a net present value of $60,000. If demand is high, the small facility is expected to earn $75,000 and can be expanded to medium size to earn $60,000 or to large to earn $125,000. A medium-size facility is expected to lose an estimated $25,000 if demand is low and earn $140,000 if demand is average. If demand is high, the medium-size facility is expected to earn a net present value of $150,000; it can be expanded to a large size for a net payoff of $145,000. If a large facility is built and demand is high, earnings are expected to be $220,000. If demand is average for the large facility,…arrow_forwardA manager is trying to decide whether to build a small, medium or large facility. Demand can be low, average, or hit, with the estimated probabilities being 0.25, 0.40, and 0.35 respectively A small facility is expected to earn an after-tax net present value of just $18,000 if demand is low. If demand is average, the small facility is expected to earn $75,000; it can be increased to medium size to earn a net present value of $60,000. If demand is high, the small facility is expected to earn $75,000 and can be expanded to medium size to earn $60,000 or large to earn $125,000. A medium-size facility is expected to lose an estimated $25,000 if demand is low and earn $140,000 if demand is average. If demand is high, the medium-size facility is expected to earn a net present value of $150,000; it can be expanded to a large size for a net payoff of $145,000. If a large facility is built and demand is high, earnings are expected to be $220,000. If demand is average for the large facility,…arrow_forwardHerndon Development Group (HDG) is planning for a new investment. They would like to make a sequence of decisions that start with determining whether to purchase an apartment building or land. Cost of purchasing an apartment is $800,000 and purchasing land is $200,000. If HDG purchases the apartment building, two states of nature are possible: The town may exhibit population growth, with a probability of 0.60, or there may be no population growth or a decline, with a probability of .40. If the population grows, the investor will achieve a revenue of $2,000,000. However, if there is no population growth, the revenue is $250,000. If the decision is to purchase land, the investor will wait for 3 years and consider developing the land based on the population growth. The probability of a growing population is .60, whereas the probability of a stable or declining population is 0.40. If population growth occurs for a 3-year period, the investor will make another decision regarding land…arrow_forward
- The Hard to Beat Bakery is deciding whether to buy or repair an existing oven thatthey have been using for over 8 years. If they elect to repair, it will cost the entity$950,000 and either of two outcomes is likely: 1. A 20% probability it will perform okay and generate revenues of$10,000,000, or 2. An 80% chance that it will be partially restored and generate revenue of$2,000,000. If on the other hand however, they purchase a new oven, they can either buy animported oven for $3,500,000 or they can buy a locally made one for $2,200,000.If the elect to purchase the imported oven, production will earn them revenues of$15,550,000, but if they buy the locally made oven, there is a 70% likelihood thatit perform as expected and generate revenues of $12,000,000; and a 30% chancethat it will not and generate revenues of $6,000,000. Required: 1. Draw a decision tree of this problem and determine the expected value.2. Advise the management of the Bakery on how to proceed.3. Briefly discuss the…arrow_forwardIf the values (Revenue - Cost) for the option for a retail store to move to a new location associated with the events strong growth and weak growth are $ 200000 and $100000 respectively, calculate the expected value for the option to move to a new location. The probability of strong growth = 55%.arrow_forwardA manager is trying to decide whether to build a small, medium, or large facility. Demand can be low, average, or high, with the estimated probabilities being 0.40, 0.35, and 0.25, respectively. A small facility is expected to earn an after-tax net present value of just $13,000 if demand is low. If demand is average, the small facility is expected to earn $15,000; it can be increased to medium size to earn a net present value of $30,000. If demand is high, the small facility is expected to earn $25,000 and can be expanded to medium size to earn $50,000 or to large size to earn $100,000. A medium-sized facility is expected to lose an estimated $50,000 if demand is low and earn $100,000 if demand is average. If demand is high, the medium-sized facility is expected to earn a net present value of $125,000; it can be expanded to a large size for a net payoff of $175,000. If a large facility is built and demand is high, earnings are expected to be $180,000. If demand is average for the large…arrow_forward
- A manager is trying to decide whether to build a small, medium, or large facility. Demand can be low, average, or high, with the estimated probabilities being 0.25, 0.40, and 0.35, respectively. A small facility is expected to earn an after-tax net present value of just $18,000 if demand is low. If demand is average, the small facility is expected to earn $75,000; it can be increased to medium size to earn a net present value of $60,000. If demand is high, the small facility is expected to earn 75,000 and can be expanded to medium size to earn $60,000 or to large size to earn $125,000. A medium-sized facility is expected to lose an estimated $25,000 if demand is low and earn $140,000 if demand is average. If demand is high, the medium-sized facility is expected to earn a net present value of $150,000; it can be expanded to a large size for a net payoff of $145,000. If a large facility is built and demand is high, earnings are expected to be $220,000. If demand is average for the…arrow_forwardA manager is trying to decide whether to build a small, medium, or large facility. Demand can be low, average, or high, with the estimated probabilities being 0.25, 0.40, and 0.35, respectively. A small facility is expected to earn an after-tax net present value of just $18,000 if demand is low. If demand is average, the small facility is expected to earn $75,000; it can be increased to medium size to earn a net present value of $60,000. If demand is high, the small facility is expected to earn $75,000 and can be expanded to medium size to earn $60,000 or to large size to earn $125,000. A medium-sized facility is expected to lose an estimated $25,000 if demand is low and earn $140,000 if demand is average. If demand is high, the medium-sized facility is expected to earn a net present value of $150,000; it can be expanded to a large size for a net payoff of $145,000. If a large facility is built and demand is high, earningsare expected to be $220,000. If demand is average for the large…arrow_forwardJeffrey Mogul is a Hollywood film producer, and he is currently evaluating a script by a new screenwriter and director, Betty Jo Thurston. Jeffrey knows that the probability of a film by a new director being a success is about .10 and that the probability it will flop is .90. The studio accounting department estimates that if this film is a hit, it will make $25 million in profit, whereas if it is a box office failure, it will lose $8 million. Jeffrey would like to hire noted film critic Dick Roper to read the script and assess its chances of success. Roper is generally able to correctly predict a successful film 70% of the time and correctly predict an unsuccessful film 80% of the time. Roper wants a fee of $1 million. Determine whether Roper should be hired, the strategy Mogul should follow if Roper is hired, and the expected value.arrow_forward
- A manufacturing plant has reached full capacity. The company must build a second plant—either small or large—at a nearby location. The demand is likely to be high or low. The probability of low demand is 0.3. If demand is low, the large plant has a present value of $5 million and the small plant, apresent value of $8 million. If demand is high, the large plant pays off with a present value of $18 million, and the small plant with a present value of only $10 million. However, the small plant can be expanded later if demand proves to be high for a present value of $14 million.a. Draw a decision tree for this problem.b. What should management do to achieve the highest expected payoff?arrow_forwardHoward Weiss, Inc., is considering building a sensitive new radiation scanning device. His managers believe that ther is a probability of 0.40 that the ATR Co. does not follow with a competitive product. Weiss's expected profit is $50,000; If weiss adds an assembley line and ATR follows suit, Weiss still expects $15,000 profit. If Weiss adds a new plant addition adn ATR does not produce a competitive product, weiss expects a profit of $600,000; if ATR does compete for this market, weiss expects a loss of $100,000 a) Expected value for the Add Assembly Line option=$____arrow_forward1. Kirsten is trying to decide where to go for her well-earned vacation. She would like to camp, but if the weather is bad, she will have to go to a motel. Given the costs and probabilities of bad weather given below, which destination should she choose? Camping cost Motel cost Probability of bad weather Nevada $21.2 $80.9 0.2 Oregon $15.9 $84.6 0.4 California $30 $95 0.1 a. California, because its EMV = $33.14 b. Nevada, because its EMV = $33.14 c. California, because its EMV = $36.5 d. Any of the 3 choices. e. Oregon, because its EMV = $43.38 f. Nevada, because its EMV = $43.38 g. None of the 3 choices. h. Oregon, because its EMV is $36.50.arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning

