
Concept explainers
(a)
The minimum possible speed of the bob if the bob is at the top of the circle.
(a)
Answer to Problem 141P
The minimum possible speed of the bob if the bob is at the top of the circle is
Explanation of Solution
The bob as a particle in uniform circular motion, it exerts a centripetal acceleration towards the peg.
The free body diagram of the bob at the top of the circle is shown in the Figure 1.
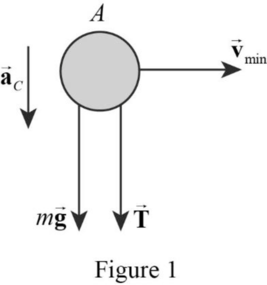
From the free body diagram, write the expression for net force in the vertical direction.
Here,
The minimum speed of the bob occurs corresponds to a tension of zero in the cord.
Substitute,
Conclusion:
Therefore, the minimum possible speed of the bob if the bob is at the top of the circle is
(b)
The distance from a point B moved by the bob if the string breaks at point A.
(b)
Answer to Problem 141P
The distance from a point B moved by the bob if the string breaks at point A is
Explanation of Solution
Let C be the point at the same height as B reached by the bob when the string breaks. Assume the bob is in the x direction and moving with constant acceleration.
Consider the Figure 2.
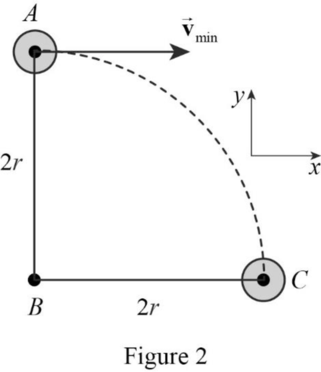
Write the expression for distance in the x-direction
Here,
Substitute,
Write the expression for distance in the y-direction
Here,
Substitute,
Use equation (VI) in (IV).
Conclusion:
Therefore, the distance from a point B moved by the bob if the string breaks at point A is
(c)
The minimum value of
(c)
Answer to Problem 141P
The minimum value of
Explanation of Solution
The system of the bob and Earth as an isolated system for energy with no non conservative forces acting, then the total energy is zero.
Here,
Use
Here,
Substitute,
Since
Conclusion:
Therefore, the minimum value of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf For College Physics With Connect Access Card (1 Semester)
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





