
Concept explainers
Determining the effect of
Three different companies each purchased trucks on January 1, 2018, for $50,000. Each truck was expected to last four years or 200,000 miles. Salvage value was estimated to be $5,000. All three trucks were driven 66,000 miles in 2018, 42,000 miles in 2019, 40,000 miles in 2020, and 60,000 miles in 2021. Each of the three companies earned $40,000 of cash revenue during each of the four years. Company A uses straight-line depreciation, company B uses double-declining-balance depreciation, and company C uses units-of-production depreciation.
Required
Answer each of the following questions. Ignore the effects of income taxes.
a. Which company will report the highest amount of net income for 2018?
b. Which company will report the lowest amount of net income for 2021?
c. Which company will report the highest book value on the December 31, 2020,
d. Which company will report the highest amount of
e. Which company will report the lowest amount of cash flow from operating activities on the 2020 statement of cash flows?
a.
Identify the company which will report the highest amount of net income for 2018.
Explanation of Solution
Net Income
Net income is the sum total of all the revenues generated in a particular accounting period after deducting cost of goods sold and expenses and losses, such as rent expense, depreciation of that particular accounting period.
Book value:
The amount of acquisition cost of less accumulated depreciation as on a particular date is referred to as book value.
Formula for book value:
Accumulated depreciation:
The total amount of depreciation expense deducted, from the time asset acquired till date, as reported in the account as on a particular date, is referred to as accumulated depreciation.
Formula for accumulated depreciation:
Identify the company which will report the highest amount of net income for 2018.
| Net Income for 2018 | |||
| Company A (in $) | Company B (in $) | Company C (in $) | |
| Revenue | 40,000 | 40,000 | 40,000 |
| Less: Depreciation expense |
11,250 (W.N. 1) |
25,000 (W.N. 2) |
14,850 (W.N. 3) |
| Net Income | $28,750 | $15,000 | $25,150 |
Table (1)
Working Note 1:
Prepare depreciation schedule under straight-line method for Company A.
| Date | Depreciable Cost (in $) (A) | Depreciation Rate (B) | Depreciation expense (in $) |
| 2018 | 45,000 | 1/4 | 11,250 |
| 2019 | 45,000 | 1/4 | 11,250 |
| 2020 | 45,000 | 1/4 | 11,250 |
| 2021 | 45,000 | 1/4 | 11,250 |
Table (2)
Note:
- 1. Calculate the depreciable cost.
Working note 2:
Prepare depreciation schedule under double-declining-balance (DDB) method for Company B.
| Date | Double-Declining-Balance Depreciation Rate (A) | Book Value (Refer note) (in $) (B) | Depreciation expense (in $) |
| 2018 | 0.50 | 50,000 | 25,000 |
| 2019 | 0.50 | 25,000 | 12,500 |
| 2020 | 0.50 | 12,500 | 6,250 |
| 2021 | 0.50 | 6,250 | 1,250 |
Table (3)
Note:
- 1. Determine the depreciation rate applied each year.
Useful life = 4 years
- 2. Compute depreciation expense on 2021.
Working note 3:
Prepare depreciation schedule under units-of-production method for Company C.
| Date | Depreciation per unit (A) | Number of miles (B) | Depreciation expense (in $) |
| 2018 | $0.225 | 66,000 | 14,850 |
| 2019 | $0.225 | 42,000 | 9,450 |
| 2020 | $0.225 | 40,000 | 9,000 |
| 2021 | $0.225 | 60,000 | 11,700 |
Table (4)
Note:
- 1. Compute depreciation per unit.
- 2. Compute depreciation expense on 2021.
Hence, the company which will report the highest amount of net income for 2018 is Company A.
b.
Identify the company which will report the lowest amount of net income for 2021.
Explanation of Solution
Identify the company which will report the lowest amount of net income for 2021.
| Net Income for 2021 | |||
| Company A (in $) | Company B (in $) | Company C (in $) | |
| Revenue | 40,000 | 40,000 | 40,000 |
| Less: Depreciation expense |
11,250 (W.N. 4) |
1,250 (W.N. 5) |
11,700 (W.N. 6) |
| Net Income | $28,750 | $38,750 | $28,300 |
Table (5)
Working Note 4:
Prepare depreciation schedule under straight-line method for Company A.
| Date | Depreciable Cost (in $) (A) | Depreciation Rate (B) | Depreciation expense (in $) |
| 2018 | 45,000 | 1/4 | 11,250 |
| 2019 | 45,000 | 1/4 | 11,250 |
| 2020 | 45,000 | 1/4 | 11,250 |
| 2021 | 45,000 | 1/4 | 11,250 |
Table (6)
Note:
Calculate the depreciable cost.
Working note 5:
Prepare depreciation schedule under double-declining-balance (DDB) method for Company B.
| Date | Double-Declining-Balance Depreciation Rate (A) | Book Value (Refer note) (in $) (B) | Depreciation expense (in $) |
| 2018 | 0.50 | 50,000 | 25,000 |
| 2019 | 0.50 | 25,000 | 12,500 |
| 2020 | 0.50 | 12,500 | 6,250 |
| 2021 | 0.50 | 6,250 | 1,250 |
Table (7)
Note:
- 1. Determine the depreciation rate applied each year.
Useful life = 4 years
- 2. Compute depreciation expense on 2021.
Working note 6:
Prepare depreciation schedule under units-of-production method for Company C.
| Date | Depreciation per unit (A) | Number of miles (B) | Depreciation expense (in $) |
| 2018 | $0.225 | 66,000 | 14,850 |
| 2019 | $0.225 | 42,000 | 9,450 |
| 2020 | $0.225 | 40,000 | 9,000 |
| 2021 | $0.225 | 60,000 | 11,700 |
Table (8)
Note:
- 1. Compute depreciation per unit.
- 2. Compute depreciation expense on 2021.
Hence, the company which will report the lowest amount of net income for 2021 is Company C.
c.
Identify the company which will report the highest book value on the December 31, 2020, balance sheet.
Explanation of Solution
Book value:
The amount of acquisition cost of less accumulated depreciation as on a particular date is referred to as book value.
Formula for book value:
Identify the company which will report the highest book value on the December 31, 2020, balance sheet.
| Book value on December 31, 2020 | |||
| Company A (in $) | Company B (in $) | Company C (in $) | |
| Cost | 50,000 | 50,000 | 50,000 |
| Less: Accumulated depreciation |
33,750 (W.N. 7) |
43,750 (W.N. 8) |
33,300 (W.N. 9) |
| Book value | $16,250 | $6,250 | $16,700 |
Table (9)
Working note 7:
Prepare depreciation schedule under straight-line method for Company A.
| Date | Depreciable Cost (in $) (A) | Depreciation Rate (B) | Depreciation expense (in $) | Accumulated Depreciation (in $) |
| 2018 | 45,000 | 1/4 | 11,250 | 11,250 |
| 2019 | 45,000 | 1/4 | 11,250 | 22,500 |
| 2020 | 45,000 | 1/4 | 11,250 | 33,750 |
Table (10)
Note:
Calculate the depreciable cost.
Working note 8:
Prepare depreciation schedule under double-declining-balance (DDB) method for Company B.
| Date | Double-Declining-Balance Depreciation Rate (A) | Book Value (Refer note) (in $) (B) | Depreciation expense (in $) | Accumulated Depreciation (in $) |
| 2018 | 0.50 | 50,000 | 25,000 | 25,000 |
| 2019 | 0.50 | 25,000 | 12,500 | 37,500 |
| 2020 | 0.50 | 12,500 | 6,250 | 43,750 |
Table (11)
Note:
Determine the depreciation rate applied each year.
Useful life = 4 years
Working note 9:
Prepare depreciation schedule under units-of-production method for Company C.
| Date | Depreciation per unit (A) | Number of miles (B) | Depreciation expense (in $) | Accumulated Depreciation (in $) |
| 2018 | $0.225 | 66,000 | 14,850 | 14,850 |
| 2019 | $0.225 | 42,000 | 9,450 | 24,300 |
| 2020 | $0.225 | 40,000 | 9,000 | 33,300 |
Table (12)
Note:
Compute depreciation per unit.
Hence, the company which will report the highest book value on the December 31, 2020, balance sheet is Company C.
d.
Identify the company which will report the highest amount of retained earnings on the December 31, 2021, balance sheet.
Explanation of Solution
Retained earnings:
The retained earnings statement is that financial statement which shows the amount of net income which is actually retained by the Company on a particular date. These earnings can be utilized by the Company for the reinvestment and to pay its debts.
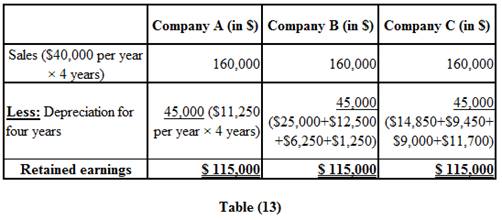
Hence, the retained earnings for all the companies are the same on the December 31, 2021, balance sheet, as the total depreciation over the four year period is the same for all the three companies.
e.
Identify the company which will report the lowest amount of cash flow from operating activities on the 2020 statement of cash flows.
Explanation of Solution
Statement of cash flows:
This statement reports all the cash transactions which are responsible for inflow and outflow of cash, and result of these transactions is reported as ending balance of cash at the end of reported period.
Cash flows from operating activities:
These refer to the cash received or cash paid in day-to-day operating activities of a company. In this direct method, cash flow from operating activities is computed by using all cash receipts and cash payments during the year.
Depreciation expense is not a cash outflow item. If the income tax is not considered, all the three companies will report the same amount of cash flow from operating activities on the 2020 statement of cash flows.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
SURVEY OF ACCOUNTING 360DAY CONNECT CAR
- Revision of Depreciation On January 1, 2017, Blizzards-R-Us purchased a snow-blowing machine for $125,000. The machine was expected to have a residual value of $12,000 at the end of its 5-year useful life. On January 1, 2019, Blizzards-R-Us concluded that the machine would have a remaining useful life of 6 years with a residual value of $3,600. Required: 1. Determine the revised annual depreciation expense for 2019 using the straight-line method. 2. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION How does the revision in depreciation affect the Blizzards-R-Us financial statements?arrow_forwardDepreciation Methods Sorter Company purchased equipment for 200,000 on January 2, 2019. The equipment has an estimated service life of 8 years and an estimated residual value of 20,000. Required: Compute the depreciation expense for 2019 under each of the following methods: 1. straight-line 2. sum-of-the-years-digits 3. double-declining-balance 4. Next Level What effect does the depreciation of the equipment have on the analysis of rate of return?arrow_forwardIMPACT OF IMPROVEMENTS AND REPLACEMENTS ON THE CALCULATION OF DEPRECIATION On January 1, 20-1, Dans Demolition purchased two jackhammers for 2,500 each with a salvage value of 100 each and estimated useful lives of four years. On January 1, 20-2, a stronger blade to improve performance was installed in Jackhammer A for 800 cash and the compressor was replaced in Jackhammer B for 200 cash. The compressor is expected to extend the life of Jackhammer B one year beyond the original estimate. REQUIRED 1. Using the straight-line method, prepare general journal entries for depreciation on December 31, 20-1, for Jackhammers A and B. 2. Enter the transactions for January 20-2 in a general journal. 3. Assuming no other additions, improvements, or replacements, calculate the depreciation expense for each jackhammer for 20-2 through 20-4.arrow_forward
- Depreciation Methods Nickle Company purchased three identical assets for 17,000 on January 2, 2019. Each asset has an expected residual value of 1,000. The depreciation expense for 2019 and 2020 is shown below for three assets: Required: 1. Next Level Which depreciation method is the company using for each asset? 2. Compute the depreciation expense for 2021 and 2022 for each asset.arrow_forwardWorking Backward: Depreciation Polk Corp. purchased new store fixtures for $55,000 on January 31, 2014. Polk depreciates assets using the straight-line method and estimated a salvage value for the machine of $5,000. On its December 31, 2016, balance sheet, Polk reported the following: Required What is the yearly amount of depreciation expense for the store fixtures? What is the estimated useful life in years for the store fixtures? Explain your answer.arrow_forwardChange in Estimate Assume that Bloomer Company purchased a new machine on January 1, 2016, for $80,000. The machine has an estimated useful life of nine years and a residual value of $8,000. Bloomer has chosen to use the straight-line method of depreciation. On January 1, 2018, Bloomer discovered that the machine would not be useful beyond December 31, 2021, and estimated its value at that time to be $2,000. Required Calculate the depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value of the asset for each year 2016 to 2021. Was the depreciation recorded wrong in 2016 and 2017? If so, why was it not corrected?arrow_forward
- On July 1, 2018, Mundo Corporation purchased factory equipment for 50,000. Residual value was estimated at 2,000. The equipment will be depreciated over 10 years using the double-declining balance method. Counting the year of acquisition as one-half year, Mundo should record 2019 depredation expense of: a. 7,680 b. 9,000 c. 9,600 d. 10,000arrow_forwardHunter Company purchased a light truck on January 2, 2019 for 18,000. The truck, which will be used for deliveries, has the following characteristics: Estimated life: 5 years Estimated residual value: 3,000 Depreciation method for financial statements: straight-line method Depreciation for income tax purposes: MACRS (3-year life) From 2019 through 2023, each year, Hunter had sales of 100,000, cost of goods sold of 60,000, and operating expenses (excluding depreciation) of 15,000. The truck was disposed of on December 31, 2023, for 2,000. Required: 1. Prepare an income statement for financial reporting through pretax accounting income for each of the 5 years, 2019 through 2023. 2. Prepare, instead, an income statement for income tax purposes through taxable income for each of the 5 years, 2019 through 2023. 3. Compare the total income for all 5 years under Requirements 1 and 2.arrow_forwardMontello Inc. purchases a delivery truck for $15,000. The truck has a salvage value of $3,000 and is expected to be driven for eight years. Montello uses the straight-line depreciation method. Calculate the annual depreciation expense.arrow_forward
- On May 10, 2019, Horan Company purchased equipment for 25,000. The equipment has an estimated service life of 5 years and zero residual value. Assume that the straight-line depreciation method is used. Required: Compute the depreciation expense for 2019 for each of the following four alternatives: 1. Horan computes depreciation expense to the nearest day. (Use 12 months of 30 days each and round the daily depreciation rate to 2 decimal places.) 2. Horan computes depreciation expense to the nearest month. Assets purchased in the first half of the month are considered owned for the whole month. 3. Horan computes depreciation expense to the nearest whole year. Assets purchased in the first half of the year are considered owned for the whole year. 4. Horan records one-half years depreciation expense on all assets purchased during the year.arrow_forwardMontello Inc. purchases a delivery truck for $25,000. The truck has a salvage value of $6,000 and is expected to be driven for ten years. Montello uses the straight-line depreciation method. Calculate the annual depreciation expense.arrow_forwardMontello Inc. purchases a delivery truck for $15,000. The truck has a salvage value of $3,000 and is expected to be driven for 120,000 miles. Montello uses the units-of-production depreciation method and in year one it expects to use the truck for 23,000 miles. Calculate the annual depreciation expense.arrow_forward
 Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College





