
Recording Sales with Discounts and Returns and Analyzing Gross Profit Percentage
Hair World Inc. is a wholesaler of hair supplies. Hair World uses a perpetual inventory system. The following transactions (summarized) have been selected for analysis:
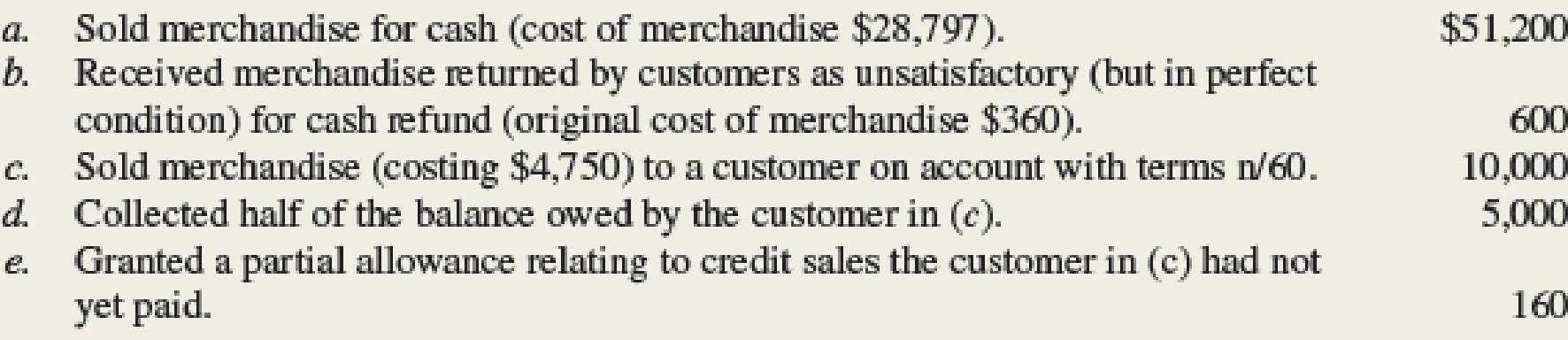
Required:
- 1. Compute Net Sales and Gross Profit for Hair World. No additional sales returns/allowances are expected.
- 2. Compute the gross profit percentage (using the formula shown in this chapter and rounding to one decimal place).
- 3. Prepare
journal entries to record transactions (a)–(e). - 4. Hair World is considering a contract to sell merchandise to a hair salon chain for $15,000. This merchandise will cost Hair World $10,000. Would this contract increase (or decrease) Hair World’s dollars of gross profit and its gross profit percentage?
1.
Calculate the sales revenue and gross profit of Incorporation H.
Explanation of Solution
Sales revenue:
Sales revenue is the amount received by the company from the sale of goods and services during day-to-day operations of the company within specified period of time.
Gross Profit:
Gross Profit is the difference between the net sales, and the cost of goods sold. Gross profit usually appears on the income statement of the company.
Calculate the sales revenue and gross profit of Incorporation H as follows:
| Particulars | Amount($) |
| Sales Revenue (1) | 61,200 |
| Less: Sales Returns and Allowances(2) | (760) |
| Net Sales | 60,440 |
| Less: Cost of Goods Sold (3) | 33,187 |
| Gross Profit | 27,253 |
Table (1)
Working note 1:
Calculate the value of sales revenue:
Working note 2:
Calculate the sales returns and allowances:
Working note 3:
Calculate the cost of goods sold:
Therefore, the net sales and gross profit of Incorporation H are $60,440 and $27,253 respectively.
2.
Calculate the gross profit percentage of Incorporation H.
Explanation of Solution
Gross Profit Percentage:
Gross profit is the financial ratio that shows the relationship between the gross profit and net sales. It represents gross profit as a percentage of net sales. Gross Profit is the difference between the net sales revenue, and the cost of goods sold. It can be calculated by dividing gross profit and net sales.
Calculate the gross profit percentage of Incorporation H as follows:
Therefore, the gross profit percentage of Incorporation H is 45.1%.
3.
Prepare journal entries to record the transaction from (a) to (e).
Explanation of Solution
Journal Entry:
Journal entry is the method of recording monetary business transactions in chronological order. It records the debit and credit aspects of each transaction to abide by the double-entry system.
Prepare journal entries to record the transaction from (a) to (e) as follows:
a. Record the sales revenue and cost of goods sold:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Cash | 51,200 | ||
| Sales Revenue | 51,200 | ||
| (To record the sales revenue received in cash ) |
Table (2)
- Cash is an asset and it increases the value of assets. Therefore, debit cash by $51,200.
- Sales revenue is component of stockholders’ equity and it increases the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, credit sales revenue by $51,200.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Cost of goods sold | 28,797 | ||
| Inventory | 28,797 | ||
| (To record the cost of goods sold incurred during the year) |
Table (3)
- Cost of goods sold is a component of stockholders’ equity and it decreases the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, debit cost of goods sold by $28,797.
- Inventory is an asset and it decreases the value of asset. Therefore, credit inventory by $28,797.
b. Record the sales return and the cost of inventory used for production.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Sales revenue | 600 | ||
| Cash | 600 | ||
| (To record the sales returns from customer) |
Table (4)
- Sales revenue is a component of stockholders’ equity and it increases the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, debit sales revenue by $600.
- Cash is an asset and it decreases the value of assets. Therefore, credit cash by $600
| .Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Inventory | 360 | ||
| Cost of goods sold | 360 | ||
| (To record the cost of inventory return) |
Table (5)
- Inventory is an asset and it increases the value of assets. Therefore, debit inventory by $360.
- Cost of goods sold is a component of stockholders’ equity and it decreases the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, credit cost of goods sold by $360.
c. Record the sale of merchandise on account:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Accounts Receivable | 10,000 | ||
| Sales Revenue | 10,000 | ||
| (To record the sales revenue received on account) |
Table (6)
- Accounts receivable is an asset and it increases the value of assets. Therefore, debit accounts receivable by $10,000.
- Sales revenue is component of stockholders’ equity and it increases the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, credit sales revenue by $10,000.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Cost of goods sold | 4,750 | ||
| Inventory | 4,750 | ||
| (To record the cost of inventory return) |
Table (7)
- Cost of goods sold is a component of stockholders’ equity and it decreases the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, debit cost of goods sold by $4,750.
- Inventory is an asset and it decreases the value of asset. Therefore, credit inventory by $4,750.
d. Record the cash receipt from customer.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Cash | 5,000 | ||
| Accounts Receivable | 5,000 | ||
| (To record the cash received from customers) |
Table (8)
- Cash is an asset and it increases the value of assets. Therefore, debit cash by $5,000.
- Accounts receivable is an asset and it decreases the value of assets. Therefore, credit accounts receivable by $5,000.
e. Record the sales return and allowances:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Sales revenue | 160 | ||
| Accounts receivable | 160 | ||
| (To record the sales returns from customer and allowances ) |
Table (9)
- Sales revenue is a component of stockholders’ equity and it decreases the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, debit sales returns and allowances by $160.
- Accounts receivable is an asset and it decreases the value of assets. Therefore, credit accounts receivable by $160.
4.
Describe whether the sale of given contract would increase (or decrease) the gross profit and gross profit percentage of Incorporation H.
Explanation of Solution
Describe whether the sales of given contract would increase (or decrease) the gross profit and gross profit percentage of Incorporation H as follows:
In this case, the gross profit percentage is decreased from 45.1% to 42.8% (5), because of the sale of contract.
Working note 4:
Calculate the gross profit from the sale of contract.
Working note 5:
Calculate the gross profit percentage of Company after the sale of contract.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING (LL)W/CONNECT
- Use the first-in, first-out (FIFO) cost allocation method, with perpetual inventory updating, to calculate (a) sales revenue, (b) cost of goods sold, and c) gross margin for A75 Company, considering the following transactions.arrow_forwardInventory Costing Methods Andersons Department Store has the following data for inventory, purchases, and sales of merchandise for December. Andersons uses a perpetual inventory system. All purchases and sales were for cash. Required: 1. Compute cost of goods sold and the cost of ending inventory using FIFO. 2. Compute cost of goods sold and the cost of ending inventory using LIFO. 3. Compute cost of goods sold and the cost of ending inventory using the average cost method. ( Note: Use four decimal places for per-unit calculations.) 4. Prepare the journal entries to record these transactions assuming Anderson chooses to use the FIFO method. 5. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Which method would result in the lowest amount paid for taxes?arrow_forwardUse the first-in, first-out method (FIFO) cost allocation method, with perpetual inventory updating, to calculate (a) sales revenue, (b) cost of goods sold, and c) gross margin for B75 Company, considering the following transactions.arrow_forward
- Use the last-in, first-out (LIFO) cost allocation method, with perpetual inventory updating, to calculate (a) sales revenue, (b) cost of goods sold, and c) gross margin for A75 Company, considering the following transactions.arrow_forwardBeginning inventory, purchases, and sales data for portable game players are as follows: The business maintains a perpetual inventory system, costing by the first-in, first-out method. a. Determine the cost of the merchandise sold for each sale and the inventory balance after each sale, presenting the data in the form illustrated in Exhibit 3. b. Based upon the preceding data, would you expect the inventory to be higher or lower using the last-in, first-out method?arrow_forwardUse the last-in, first-out method (LIFO) cost allocation method, with perpetual inventory updating, to calculate (a) sales revenue, (b) cost of goods sold, and c) gross margin for B75 Company, considering the following transactions.arrow_forward
- Uncle Butchs Hunting Supply Shop reports the following information related to inventory: Calculate Uncle Butchs ending inventory using the retail inventory method under the FIFO cost flow assumption. Round the cost-to-retail ratio to 3 decimal places.arrow_forwardAssume that the business in Exercise 7-3 maintains a perpetual inventory system, costing by the last-in, first-out method. Determine the cost of merchandise sold for each sale and the inventory balance after each sale, presenting the data in the form illustrated in Exhibit 4.arrow_forwardPerpetual inventory using FIFO Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales data for DVD players are as follows: The business maintains a perpetual inventory system, costing by the first-in, first-out method. A. Determine the cost of goods sold for each sale and the inventory balance after each sale, presenting the data in the form illustrated in Exhibit 3. B. Based upon the preceding data, would you expect the inventory to be higher or lower using the last-in, first-out method?arrow_forward
- Selected data on merchandise inventory, purchases, and sales for Celebrity Tan Co. and Ranchworks Co. are as follows: Instructions 1. Determine the estimated cost of the merchandise inventory of Celebrity Tan Co. on August 31 by the retail method, presenting details of the computations. 2. a. Estimate the cost of the merchandise inventory of Ranchworks Co. on November 30 by the gross profit method, presenting details of the computations. b. Assume that Ranchworks Co. took a physical inventory on November 30 and discovered that 369,750 of merchandise was on hand. What was the estimated loss of inventory due to theft or damage during March through November?arrow_forwardInventoriable Costs During the first month of operations, ABC Company incurred the following costs in ordering and receiving merchandise for resale. No inventory was sold. Required What amount do you recommend the company record as merchandise inventory on its balance sheet? Explain your answer. For any items not to be included in inventory, indicate their appropriate treatment in the financial statements.arrow_forwardInventory Costing: Average Cost Refer to the information for Filimonov Inc. and assume that the company uses a perpetual inventory system. Required: Calculate the cost of goods sold and the cost of ending inventory using the average cost method. ( Note: Use four decimal places for per-unit calculations and round all other numbers to the nearest dollar.)arrow_forward
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning





