
Concept explainers
Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold for four Inventory methods (LO6–3)
PROBLEMS: SET A
Sandra’s Purse Boutique has the following transactions related to its top-selling Cued purse for the month of October.
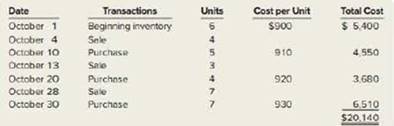
Required:
1 Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at October 31, using the specific identification method. The October 4 sale consists of purses from beginning inventory, the October 13 sale consists of one purse from beginning inventory and two purses from the October 10 purchase, and the October 28 sale consists of three purses from the October 10 purchase and four purses from the October 20 purchase.
2. Using FIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at October 31.
3. Using LIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at October 31.
4. Using weighted-average cast, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at October 31.
Calculate coding inventory, cost of goods
1.
To Compute: The ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the specific identification method.
Explanation of Solution
Specific identification method:
Specific identification method is a method in which the company records each item of the inventory at its original cost. Under this method, when the goods are sold, the company can easily identify the original costs at which they were purchased for. This method helps in arriving at the accurate cost of goods sold, and ending inventory.
Calculate the units of ending inventory.
| Calculation of Ending Inventory | |||
| Details | Number of Units | Rate Per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| Beginning balance | 6 | ||
| Less: Sales - October 4 | (4) | ||
| Balance | 2 | ||
| Less: Sales - October 13 | (1) | ||
| Balance | 1 | 900 | 900 |
| Purchases: | |||
| October 10 | 5 | ||
| Less: Sales - October 13 | (2) | ||
| Less: Sales - October 28 | (3) | ||
| Balance | 0 | 910 | 0 |
| Purchases: | |||
| October 20 | 4 | ||
| Less: October 28 | (4) | - | |
| Balance | 0 | 920 | - |
| October 30 | 7 | 930 | 6,510 |
| Ending Inventory | 7,410 | ||
Table (1)
Therefore, the cost of Ending Inventory in specific identification method is $7,410.
Calculate the cost of goods sold:
| Calculation of Cost of Goods Sold | |||
| Details | Number of Units | Rate Per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| October 1: Beginning balance | 4 | 900 | 3,600 |
| October 1: Beginning balance | 1 | 900 | 900 |
| October 10: Purchase | 2 | 910 | 1,820 |
| October 10: Purchase | 3 | 910 | 2,730 |
| October 20: Purchase | 4 | 920 | 3,680 |
| March 22 Purchase | 4 | 920 | 3,680 |
| Cost of Goods Sold | 14 | 12,730 | |
Table (2)
Therefore, the Cost of Goods Sold in specific identification method is $12,730.
2.
To Compute: The ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the FIFO method.
Explanation of Solution
First-in-First-Out:
In First-in-First-Out method, the costs of the initially purchased items are considered as cost of goods sold, for the items which are sold first. The value of the ending inventory consists of the recent purchased items.
Calculate the total Cost and units of Goods Available for Sales.
| Calculation of Goods Available for Sales | |||
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| Beginning balance | 6 | 900 | 5,400 |
| Add: Purchases | |||
| October 10 | 5 | 910 | 4,550 |
| October 20 | 4 | 920 | 3,680 |
| October 30 | 7 | 930 | 6,510 |
| Total Goods available for Sale | 22 | 20,140 | |
Table (3)
Calculate the units of ending inventory.
| Calculation of Ending Inventory (Units) | ||
| Details | Number of Units | Number of Units |
| Beginning balance | 6 | |
| Add: Purchases | ||
| October 10 | 5 | |
| October 20 | 4 | |
| October 30 | 7 | |
| Total Goods available for Sale | 22 | |
| Less: Sales | ||
| October 4 | 4 | |
| October 13 | 3 | |
| October 28 | 7 | |
| Total Sales | (14) | |
| Ending Inventory | 8 | |
Table (4)
Calculate the cost of ending inventory.
The ending inventory is 8 units.
| Calculation of Cost of Ending Inventory | |||
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| October 20 | 1 | 920 | 920 |
| October 30 | 7 | 930 | 6,510 |
| Ending Inventory | 8 | 7,430 | |
Table (5)
In FIFO method the ending inventory comprises of the inventory purchased last, because the inventory purchased first were sold first.
Therefore, the cost of Ending Inventory in the FIFO is $7,430.
Cost of Goods Sold.
14 units are sold.
| Calculation of Cost of Goods Sold | |||
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| Beginning Inventory | 6 | 900 | 5,400 |
| March 9 Purchase | 5 | 910 | 4,550 |
| March 22 Purchase | 3 | 920 | 2,760 |
| Cost of Goods Sold | 14 | 12,710 | |
Table (6)
As it is FIFO method the earlier purchased items will sell first.
Therefore, the Cost of Goods Sold in the FIFO Method is $12,710
3.
To Compute: The ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the LIFO method.
Explanation of Solution
Last-in-Last-Out:
In Last-in-First-Out method, the costs of last purchased items are considered as the cost of goods sold, for the items which are sold first. The value of the closing stock consists of the initial purchased items.
Ending Inventory:
Calculate the cost of ending inventory.
| Calculation of Cost of Ending Inventory | |||
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| Beginning Inventory | 6 | 900 | 5,400 |
| Ending Inventory | 6 | 900 | 5,400 |
Table (7)
- The ending inventory is 8 units (Refer to Table 4).
- In LIFO method, the ending inventory comprises of the inventory purchased first, because the inventory purchased last were sold first.
- Therefore, the ending inventory of 8 units is from the beginning inventory.
Therefore, the cost of Ending Inventory in the LIFO method is $5,400.
Cost of Goods Sold:
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| October10 Purchase | 3 | 910 | 2,730 |
| October20 Purchase | 4 | 920 | 3,680 |
| October30 Purchase | 7 | 930 | 6,510 |
| Cost of Goods Sold |
14 | 2,760 |
12,920 |
Table (8)
- 8 units are sold (Refer to Table 4).
- As it is LIFO method the recent purchased items will sell first.
- Hence, the cost of goods sold will be the recent purchased items.
Therefore, the Cost of Goods Sold in the LIFO Method is $12,920.
4.
To Compute: The ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the Weighted-average method.
Explanation of Solution
Weighted-average cost method:
Under Weighted average cost method, the company calculates a new average cost after every purchase is made. It is determined by dividing the cost of goods available for sale by the units on hand.
Calculate the Weighted-average cost.
Total cost of goods available for sale = $20,140 (Refer to table - 3)
Total units of goods available for sale = 22 units (Refer to table - 3)
Calculate the amount of Ending Inventory.
Weighted- average cost per unit = $915.45 (1)
Number of units in ending inventory = 22 units (Refer to table - 4)
Therefore, the cost of Ending Inventory in the Weighted-average-cost Method is $7,323.6.
Calculate the Cost of Goods Sold.
Weighted- average cost per unit= $915.45 (1)
Units sold = 14 units
Therefore, the Cost of goods sold in the Weighted-average-cost Method is $12,816.30.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING W/ACCESS >CI<
- Refer to the information for Morgan Inc. above. If Morgan uses a perpetual inventory system, what is the cost of ending inventory under FIFO at April 30? a. $32,500 b. $38,400 c. $63,600 d. $69,500arrow_forward( Appendix 6B) Refer to the information for Morgan Inc. above. If Morgan uses a periodic inventory system, what is the cost of ending inventory under LIFO at April 30? a. $32,800 b. $38,400 c. $63,600 d. $69,200arrow_forwardLongmire Sons nude sales un credit to Alderman Sports totaling 500,000 on April 18. The cost of the goods sold is 400,000. Longmire estimates 3% of its sales to Alderman may be returned. On May 22, 9,000 worth of goods (with a cost of 7,200) are returned by Alderman. Longmire uses a periodic inventory system. Prepare the related journal entries for Longmire Sons.arrow_forward
- Company Elmira reported the following cost of goods sold but later realized that an error had been made in ending inventory for year 2021. The correct inventory amount for 2021 was 32,000. Once the error is corrected, (a) how much is the restated cost of goods sold for 2021? and (b) how much is the restated cost of goods sold for 2022?arrow_forwardRefer to the information in E22-13. Required: Prepare the correcting journal entries if the company discovers each error 2 years after it is made and it has closed the books for the second year. Ignore income taxes. E22-13: The following are independent errors made by a company that uses the periodic inventory system: a. Goods in transit, purchased on credit and shipped FOB destination, 10,000, were included in purchases but not in the physical count of ending inventory. b. Purchase of a machine for 2,000 was expensed. The machine has a 4-vear life, no residual value, and straight-line depreciation is used. c. Wages payable of 2,000 were not accrued. d. Payment of next years rent, 4,000, was recorded as rent expense. e. Allowance for doubtful accounts of 5,000 was not recorded. The company normally uses the aging method. f. Equipment with a book value of 70,000 and a fair value of 100,000 was sold at the beginning of the year. A 2-year, non-interest-bearing note for 129,960 was received and recorded at its face value, and a gain of 59,960 was recognized. No interest revenue was recorded and 14% is a fair rate of interest.arrow_forwardhow do I calculate ending inventory for FIFO, LiFO, and average. I am working on problem p7-2 page 7-48 of the Intermediate accounting book. As an accountant for Lee Co. Your supervisor gave you the following calculations of the gross profit for the first quarter. Prepare the ending inventory in units and dollars and proving the cost of good sold shown here. example: Sales 500,000 @ $50 each COGS 200,000 GProfit 300,000 Begin inventory 12,000 units @ 20.00 Purch 4,000 units @ 21.00 Purch 6,000 units @ 22.00 Purch 8,000 units @ 23.00 beginning inventory + purchases = 30,000 units, & $640,000. Just not sure how to calculate my ending inventory.arrow_forward
- A company just starting a business purchased three inventory items at the following prices: March 2, $205; March 7, $215; and March 15, $235. If the company sold one unit for $285 on March 10 and one unit for $305 on March 20 and uses the average cost formula in a perpetual inventory system, what is the cost of ending inventory? $218.33 $222.50 $305.00 $235.00arrow_forwardFlair Company sells a variety of items to its customers. At December 31, the balance of Flair's ending inventory account was P5,000,000 and the allowance for inventory write down account before any adjustment was P200,000. Relevant information about the inventories and the breakdown of inventory cost and market data at December 31 follows: (see attached picture) Question: How much is the loss on inventory write down to be included in Flair's cost of sales? A. P550,000B. P350,000 C. P200,000 D. P100,000arrow_forwardM7-11 to 13 Calculating Cost of Goods Available for Sale, Cost of Goods Sold, and Ending Inventory under Periodic FIFO, LIFO, and Weighted Average Cost [LO 7-3] [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] In its first month of operations, Literacy for the Illiterate opened a new bookstore and bought merchandise in the following order: (1) 340 units at $9 on January 1, (2) 630 units at $10 on January 8, and (3) 930 units at $12 on January 29. M7-11 Calculating Cost of Goods Available for Sale, Cost of Goods Sold, and Ending Inventory under Periodic FIFO [LO 7-3] Assume 1,170 units are on hand at the end of the month, calculate the cost of goods available for sale, ending inventory, and cost of goods sold under FIFO. Assume a periodic inventory system is used. (Round "Cost per Unit" to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forward
- Required information Problem 6-1A (Algo) Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold for four inventory methods (LO6-3) Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.]Sara's Boutique has the following transactions related to its top-selling Gucci purse for the month of October. Sara's Boutique uses a periodic inventory system. Date Transactions Units Unit Cost Total Cost October 1 Beginning inventory 6 $760 $4,560 October 4 Sale 4 October 10 Purchase 5 770 3,850 October 13 Sale 3 October 20 Purchase 4 780 3,120 October 28 Sale 7 October 30 Purchase 8 790 6,320 $17,850 Problem 6-1A (Algo) Part 3 3. Using LIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at October 31.arrow_forwardRequired information Problem 6-1A (Algo) Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold for four inventory methods (LO6-3) Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.]Sara's Boutique has the following transactions related to its top-selling Gucci purse for the month of October. Sara's Boutique uses a periodic inventory system. Date Transactions Units Unit Cost Total Cost October 1 Beginning inventory 6 $760 $4,560 October 4 Sale 4 October 10 Purchase 5 770 3,850 October 13 Sale 3 October 20 Purchase 4 780 3,120 October 28 Sale 7 October 30 Purchase 8 790 6,320 $17,850 Problem 6-1A (Algo) Part 4 4. Using weighted-average cost, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at October 31. (Round your intermediate calculations to 4 decimal places and final answers to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forwardCalculate ending inventory, cost of goods sold, sales revenue, and gross profit for four inventory methods (LO6-3, 6-4, 6-5) Ariana Bicycle Shop has the following transactions related to its top-selling Mongoose mountain bike for the month of March. Ariana Bicycle Shop uses a periodic inventory system. Date Transactions Units Unit Cost Total Cost March 1 Beginning inventory 20 $235 $4,700 March 5 Sale ($370 each) 15 March 9 Purchase 10 255 2,550 March 17 Sale ($420 each) 8 March 22 Purchase 10 265 2,650 March 27 Sale ($445 each) 12 March 30 Purchase 9 285 2,565 $12,465 For the specific identification method, the March 5 sale consists of bikes from beginning inventory, the March 17 sale consists of bikes from the March 9 purchase, and the March 27 sale consists of four bikes from beginning inventory and eight bikes from the March 22 purchase. Required: 1. Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31, using the specific identification method.arrow_forward
 Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College



