
(a)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given solvent is suitable for a reaction involving
Concept introduction:
Leveling effects refers to the effect of a solvent on the behavior of acids and bases. If the reactant is a very strong acid or base, it can react with the solvent in an undesired proton transfer reaction. At equilibrium, the strongest acid that can occur in solution is the protonated solvent, and the strongest base that can occur in solution is the deprotonated solvent. For the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant if the reactant (lower
Answer to Problem 6.9P
With respect to the leveling effect, water is not a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
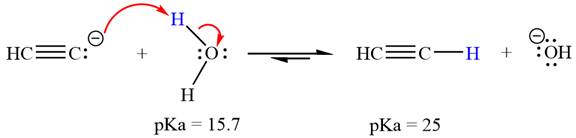
Water,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(b)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given solvent is suitable for a reaction involving
Concept introduction:
Leveling effects refers to the effect of a solvent on the behavior of acids and bases. If the reactant is a very strong acid or base, it can react with the solvent in an undesired proton transfer reaction. At equilibrium, the strongest acid that can occur in solution is the protonated solvent, and the strongest base that can occur in solution is the deprotonated solvent. For the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant if the reactant (lower
Answer to Problem 6.9P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanol is not a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of

Ethanol,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(c)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given solvent is suitable for a reaction involving
Concept introduction:
Leveling effects refers to the effect of a solvent on the behavior of acids and bases. If the reactant is a very strong acid or base, it can react with the solvent in an undesired proton transfer reaction. At equilibrium, the strongest acid that can occur in solution is the protonated solvent, and the strongest base that can occur in solution is the deprotonated solvent. For the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant if the reactant (lower
Answer to Problem 6.9P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanamide is not a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
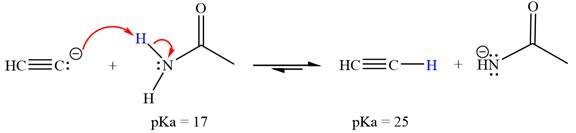
Ethanamide,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(d)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given solvent is suitable for a reaction involving
Concept introduction:
Leveling effects refers to the effect of a solvent on the behavior of acids and bases. If the reactant is a very strong acid or base, it can react with the solvent in an undesired proton transfer reaction. At equilibrium, the strongest acid that can occur in solution is the protonated solvent, and the strongest base that can occur in solution is the deprotonated solvent. For the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant if the reactant (lower
Answer to Problem 6.9P
With respect to the leveling effect,
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
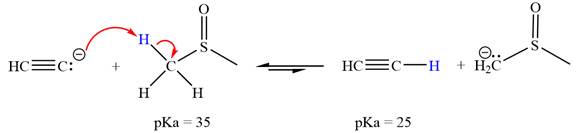
Acetylene,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(e)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given solvent is suitable for a reaction involving
Concept introduction:
Leveling effects refers to the effect of a solvent on the behavior of acids and bases. If the reactant is a very strong acid or base, it can react with the solvent in an undesired proton transfer reaction. At equilibrium, the strongest acid that can occur in solution is the protonated solvent, and the strongest base that can occur in solution is the deprotonated solvent. For the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant if the reactant (lower
Answer to Problem 6.9P
With respect to the leveling effect,
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
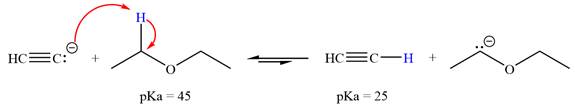
Acetylene,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms: Study Guide/solutions Manual (second)
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





