
a)
Graph showing
a)
Answer to Problem 2CYU
MC’ is the marginal cost curve which is horizontal at $400.
Explanation of Solution
When the marginal cost curve increases from $200 to $400, then the marginal cost curve shifts upward parallelly.
Introduction:
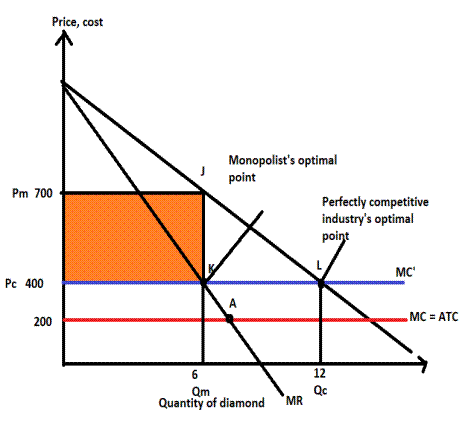
In the monopoly market, the profit-maximizing output level is determined where MR=MC, and in the
b)
Graph showing profit-maximizing maximizing price and output.
b)
Answer to Problem 2CYU
Output is 6 and the price is $700.
Explanation of Solution
Monopolist optimal point at K where MR=MC, which determines the profit-maximizing output i.e., 6 and price i.e., $700.
Introduction:
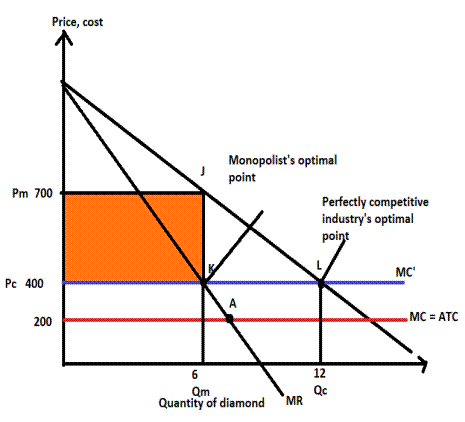
A monopolist charges a different price from different consumers for the same quantity. Profit-maximizing output and price are determined at the point where the marginal revenue curve intersects the marginal cost curve.
c)
Graph showing the profit of the monopolist.
c)
Answer to Problem 2CYU
Orange-shaded region.
Explanation of Solution
The orange-shaded region is the profit of the monopolist where marginal cost and marginal revenue equate.
Introduction:
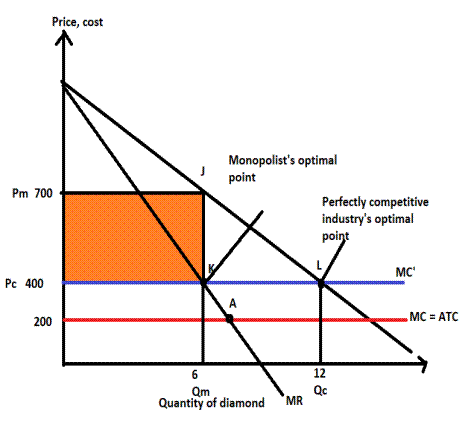
Profit is the difference between total revenue and total cost.
d)
Quantity and associated profit produced in the case of a perfectly competitive market.
d)
Answer to Problem 2CYU
The optimal output level is 12 and zero economic profit.
Explanation of Solution
Point L is the optimal point in a perfectly competitive industry because P=MC, which determines 12
Introduction:
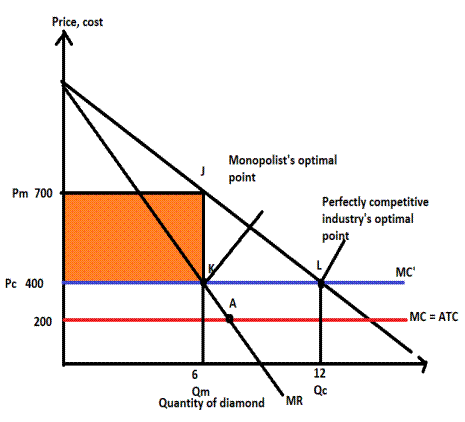
Perfectly competitive market output is determined where price equates to marginal cost.
Chapter 61 Solutions
Krugman's Economics For The Ap® Course

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





