
Concept explainers
(a)
Find the standard deviation of the x distribution.
(a)
Answer to Problem 34P
The standard deviation of the x distribution is 5.25 ounces.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Rule of Thumb:
The formula for standard deviation using
In the formula, range is the obtained by subtracting the low value from the high value.
The variable x is a random variable that represents the weight (in ounces) of a healthy 10-week-old kitten.
The 95% of data range from 14 to 35 ounces.
The standard deviation is,
Hence, the standard deviation of the x distribution is 5.25 ounces.
(b)
Find the probability that a healthy 10-week-old kitten would weigh less than 14 ounces.
(b)
Answer to Problem 34P
The probability that a healthy 10-week-old kitten would weigh less than 14 ounces is 0.0228.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Z score:
The number of standard deviations the original measurement x is from the value of mean
In the formula, x is the raw score,
Substitute x as 14,
Use the Appendix II: Tables, Table 5: Areas of a Standard Normal Distribution: to obtain probability less than –2.
- Locate the value –2.0 in column z.
- Locate the value 0.00 in top row.
- The intersecting value of row and column is 0.0228.
The probability is,
Hence, the probability that a healthy 10-week-old kitten would weigh less than 14 ounces is 0.0228.
(c)
Find the probability that a healthy 10-week-old kitten would weigh more than 33 ounces.
(c)
Answer to Problem 34P
The probability that a healthy 10-week-old kitten would weigh more than 33 ounces is 0.0526.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Substitute x as 33,
Use the Appendix II: Tables, Table 5: Areas of a Standard
- Locate the value 1.6 in column z.
- Locate the value 0.02 in top row.
- The intersecting value of row and column is 0.9474.
The probability is,
Hence, the probability that a healthy 10-week-old kitten would weigh more than 33 ounces is 0.0526.
(d)
Find the probability that a healthy 10-week-old kitten would weigh between 14 and 33 ounces.
(d)
Answer to Problem 34P
The probability that a healthy 10-week-old kitten would weigh between 14 and 33 ounces is 0.9246.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Substitute x as 14,
Substitute x as 33,
Use the Appendix II: Tables, Table 5: Areas of a Standard Normal Distribution: to obtain probability less than –2.
- Locate the value –2.0 in column z.
- Locate the value 0.00 in top row.
- The intersecting value of row and column is 0.0228.
Use the Appendix II: Tables, Table 5: Areas of a Standard Normal Distribution: to obtain probability less than 1.62.
- Locate the value 1.6 in column z.
- Locate the value 0.02 in top row.
- The intersecting value of row and column is 0.9474.
The probability is,
Hence, the probability that a healthy 10-week-old kitten would weigh between 14 and 33 ounces is 0.9246.
(e)
Find the cutoff point for the weight of an undernourished kitten.
(e)
Answer to Problem 34P
The cutoff point for the weight of an undernourished kitten is 17.8 ounces.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The weight is in the bottom 10% of the probability distribution of weights is called undernourished.
Step by step procedure to obtain probability plot using MINITAB software is given below:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability > OK.
- Enter the Mean as 24.5, and Standard deviation as 5.25.
- From Distribution, choose ‘Normal’ distribution.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Choose Probability and Left Tail, for the region of the curve to shade.
- Enter the Probability as 0.10.
- Click OK.
Output using MINITAB software is given below:
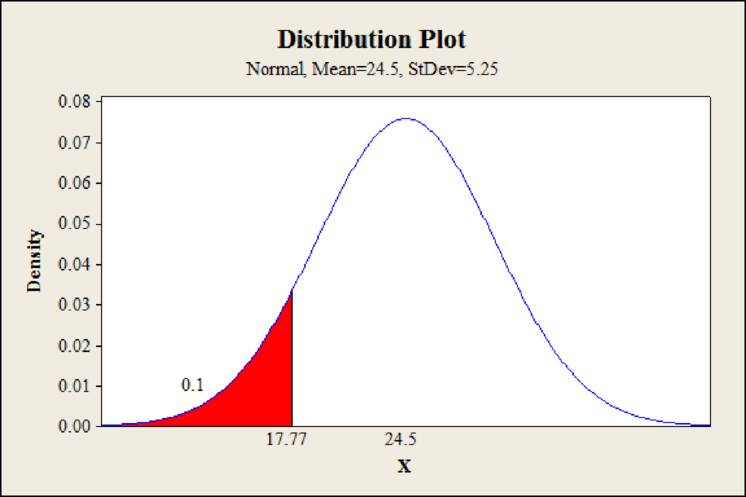
From Minitab output, the cutoff point for the weight of an undernourished kitten is 17.77.
Hence, the cutoff point for the weight of an undernourished kitten is 17.8 ounces.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Bundle: Understandable Statistics: Concepts And Methods, 12th + Webassign, Single-term Printed Access Card
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





