
a (1).
Calculate amount of cash that Company A pay for interest during 2014.
a (1).
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the amount of cash did Company A pay for interest during 2014.
On March 1, 2014, Company A borrowed $60,000 cash from bank at 6% interest rate and due on September 1, 2014.
Hence, cash paid for interest expense during 2014 is $1,800.
a (2).
Calculate the amount of interest expense is reported on Company A’s income statement for 2014.
a (2).
Explanation of Solution
Interest expense: Interest expense is an expense account, and it decreases the value of net income. Hence, interest expense appears in the income statement.
Calculate the Amount of interest expense is reported on Company A’s income statement for 2014.
On March 1, 2014, Company A borrowed $60,000 cash from bank at 6% interest rate and due on September 1, 2014. On October 1, 2014, Company A borrowed $50,000 cash from bank at 7% interest rate and a one-year term to maturity.
| Interest expense on $70,000 borrowings | $1,800 |
| Interest expense om$20,000 borrowings | $875 |
| Total interest expense amount | $2,675 |
Table (1)
Hence, the amount of interest expense is reported on Company A’s income statement for 2014 is $2,675.
a (3).
Calculate the amount of warranty expense for 2014.
a (3).
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the amount of warranty expense for 2014.
Company A provides a 90-days warranty on the merchandise sold. The estimated warranty expense is to be 2% of sales. Total sales are $240,000.
Hence, the amount of warranty expense for 2014 is $4,800.
b.
Prepare the current liabilities section of the balance sheet at December 31, 2014.
b.
Answer to Problem 28P
Current liabilities: The debts obligations owed by a company to creditors and suppliers and are to be paid within a year are referred to as current liabilities.
Prepare the current liabilities section of the balance sheet at December 31, 2014.
| Company A | |
| Balance sheet (partial) | |
| As on December 31, 2014 | |
| Current Liabilities: | |
| Interest Payable (1) | $875 |
| Sales Tax Payable (2) | 2,800 |
| Warranty Payable (3) | 1,000 |
| Notes Payable (4) | 50,000 |
| Total Current Liabilities | $54,675 |
Table (2)
Hence, total current liabilities as on December 31, 2014 are $54,675.
Explanation of Solution
Current liability: Current liability is an obligation that the companies need to pay from its current assets or creation of other current liabilities within a fiscal year or the operating cycle whichever is higher.
Working note 1: Prepare interest payable account:
| Interest payable | |||
| 6. Refer table (1) | $875 | ||
| Ending Balance | $875 | ||
Working note 2: Prepare sales tax payable account:
| Sales tax payable | |||
| 4. | $14,000 | 2. | $16,800 |
| Ending Balance | 2,800 | ||
Working note 3: Prepare warranty payable account:
| Warranty payable | |||
| 7. | $3,800 | 3. | $4,800 |
| Ending Balance | 1,000 | ||
Working note 4: Prepare Note payable account:
| Notes payable | |||
| 1. | 60,000 | ||
| 5. | 60,000 | 6. | 50,000 |
| Ending Balance | 50,000 | ||
Note: A customer filed a lawsuit against Company A for $150,000 for breach of contract. Company A’s attorney does not believe the suit has merit. Hence, it is deemed to be remote obligation (
c.
Show the effect of these transactions on the financial statements using a horizontal statements model. Use + for increase, − for decrease, and NA for not affected. In the Cash Flow column, indicate whether the item is an operating activity (OA), investing activity (IA), or financing activity (FA).
c.
Explanation of Solution
Show the effect of these transactions on the financial statements using a horizontal statements model.
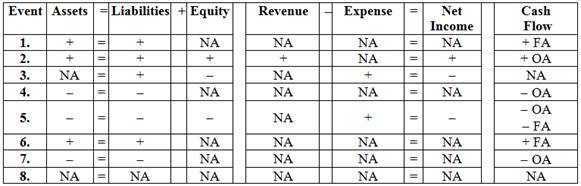
Table (3)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
SURVEY OF ACCOUNTING-ACCESS

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





