
Using Appendix G, complete the following table that describes the characteristics of the Galilean moons of Jupiter, starting from Jupiter and moving outward in distance.
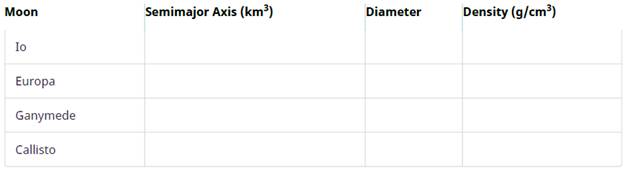
Table A
This system has often been described as a mini solar system. Why might this be so? If Jupiter were to represent the Sun and the Galilean moons represented planets, which moons could be considered more terrestrial in nature and which ones more like gas/ice giants? Why? (Hint: Use the values in your table to help explain your categorization.)
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
Astronomy
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
An Introduction to Thermal Physics
Sears And Zemansky's University Physics With Modern Physics
University Physics Volume 2
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (4th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
- Calculate the radius of Jupiters Roche limit for a satellite with density equal to the planet. Which of Jupiters moons is closest to the Roche limit? What might that tell you about the relationship between that moon and Jupiters ring? (Note: Necessary data are given in Celestial Profile: Jupiter and Appendix Table A-11.)arrow_forwardWhat is the density of Jupiter’s moon Europa (see Appendix G for data on moons)? Show your work.arrow_forwardAgain using Appendix F, which planets might you expect to have extreme seasons? Whyarrow_forward
- Describe the different processes that lead to substantial internal heat sources for Jupiter and Saturn. Since these two objects generate much of their energy internally, should they be called stars instead of planets? Justify your answer.arrow_forwardUse the information in Appendix G to calculate what you would weigh on Titan, Io, and Uranus’ moon Miranda.arrow_forwarda) What are the characteristics of a terrestrial planet? b) What are the characteristics of aJovian planet?arrow_forward
- I would like you to compare the size of some of the largest moons of the solar system to their host planets. Using diameters of 12,700 km, and 140,000 km, 116,000 km for Earth, Jupiter, and Saturn respectively, please provide the ratios of the following moons to their host planets (you can use Table 12.1 from the book to get the diameters of the moons): Luna (Earth's moon), Io, Callisto, Ganymede, Europa, and Titan. After collecting those ratios, please tell me one thing that you notice that stands out about those results.arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements accurately describes our current understanding of the solar system? a. There are no metals in the solar system beyond Jupiter and its orbit. b. Terrestrial worlds are so small because their large atmospheres were stripped away in time by Jupiter. c. Jupiter and Saturn are made of strictly a combination of hydrogen and helium, and both objects lack a planetary core. d. Various ices can contribute to the mass of planetary cores if we are at a great enough distance from the sun.arrow_forwardLet's use Kepler's laws for the inner planets. Use the following distances from the sun to calculate the orbital period for each of these planets. Express your answer in terms of Earth years to two significant figures. Note: Use Kepler's law directly. Don't just Google the answers, as they will be a little bit different. When you have calculated them, only submit the value for Mercury. Planet Distance from the sun Period of orbit around the sun Earth 150 million km ___ Earth years Mercury 58 million km ___ Earth years Venus 108 million km ___ Earth years Mars 228 million km ___ Earth yearsarrow_forward
- What is the angular diameter of Saturn (in arc seconds) as seen from Earth when the two planets are closest together? Hint: Use the small-angle formulaarrow_forwardb. From the above data, determine the period of Europa, the distance between Jupiter and Ganymede, and the speed of Callisto. Show all work.arrow_forwardNeptune is an average distance of 4.5×10^9 km from the Sun. - How many astronomical units (AU) is Neptune from the Sun? One AU is 1.50×10^8 km. - Estimate the length of the Neptunian year using your answer from part (a).arrow_forward
 AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning




