
Concept explainers
(a)
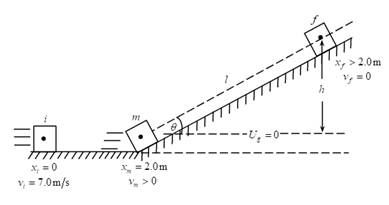
The distance traveled by block along the incline plane.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The mass of block is
The initial speed of block is
The coefficient of friction is
The angle of incline with the horizontal is
Formula used:
Write the expression for friction force along the incline.
Here,
Write the expression for thermal energy.
Here,
Substitute
Write the expression for change in potential energy.
Here,
Write the expression for change in kinetic energy.
Here,
Total energy of block is conserved at all points. Work done by external force is equal to the sum of change in gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy and thermal energy.
Write the expression of work done by external force.
Here,
There is no external force acting on the block; so, the work done by external force is zero.
Substitute
Substitute
Calculation:
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the distance traveled by block along the incline is
(b)
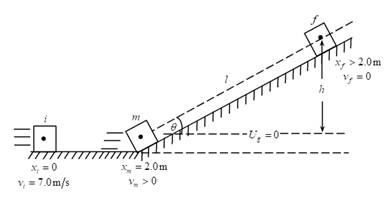
The speed of the block when it has traveled half the distance in part (a).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The mass of block is
The initial speed of block is
The coefficient of friction is
The angle of incline with the horizontal is
Formula used:
Write the expression for friction force along the incline.
Here,
Write the expression for thermal energy.
Here,
Substitute
Write the expression for change in potential energy.
Here,
Write the expression for change in kinetic energy.
Here,
Total energy of block is conserved at all points. Work done by external force is equal to the sum of change in gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy and thermal energy.
Write the expression of work done by external force.
Here,
There is no external force acting on the block; so, the work done by external force is zero.
Substitute
Substitute
For object velocity at halfway on incline plane:
Substitute
Substitute
Calculation:
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the speed of the block when it has traveled half the distance in part (a)is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Vol. 3
- At what initial speed should a box of mass m be thrown parallel to the surface of the inclined plane from the lower end of an inclined plane with friction making a 30 degree angle with the horizontal direction so that it can travel 3m on the inclined plane? (The kinetic coefficient of friction between the box and the surface of the inclined plane is mk = 0.02.)arrow_forwardA brick of mass m is initially at rest at the peak of an inclined plane which has a height of 5.52m and has an angle of θ=20.3∘ with respect to the horizontal. After it has been released, it is found to be traveling at v=0.84m/s a distance d after the end of the inclined plane, as shown. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the brick and the plane is μp=0.1, and the coefficient of friction on the horizontal surface is μr=0.2. What is the speed of the brick, in meters per second, just after it leaves the inclined plane? Find the distance, d, in meters.arrow_forwardA skier is on a 25 degree slope and his mass is 80kg. If his constant velocity and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the ski and the snow is 9 m/s and 0.80, respectively, compute his velocity when he has skid 20m from his initial position and a drag force experienced by the skier equivalent to a magnitude of 0.6V^2.arrow_forward
- A 3.0 kg block is set moving with an initial speed of 20 m/s on a rough horizontal surface. If the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.40, how far does the block travel before it stops?arrow_forwardA skier starts from rest at the top of a hill that is inclined 10.5°with respect to the horizontal. The hillside is 2.00 x 102 m long,and the coefficient of friction between snow and skis is 0.075 0.At the bottom of the hill, the snow is level and the coefficientof friction is unchanged. How far does the skier glide along thehorizontal portion of the snow before coming to rest?arrow_forwardStarting from rest, a 92-kg firefighter slides down a fire pole. The average frictional force exerted on him by the pole has a magnitude of 710 N, and his speed at the bottom of the pole is 3.5 m/s. How far did he slide down the pole?arrow_forward
- A crate of mass mm is initially at rest at the peak of an inclined plane which has a height of 4.43m4.43m and makes an angle of θ=24.2 with respect to the horizontal. After it has been released, it is found to be traveling at v=0.99m/s a distance d after the end of the inclined plane, as shown. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the plane is μp=0.1, and the coefficient of friction on the horizontal surface is μr=0.2. a.-Find the distance, d, in meters.arrow_forwardIn the figure, a block of mass m is moving along the horizontal frictionless surface with a speed of 10 m/s. If the slope is 37° and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the incline is 02 how far (D) does the block travel up the incline?arrow_forwardA horizontal force is applied to an object weighing 392 N that causes its speed to increase uniformly from 0 m/s to 6 m/s in 3 seconds. If we disregard the friction value, calculate the applied forcearrow_forward
- a block of mass m is initially at rest at the highest point of an inclined plane, which has a height of 6.8 m and has an angle of 0=16 degrees with respect to the horizontal. After it has been released, you perceived it to be moving at v=0.55 m/s a distance d after the end of the inclined plane as shown. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the plane i sup=0.1 and the coefficient of friction on the horizontal surface its ur=0.2. a)what is the speed of the block, in meters per second, just after it leaves the inclined plane? b)Find the distance, d, in meters.arrow_forwardA block of mass m is initially at rest at the top of an inclined plane which has a height of 6.18m and makes an angle of θ=25.2∘ with respect to the horizontal. After being released, it is observed to be traveling at v=0.14m/s a distance d after the end of the inclined plane, as shown. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the plane is μp=0.1, and the coefficient of friction on the horizontal surface is μr=0.2. Find the distance, d, in meters.arrow_forwardA 1.5-kg box is released from rest on a frictionless surface that is sloped at θ = 35◦ above the horizontal.After sliding 1.0 m down the slope, the box transitions smoothly to a rough, horizontal surface, slides forsome distance, and then comes to a stop. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and thehorizontal surface is 0.12, how far along the horizontal surface does the box travel?arrow_forward
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
