
Concept explainers
The discrete time signal of given analog voltage by using different time samples. Also, plot each series as a function of time and state the difference between the discrete representations of analog signal.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Concept Used:
At any sampling interval
Calculation:
For
At time
At time
To compute the remaining points ofE(t) using an increment of 0.125s, we use a spreadsheet tool.
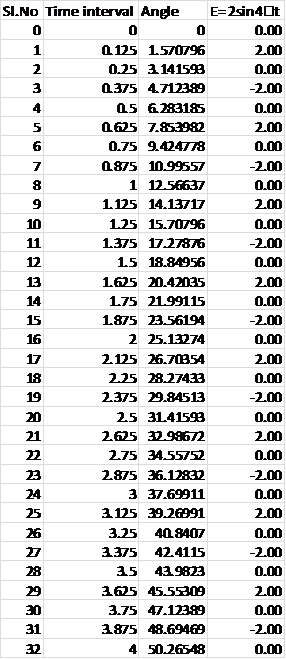
The graph plotted between the amplitude and time interval is:
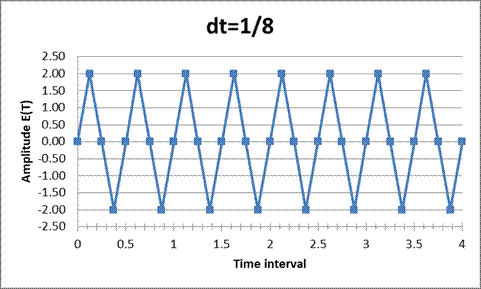
The analog signal was converted into a discrete time signal using a spreadsheet tool and a plot of amplitude vs time has been plotted for the time increment of 1/8 s.
For
At time
At time
To compute the remaining points ofE(t) using an increment of 0.2s, we use a spreadsheet tool.
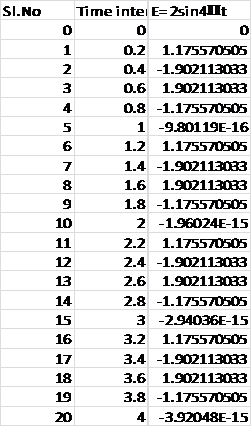
The graph plotted between the amplitude and time interval is:
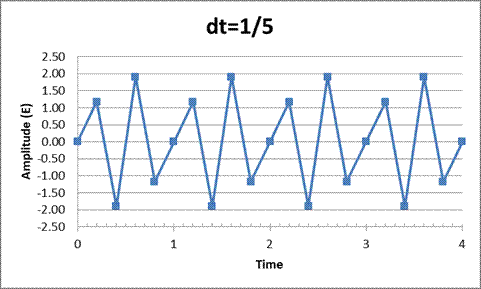
The analog signal was converted discrete time signal using a spreadsheet tool and a plot of amplitude vs time has been plotted for the time increment of 1/5 s.
For
At time
At time
To compute the remaining points ofE(t) using an increment of 0.333 s, we use a spreadsheet tool.

The graph plotted between the amplitude and time interval is:
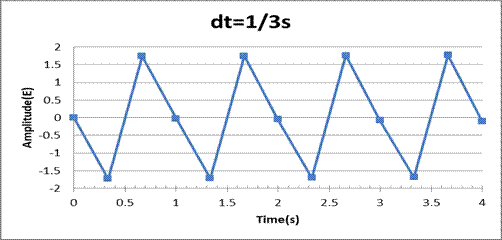
The analog signal was converted discrete time signal using a spreadsheet tool and a plot of amplitude vs time has been plotted for the time increment of 1/3 s.
At time
At time
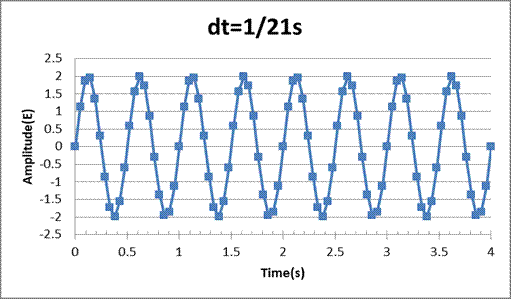
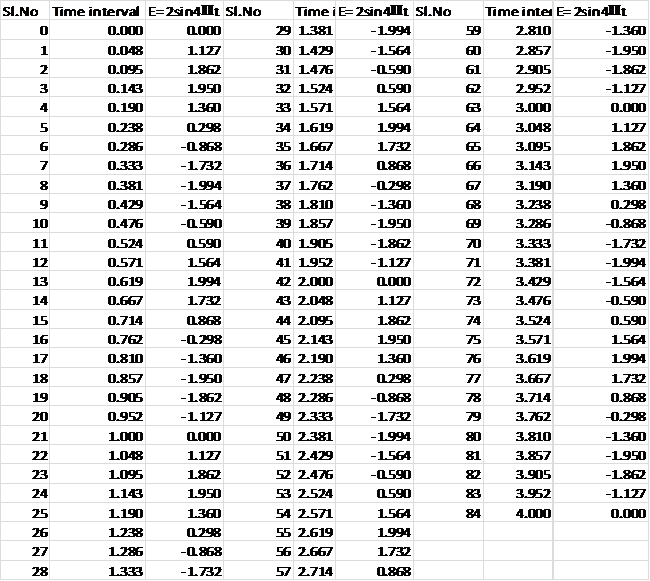
To compute the remaining points ofE(t) using an increment of 0.0476s, we use a spreadsheet tool, The graph plotted between the amplitude and time interval is:
The data set is given below:
The analog signal was converted discretized time signal using a spreadsheet tool and a plot of amplitude vs time has been plotted for the time increment of 1/21 s.
The nature of the plot for
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





