
Study Guide for Campbell Biology
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134443775
Author: Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Jane B. Reece, Martha R. Taylor, Michael A. Pollock
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 7, Problem 7TYK
Use the following U-tube setup to answer questions 6 through 8.
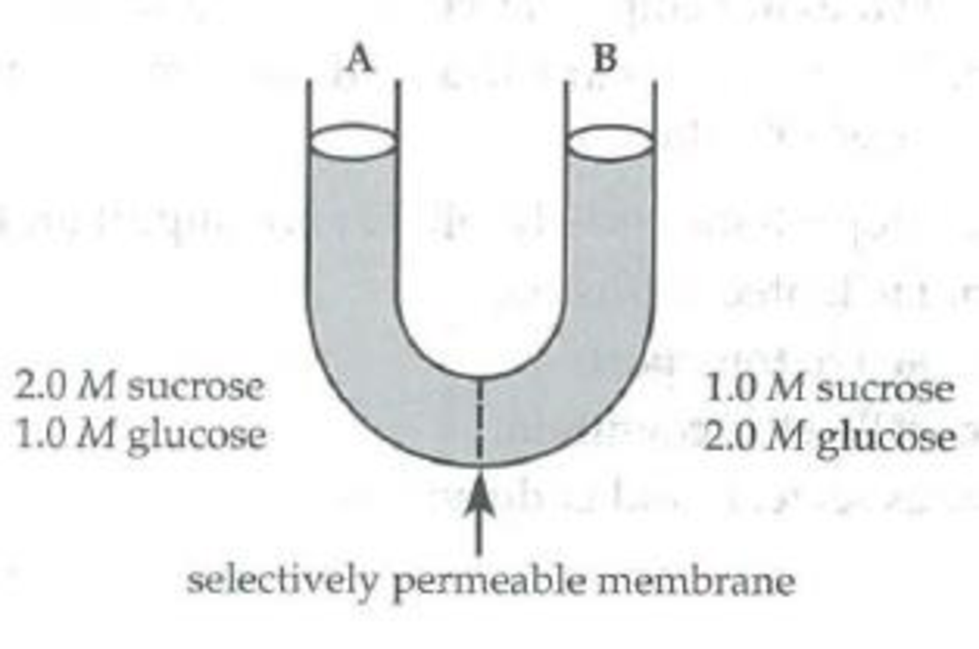
The solutions in the two arms of this U-tube are separated by a membrane that is permeable to water and glucose but not to sucrose. Side A is filled with a solution of 2.0 M sucrose and 1.0 M glucose. Side B is filled with 1.0 M sucrose and 2.0 M glucose.
During the period before equilibrium is reached, which molecule(s) will show net movement through the membrane?
- a. water
- b. glucose
- c. water and sucrose
- d. water and glucose
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
When a semipermeable sac filled with a solution containing 10% glucose is immersed in water, the fluid volume in the sac increases. What would happen if the sac solution was replaced with a 20% glucose solution?
Which statement is NOT correct concerning the cell membrane?
1. The fatty acid hydrophobic "tails" are contained within what becomes a double-
layered molecule.
2. This molecule provides an impermeable barrier for the cell from the watery outer
environment.
3. The overall structure of the cell membrane results from the amphiphilic phospholipid
molecules.
4. Because of the hydrophilic property of the phosphate containing "head", this "head*
orients itself toward the "watery." cytoplasm and the extracellular fluid.
You have a beaker filled with a solution containing 2M glucose, 4M urea and 1M salt.Suspended in the solution is a cell that containing a solution of 1M glucose, 8M urea and 3Msalt. The membrane of the cell is permeable to glucose and salt but not urea. Answer each of thefollowing questions:a. Where will water move?b. Where will urea move?c. Where will glucose move?d. Where will salt move?e. What will happen to the volume of fluid inside the cell?f. What will happen to the osmolarity of the fluid inside the cell?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Study Guide for Campbell Biology
Ch. 7 - Label the components in the following diagram of a...Ch. 7 - a. Cite some experimental evidence that indicates...Ch. 7 - List the six major functions that membrane...Ch. 7 - What types of molecules have difficulty crossing...Ch. 7 - A solution of 1 M glucose is separated by a...Ch. 7 - a. What osmotic problems does the freshwater...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7IQCh. 7 - Prob. 8IQCh. 7 - a. How is cholesterol transported into human...Ch. 7 - Create a concept map to illustrate your...
Ch. 7 - The following diagram illustrates passive and...Ch. 7 - If a single layer of phospholipids coats the water...Ch. 7 - Glycoproteins and glycolipids are important for a....Ch. 7 - Prob. 3TYKCh. 7 - Prob. 4TYKCh. 7 - Prob. 5TYKCh. 7 - Use the following U-tube setup to answer questions...Ch. 7 - Use the following U-tube setup to answer questions...Ch. 7 - Use the following U-tube setup to answer questions...Ch. 7 - How much work is expended in diffusion? a. an...Ch. 7 - Prob. 10TYKCh. 7 - Prob. 11TYKCh. 7 - Water passes quickly through cell membranes...Ch. 7 - Facilitated diffusion of ions across a cellular...Ch. 7 - Prob. 14TYKCh. 7 - Which of the following describes cotransport? a....Ch. 7 - Prob. 16TYKCh. 7 - An animal cell moves potassium against its...Ch. 7 - Prob. 18TYKCh. 7 - Prob. 19TYKCh. 7 - In response to low blood pressure, the adrenal...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Distinguish between the following pairs of terms: a. diffusion; osmosis b. passive transport; active transport c. endocytosis; exocytosisarrow_forwardThe solutions in the two arms of the U-tube are separated by a membrane that is permeable to water and glucose but not to sucrose. Side A is filled with a solution of 2.0 M sucrose and 1.0 M glucose. Side B is filled with 1.0 M sucrose and 2.0 M glucose. Initially, the solution in side A, with respect to that in side B, is what? After the system reaches equilibrium, what changes are observed?arrow_forwardDefine the following terms: a. chloride shift b. lipid raft c. caveolae d. simple diffusion e. facilitated diffusionarrow_forward
- DO NOT COPY THE ANSWER FROM THE SAME QUESTION. Sassa, a biology professor, wanted to demonstrate to her students the applicability of a dialyzing membrane (DM) as a model for the cell membrane by enclosing an aqueous solution in a DM bag and immersing in a beaker containing a different solution. Substances available which are permeable to the DM include 0.02 M NaCl, 0.03 M glucose, and 0.01 M glucose. The only substance available which is completely impermeable to the DM is the 0.01 M lactose. Using the substances given and materials such as a beaker, stirring rod, and string, draw ONLY ONE set-up that can be demonstrated by Ms. Sassa that will satisfy ALL of the following conditions:a. No solute will exhibit a net diffusion out of the cell.b. Glucose will exhibit a net diffusion into the cell.c. NaCl will exhibit a zero net d. No net movement of lactose from the inside to outside of the cell. Make sure to label properly the substance inside the beaker and inside the DM bag.arrow_forwardUsing Osmosis, Balance, Compartment, Cell, Water, Permeability, and Membrane in your explanation. Explain why the bolded lines are correct and what would happen internally if you relied on salty ocean water for survival.arrow_forwardYou set up the following two tubes: Tube 1: 1mL of alkaline phosphatase + 4mL of 400 µM p-NPP Tube 2: 1mL of alkaline phosphatase + 4mL of 200 µM p-NPP Which tube would have a faster reaction rate? Explain your reasoning (why does concentration of p-NPP matter? Relate it back to week 4 lab concepts). Week 4 lab concepts: - concentration gradient - differentially permeable membrane - solute, solvent, diffusion, osmosis, hypotonic, isotonic, hypertonic, molarity, osmolarityarrow_forward
- If a percent difference is a negative number, what does this tell us about the change in weight of the artificial cell? If the percent difference is a negative number, what does this tell us about the movement of water across the membrane?arrow_forwardA cell in placed in a beaker of water, and the cell shrinks. What can you infer about the relative concentrations of the solutes in the cell versus the beaker?arrow_forwardFor a lab on diffusion and osmosis, where a egg yolk was placed in a cup water the following question asks Consider a scenario in which the size of an egg yolk remains unchanged after in water soaking for an hour. What are two possible explanations as to why this occurs? What would two reasons be for the yolk to be unchanged after a hour in water?arrow_forward
- What type of energy helps drive the passive processes of diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion? (Pick ALL correct statements involved with this.) In other words what are all the TRUE statements regarding these processes? Select one or more: a. random motion which increases when molecules have low molecular weight b. random motion which decreases when temperature decreases c. random motion which increases when temperature increases d. random motion which increases when molecules concentration increases e. ATP energy f. random motion which increases when molecules have large molecular weight g. random motion which increases when molecules concentration decreasesarrow_forwardControlled exchange of materials occurs between compartments and across cellular membranes. Explain?arrow_forwardName the solution in which the relative concentration of water molecules and the solute on either side of the cell is same.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning
The Cell Membrane; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AsffT7XIXbA;License: Standard youtube license