
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Structures of the major organic products formed in the reaction of each of the given reagents with
Concept introduction:
Since
According to Markovnikov’s rule. when an unsymmetrically substituted alkene reacts with a hydrogen halide, hydrogen adds to the carbon that has the greater number of hydrogens and halogen adds to the carbon that has fewer hydrogens.
In a hydroboration oxidation reaction, hydrogen atom gets bonded to the carbon that has fewer hydrogens and the hydroxyl to the carbon that has a greater number of hydrogens. This is a rule opposite of Markovnikov’s addition.
Answer to Problem 29P
Solution:
a)
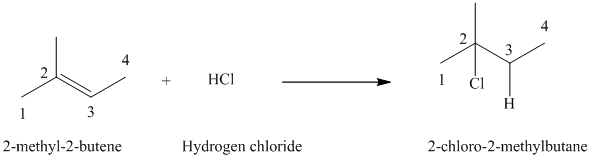
b)
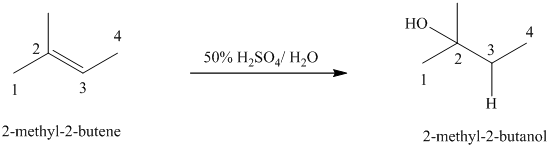
c)
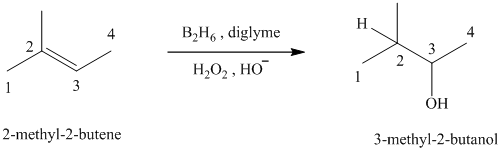
d)
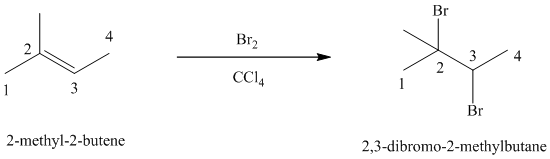
e)
f)
 g)
g)
h)
i)
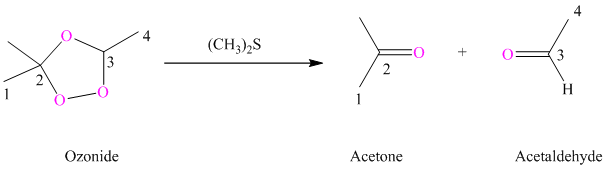
Explanation of Solution
a) The reaction is as follows:
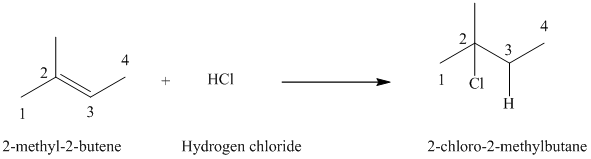
The given alkene
Hydrogen chloride adds to the double bond of
b) The reaction is as follows:
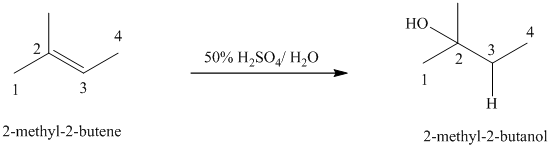
This reaction is an acid catalyzed electrophilic addition reaction of alkenes. In this reaction, water molecule gets added to the double bond in
In this reaction, the addition of water molecule to alkene follows Markovnikov’s rule. The hydrogen atom in water molecule adds to the carbon
The addition mechanism for this reaction follows Markovnikov’s rule, and so the major organic product for the above acid-catalyzed electrophilic addition reaction is
c) The reaction is as follows:
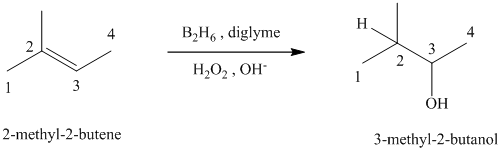
This reaction is the hydroboration-oxidation reaction of alkenes. In this reaction, water molecule gets added to the double bond in
The hydrogen atom from water molecule adds to the carbon
d) The reaction is as follows:
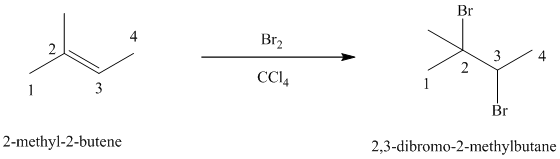
Bromine reacts rapidly with alkenes by electrophilic addition. The products are called vicinal dibromides, meaning that the bromine atoms are attached to adjacent double bonded carbon atoms. It is carried out in suitable solvents such as
Bromine adds across the double bond in
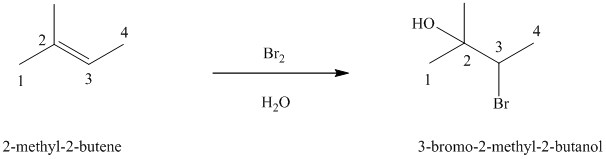
e) The reaction is as follows:
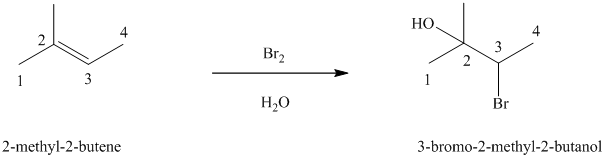
In aqueous solution, chlorine and bromine react with alkenes to give corresponding vicinal halohydrins. Halohydrin compounds have a halogen and hydroxyl group on adjacent carbon atoms. In alkene, halogen atom bonds to that carbon atom which has a larger number of hydrogens and hydroxyl group bonds to that carbon atom which has a smaller number of hydrogens.
In the reaction of
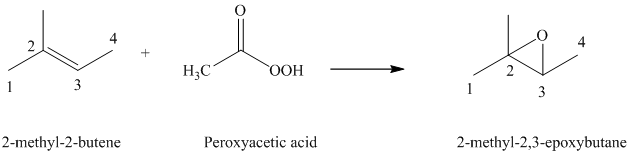
f) The reaction is as follows:
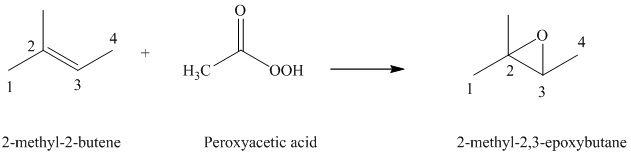
Peroxyacids transfers oxygen to the double bond of an alkene to yield epoxides. An epoxide is a three-membered oxygen-containing ring.
When
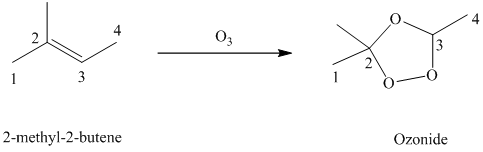
g) The reaction is as follows:
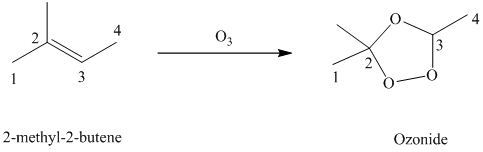
Ozone is a powerful electrophile and reacts with alkenes to cleave the double bond, forming an ozonide.
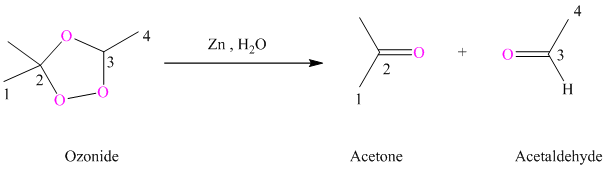
h) The reaction is as follows:
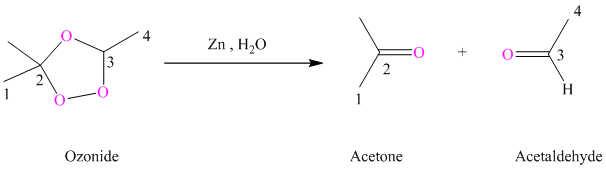
Ozonides are formed as a result of the reaction of ozone with an alkene. Ozonides undergo hydrolysis in the water giving carbonyl compounds. According to the structure of starting alkene, various carbonyl products are formed such as formaldehyde, aldehydes, or ketones.
When the corresponding ozonide of
i) The reaction is as follows:
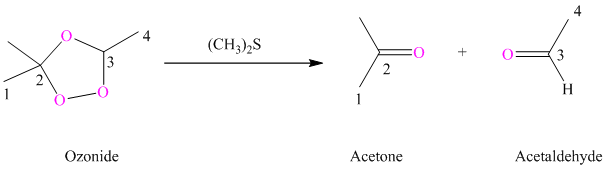
Ozonides are formed as a result of the reaction of ozone with an alkene. Ozonides undergo hydrolysis in water, giving carbonyl compounds. According to the structure of starting alkene, various carbonyl products are formed such as formaldehyde, aldehydes, or ketones.
When corresponding ozonide of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2 YEAR CONNECT ACCES
- An aromatic compound ‘A’ on treatment with aqueous ammonia and heating forms compound ‘B’ which on heating with Br2 and KOH forms a compound ‘C’ of molecular formula C6H7N. Write the structures and IUPAC names of compounds A, B and C.arrow_forwardCompound A has molecular formula C4H10, and gives two monochlorides, B and C, on photochemical chlorination. Treatment of either of these monochlorides with potassium tert-butoxide gives the same alkene (C4H8) as the product, but B leads to just one isomer of the alkene, D, where C gives D and another isomer of the alkene, E. Treatment of monochlorides B and C with aqueous ethanol gives products F and G, respectively, both of which are of molecular formula C4H10O. What are the names of compounds A-G?arrow_forwardAn unknown hydrocarbon A with the formula C6H12 reacts with 1 molar equivalent of H2 over a palladium catalyst. Hydrocarbon A also reacts with OsO4 to give diol B. When oxidized with KMnO4 in acidic solution, A gives two fragments. One fragment is propanoic acid, CH3CH2CO2H, and the other fragment is ketone C. What are the structures of A, B, and C? Write all reactions, and show your reasoning.arrow_forward
- Compound A (C6H12O2) reacts with water, acid, and heatto yield compound B (C5H10O2) and compound C (CH4O).Compound B is acidic. Deduce possible structures of compounds A, B, and Carrow_forwardAn optically active monoterpene (compound A) with molecular formula C10H18O undergoes catalytic hydrogenation to form an optically inactive compound with molecular formula C10H20O (compound B). When compound B is heated with acid, followed by reaction with O3 and then with dimethyl sulfide, one of the products obtained is 4-methylcyclohexanone. Give possible structures for compounds A and B.arrow_forwardGive the series of reactions below, identify and give the iupac name for the following compounds, in short identify and name A,B,Carrow_forward
- Explain the Mechanism - Addition of Dichlorocarbene to an Alkene ?arrow_forwardProvide the structure of the major organic product of the following reaction and? explain the stereochemistry which results in this product. 2-Pentanol reacting with 1.) PBr3, pyridine 2.) NaCNarrow_forwardCompound F may be synthesised by the method attached: When 2-chloropropane treated with NaOH and 1-chloropropane treated with NaOH separately produce two different functional groups. Provide both reactions and explain the two different functional groups produced.arrow_forward
- A nitrile compound is prepared from cyclopentene. The following is an analysis of the disconnection and its synthesis. Write the structure of A and B !arrow_forward3. Obtain acetophenone and acetaldehyde by reaction of glycols with periodic acid. Justify your answer with the reaction mechanism.arrow_forwardA compound A, C7H12, was found to be optically active. On catalytic reduction over platinum catalyst, 2 equivalents of hydrogen were absorbed, yielding compound B, C7H16. On ozonolysis of A, two fragments were obtained. One fragment was identified as acetic acid. The other fragment, compound C, was an optically active carboxylic acid, C5H10O2. Write the reactions and draw structures for A, B and C.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





