
1.
Find the test statistic value and make a decision to retain or reject the null hypothesis
1.
Answer to Problem 21CAP
The test statistic value is 4.27.
The decision is to reject the null hypothesis.
Explanation of Solution
Let
A sample of 8 rats is considered and they are rats feel sick and control group rats. The claim is the there is difference between the not consumption of saccharin-flavored water of two groups. This represents the alternative hypothesis. The level of significance is 0.05.
Null hypothesis:
That is, there is no difference between the not consumption of saccharin-flavored water of two groups.
Alternative hypothesis:
That is, there is difference between the not consumption of saccharin-flavored water of two groups.
The degrees of freedom for t distribution is,
The test is two tailed, the degrees of freedom are 6, and the alpha level is 0.05.
From the Appendix C: Table C.2 the t Distribution:
- Locate the value 6 in the degrees of freedom (df) column.
- Locate the 0.05 in the proportion in Two tails combined row.
- The intersecting value that corresponds to the 6 with level of significance 0.05 is 2.447.
Decision rules:
- If the positive test statistic value is greater than the positive critical value, then reject the null hypothesis or else retain the null hypothesis.
- If the negative test statistic value is less than negative critical value, then reject the null hypothesis or else retain the null hypothesis.
The formula of test statistic for one-sample t test is,
In the formula,
In the formula,
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain test statistic value using SPSS software is given as,
- Choose Variable view.
- Under the name, enter the names as Amounts, and Types of Rats.
- Choose Data view, enter the data.
- Choose Analyze>Compare means>Independent Samples T Test.
- In Test variables, enter the column as Amounts.
- In Grouping variables, enter the column as Types of Rats.
- Select Define Groups; enter Group 1 as 1 and Group 2 as 2.
- Click OK.
Output using SPSS software is given below:
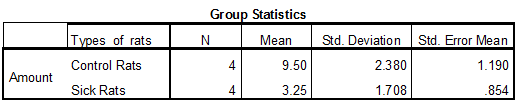
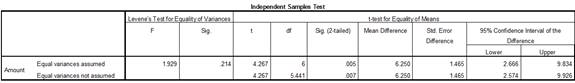
Thus, the test statistic value is 4.27.
Justification: The value of test statistic is 4.27 and critical value is 2.447. The test statistic value is greater than the critical value. The test statistic value fall under critical region and hence the null hypothesis is rejected.
2.
Find the value of eta-squared to compute the effect size.
2.
Answer to Problem 21CAP
The value of eta-squared is 1.90.
There is large effect size.
Explanation of Solution
Eta-square:
The proportion of variance is measured using eta-square. But eta-square is biased because it over estimates the proportion of variance that is explained by treatment. It is denoted by
In the formula, t is the value of test statistic and df is the corresponding degrees of freedom.
The description of effect size using eta-square:
- If value of eta-square is less than 0.01, then effect size is trivial.
- If value of eta-square is in between 0.01 and 0.09, then effect size is small.
- If value of eta-square is in between 0.10 and 0.25, then effect size is medium.
- If value of eta-square is greater than 0.25, then effect size is large.
Calculation:
From the SPSS output, the test statistic value is 4.27 and
The value of estimated eta-square is 0.75. This value is greater than 0.25. Hence the eta-square has a large effect size.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





