
Concept explainers
Dollar-value LIFO retail
• LO9–5
On January 1, 2018, HGC Camera Store adopted the dollar-value LIFO retail inventory method. Inventory transactions at both cost and retail, and cost indexes for 2018 and 2019 are as follows:
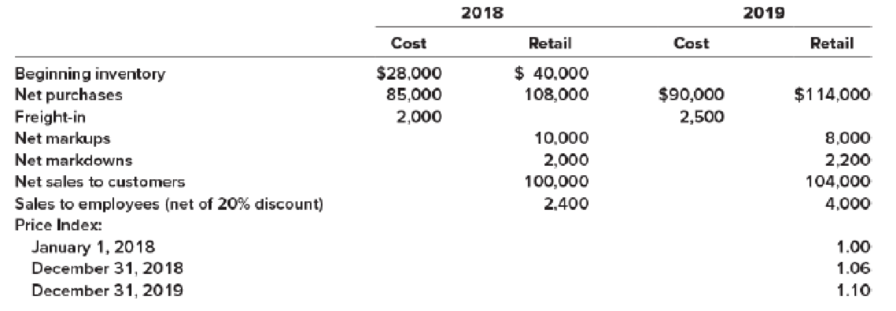
Required:
Estimate the 2018 and 2019 ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the dollar-value LIFO retail inventory method.
Dollar-Value-LIFO
This method shows all the inventory figures at dollar price rather than units. Under this inventory method, the units that are purchased last, are sold first. Thus, it starts from the selling of the units recently purchased and ending with the beginning inventory.
To Estimate: the ending inventory and cost of goods sold in 2018 using dollar-value LIFO retail method.
Explanation of Solution
Solution:
Calculate the amount of estimated ending inventory and cost of goods sold at retail.
| Details | Cost ($) | Retail ($) |
| Beginning inventory | 28,000 | 40,000 |
| Add: Net purchase | 85,000 | 108,000 |
| Freight-in | 2,000 | |
| Net markups | 10,000 | |
| Less: Net markdowns | (2,000) | |
| Goods available for sale – Excluding beginning inventory | 87,000 | 116,000 |
| Goods available for sale – Including beginning inventory | 115,000 | 156,000 |
| Less: Net sales | 0 | (102,400) |
| Employees discounts | (600) | |
| Estimated ending inventory at current year retail prices | 53,000 | |
| Estimated ending inventory at cost (Refer Table 2) | (35,950) | |
| Estimated Cost of Goods Sold | 79,050 |
Table (1)
Working Notes:
Calculate base layer cost-to retail percentage.
Calculate current year cost-to retail percentage.
Calculate the amount of estimated ending inventory at cost.
| Ending inventory at dollar-value LIFO retail cost | ||||
| Ending inventory at year-end retail prices ($) | Ending inventory at base year retail prices ($) | Inventory layers at base year retail prices ($) | Inventory layers converted to cost ($) | |
| 53,000 | 50,000 | 40,000 (Base) | 28,000 | |
| 10,000 (2018) | 7,950 | |||
| Total ending inventory at dollar-value LIFO retail cost | 35,950 | |||
Table (2)
Calculate the amount of ending inventory at base year retail prices.
Calculate the amount of inventory layers at base year retail prices.
Calculate the amount of inventory layers at current year retail prices.
Calculate the amount of inventory layers converted to cost (Base).
Calculate the amount of inventory layers converted to cost (2018).
Calculate the amount of estimated ending inventory and cost of goods sold at retail.
| Details | Cost ($) | Retail ($) |
| Beginning inventory | 35,950 | 53,000 |
| Add: Net purchase | 90,000 | 114,000 |
| Freight-in | 2,500 | |
| Net markups | 8,000 | |
| Less: Net markdowns | (2,200) | |
| Goods available for sale – Excluding beginning inventory | 92,500 | 119,800 |
| Goods available for sale – Including beginning inventory | 128,450 | 172,800 |
| Less: Net sales | 0 | (108,000) |
| Employees discounts | (1,000) | |
| Estimated ending inventory at current year retail prices | 63,800 | |
| Estimated ending inventory at cost (Refer Table 2) | (42,744) | |
| Estimated Cost of Goods Sold | 85,706 |
Table (3)
Working Notes:
Calculate base layer cost-to retail percentage.
Calculate 2018 year cost-to retail percentage.
Calculate current year cost-to retail percentage.
Calculate the amount of estimated ending inventory at cost.
| Ending inventory at dollar-value LIFO retail cost | ||||
| Ending inventory at year-end retail prices ($) | Ending inventory at base year retail prices ($) | Inventory layers at base year retail prices ($) | Inventory layers converted to cost ($) | |
| 63,800 | 58,000 | 40,000 (Base) | 28,000 | |
| 10,000 (2018) | 7,950 | |||
| 8,000 (2019) | 6,794 | |||
| Total ending inventory at dollar-value LIFO retail cost | 42,744 | |||
Table (4)
Calculate the amount of ending inventory at base year retail prices.
Calculate the amount of inventory layers at base year retail prices.
Calculate the amount of inventory layers at current year retail prices.
Calculate the amount of inventory layers converted to cost (Base).
Calculate the amount of inventory layers converted to cost (2018).
Calculate the amount of inventory layers converted to cost (2019).
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting
- Problem 9-13 (Algo) Retail inventory method; various applications [LO9-3, 9-4, 9-5] Skip to question [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] On January 1, 2021, Pet Friendly Stores adopted the retail inventory method. Inventory transactions at both cost and retail, and cost indexes for 2021 and 2022 are as follows: 2021 2022 Cost Retail Cost Retail Beginning inventory $ 162,500 $ 250,000 Purchases 800,000 1,084,000 $ 680,000 $ 1,063,000 Purchase returns 7,000 12,150 2,000 4,300 Freight-in 12,500 2,000 Net markups 6,900 11,800 Net markdowns 4,750 8,000 Net sales to customers 950,000 722,000 Sales to employees (net of 25% discount) 22,500 22,500 Normal spoilage 4,200 6,900 Price Index: January 1, 2021 1.00…arrow_forwardNOTE: Please do as Part A: Periodic direct method and Part B: Perpetual Allowance methods. the direction is not the same as text book. P9.3 (LO 1) (LCNRV–Cost-of-Goods-Sold and Loss) Malone Company determined its ending inventory at cost and at LCNRV at December 31, 2020, December 31, 2021, and December 31, 2022, as shown below. Cost NRV 12/31/20 $650,000 $650,000 12/31/21 780,000 712,000 12/31/22 905,000 830,000 Instructions a. Prepare the journal entries required at December 31, 2021, and at December 31, 2022, assuming that a perpetual inventory system and the cost-of-goods-sold method of adjusting to LCNRV is used. b. Prepare the journal entries required at December 31, 2021, and at December 31, 2022, assuming that a perpetual inventory is recorded at cost and reduced to LCNRV using the loss method.arrow_forwardP6.11 (LO 6), AP Rayre Books uses the retail inventory method to estimate its monthly ending invento- ries. The following information is available for two of its departments at October 31, 2022. Hardcovers Paperbacks Cost Retail Cost Retail Beginning inventory $ 420,000 $ 640,000 $ 280,000 $ 360,000 Purchases 2,135,000 3,200,000 1,155,000 1,540,000 Freight-in 24,000 12,000 Purchase discounts 44,000 22,000 Net sales 3,100,000 1,570,000 At December 31, Rayre Books takes a physical inventory at retail. The actual retail values of the inven- tories in each department are Hardcovers $744,000 and Paperbacks $335,000. Instructions a. Determine the estimated cost ofthe ending inventory for each department at October 31, 2022, using the retail inventory method. b. Compute the ending inventory at cost for each department atDecember 31, assuming the cost-to- retail ratios for the year are 65% for Hardcovers and 75% for Paperbacks.arrow_forward
- BUS 038 : Business Computations13 Which type of discount (trade discount or cash discount) is given as an incentive to pay the seller promptly? 14. Series discounts are a form of trade discount. (T or F) For Problems 15-19 assume that you purchase goods with a list price of $455 and a trade discount of 25%. The invoice is dated October 3 with terms of 3/15, n/45. 15. What is the net price after trade discount?arrow_forwardE8.12 (LO 3) (FIFO, LIFO, Average-Cost Inventory) Shania Twain Company was formed onDecember 1, 2019. The following information is available from Twain’s inventory records for Product BAP. Units Unit CostJanuary 1, 2020 (beginning inventory) 600 $ 8.00Purchases:January 5, 2020 1,200 9.00January 25, 2020 1,300 10.00February 16, 2020 800 11.00March 26, 2020 600 12.00 A physical inventory on March 31, 2020, shows 1,600 units on hand.InstructionsPrepare schedules to compute the ending inventory at March 31, 2020, under each of the following inventory methods.a. FIFO b. LIFO. c. Weighted-average (round unit costs to two decimal places)arrow_forwardHW Q 4 Current Attempt in Progress At the end of Bridgeport Department Store’s fiscal year on November 30, 2020, these accounts appeared in its adjusted trial balance. Freight-In $ 7,500 Inventory 39,400 Purchases 578,500 Purchase Discounts 6,600 Purchase Returns and Allowances 2,900 Sales Revenue 1,044,700 Sales Returns and Allowances 17,000 Additional facts: 1. Merchandise inventory on November 30, 2020, is $ 53,800. 2. Bridgeport Department Store uses a periodic system. Prepare an income statement through gross profit for the year ended November 30, 2020. (Enter negative amounts using either a negative sign preceding the number e.g. -45 or parentheses e.g. (45).) BRIDGEPORT DEPARTMENT STOREIncome Statement (Partial)choose the accounting period select an opening name for section one enter an income statement item $ enter a dollar amount…arrow_forward
- (Appendix 8.1) Inventory Write-Down Frost Companys inventory records tor the years 2019 and 2020 reveal the cost and market of the January 1, 2019, inventory to be 125,000. On December 31, 2019, the cost of inventory was 130,000, while the market value was only 128,000. The December 31, 2020, market value of inventory was 140,000, and the cost was only 135,000. Frost uses a periodic inventory system. Purchases for 2019 were 100,000 and for 2020 were 110,000. Required: 1. Assume the inventory that existed at the end of 2019 was sold in 2020. Prepare the journal entries at the end of 2019 and 2020 to record the lower of cost or net realizable value under the (a) allowance method and (b) direct method. 2. Prepare the cost of goods sold section of the income statement and show how the company would record the inventory on its balance sheet for 2019 and 2020 under the (a) allowance method and (b) direct method. 3. Next Level Refer to your answer for P8-3. How does the use of a periodic inventory system versus a perpetual inventory system affect the valuation of inventory and the amount reported as income?arrow_forwardHW Q 2 Current Attempt in Progress On June 10, Sunland Company purchased $ 10,000 of merchandise on account from Marigold Company, FOB shipping point, terms 1/10, n/30. Sunland pays the freight costs of $ 420 on June 11. Damaged goods totaling $ 300 are returned to Marigold for credit on June 12. The fair value of these goods is $ 75. On June 19, Sunland pays Marigold Company in full, less the purchase discount. Both companies use a perpetual inventory system. (a) Prepare separate entries for each transaction on the books of Sunland Company. (Credit account titles are automatically indented when amount is entered. Do not indent manually. Record journal entries in the order presented in the problem.) Date Account Titles and Explanation Debit Credit choose a transaction date enter an account title enter a debit amount enter a credit amount enter an account title enter a debit amount enter a credit amount…arrow_forwardMF2 9 Purchased merchandise from Keene Co. for $9,100 under credit terms of 2/15, n/60, FOB destination. Analysis Component: As the senior purchaser for Belton Company, you are concerned that the purchase discounts you have negotiated are not being taken advantage of by the accounts payable department. Calculate the cost of the lost discount regarding the July 9 purchase. Assume a 6% interest rate. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answer to 2 decimal places. Assume 365 days a year.)arrow_forward
- (i) Inventory = (60.83 – 54.75) ´ $32,876.7123 = $199,890.41. (ii) Receivables = (73 – 65.70) ´ $41,095.8904 = $300,000. (iii) Payables = (33.46 – 30.42) ´ $32,876.7123 = $99,945.21 How did you compute the $32,876.7123 for inventory, $41,095.8904 for receivables, and $32,876.7123 for payables?arrow_forwardEA5. EA5. LO 10.2Akira Company had the following transactions for the month.Chart showing Beginning Inventory of 150 units at $10 per unit, Purchase of March 31 of 160 units at $12 each, Purchase of October 15 of 130 units at $15 each, and ending inventory of 50 units at a cost of ? each.Calculate the ending inventory dollar value for the period for each of the following cost allocation methods, using periodic inventory updating. Provide your calculations. first-in, first-out (FIFO)last-in, first-out (LIFO)weighted average (AVG)arrow_forward55.XXX Company uses the average cost retail method to estimate its inventory. Data relating to the inventory at December 31, 2020 are: Cost Retail Inventory, January 1 P 2,000,000 P3,000,000 Purchases 10,600,000 14,000,000 Net markups 1,600,000 Net markdowns 600,000 Sales 12,000,000 Estimated normal shoplifting losses 400,000 Estimated normal shrinkage is 5% of sales Trinidad’s cost of goods sold for the year ended December 31, 2019 isarrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
